Passage
DNA polymerization is one of the most conserved mechanisms of genome replication. Synthesis of a complete DNA strand requires a template, primers, a polymerase enzyme, and sufficient deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) . The DNA polymerase enzyme binds consecutive base pairs on the template strand and extends the double helix by adding dNTPs to the primer. The amino acid residues in the active site of DNA polymerase form hydrogen bonds with Watson-Crick donors and acceptors on incoming DNA nucleotides to facilitate base pairing.The formation of the DNA double helix creates opposing changes in entropy and enthalpy. Favorable bonding interactions via hydrogen bonds during Watson-Crick base pairing results in negative enthalpy, and restricted rotation and flexibility of the DNA backbone generates negative entropy. Scientists hypothesize that hydrogen bonding between bases not only stabilizes the double helix but is also crucial for selective and efficient replication.Analogs that are similar in size and shape to naturally occurring bases can be used to determine the influence of hydrogen bonding on base pair selectivity. To mimic the structure of deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) , researchers synthesized dNTP derivatives of difluorotoluene (dFTP) , a nonpolar analog that lacks Watson-Crick hydrogen bonding. Klenow fragment (KF) polymerase, which has 3′-5′ but not 5′-3′ exonuclease activity, was incubated with a mixture of DNA template, primers, and dNTPs, including dFTP derivatives. The efficiency of dFTP and natural dTTP nucleotide incorporation into a growing primer strand by KF is shown in Figure 1.
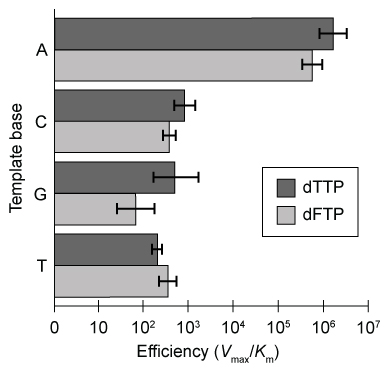 Figure 1 Template-specific selection of dFTP and dTTP by the KF enzyme
Figure 1 Template-specific selection of dFTP and dTTP by the KF enzyme
Adapted from Moran S, Ren RX, Kool ET. A thymidine triphosphate shape analog lacking Watson-Crick pairing ability is replicated with high sequence selectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(20) :10506-11.
-The Klenow fragment used in the experiment would be able to perform which of the following repair processes?
A) Excision of thymine dimers at the 5′ end of the growing strand
B) Replacement of nucleotides at the 3′ end of the growing strand
C) Correction of mismatched nucleotides in the middle of a completed strand
D) Removal of damaged bases from the middle of the template strand
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q178: In order to transport long-chain fatty acids
Q179: Passage
Diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease) is characterized in
Q180: Which amino acid substitution would result in
Q181: Passage
Leukocyte common antigen (LCA) enzymes play several
Q182: Which of the following most accurately describes
Q184: Escherichia coli bacteria containing only 15N-labeled DNA
Q185: Passage
DNA polymerization is one of the most
Q186: Passage
DNA polymerization is one of the most
Q187: Passage
Leukocyte common antigen (LCA) enzymes play several
Q188: Passage
Leukocyte common antigen (LCA) enzymes play several
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents