Passage Mitochondria Are Double Membrane-Bound Cellular Organelles That House Several Connected
Passage
Mitochondria are double membrane-bound cellular organelles that house several connected metabolic reactions. The citric acid cycle takes place inside the mitochondrial matrix and produces two reduced electron carriers, NADH and FADH2. These two carriers then pass their electrons to ubiquinone (UQ) , which is reduced to ubiquinol (UQH2) . UQH2 passes its electrons to oxidized cytochrome C (cyt-Cox) , regenerating UQ and forming reduced cytochrome C (cyt-Cred) . Finally, cyt-Cred transfers electrons to oxygen, regenerating cyt-Cox and forming water. Each reaction is facilitated by one of four protein complexes that are collectively known as the electron transport chain (ETC) .Researchers isolated mitochondria and treated them with a novel ETC inhibitor, "drug X." After an overnight incubation, they measured levels of several ETC-reduced electron carriers in the presence of drug X relative to untreated mitochondria. Their results are shown in Figure 1.
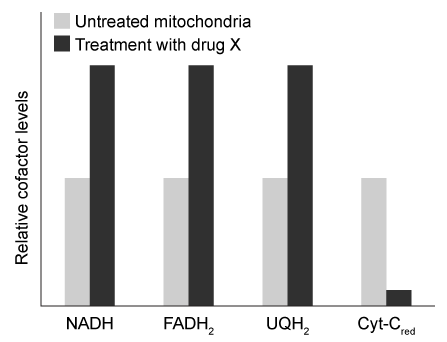 Figure 1 Relative levels of reduced electron carriers in the presence and absence of drug XNext, the researchers exposed mitochondria to FCCP, a chemical that can transport protons across membranes. They observed that in the presence of FCCP, the citric acid cycle was fully active, and all reduced cofactors were present at the same levels as in untreated mitochondria. However, the rate of ATP synthesis was significantly reduced. ATP synthesis was immediately restored when FCCP was washed away.
Figure 1 Relative levels of reduced electron carriers in the presence and absence of drug XNext, the researchers exposed mitochondria to FCCP, a chemical that can transport protons across membranes. They observed that in the presence of FCCP, the citric acid cycle was fully active, and all reduced cofactors were present at the same levels as in untreated mitochondria. However, the rate of ATP synthesis was significantly reduced. ATP synthesis was immediately restored when FCCP was washed away.
-Based on the information in the passage, FCCP most likely causes a decrease in energy production by:
A) decoupling the movement of protons down their concentration gradient from ATP synthase.
B) carrying more protons into the intermembrane space than are pumped by the ETC alone.
C) shifting the proton gradient further away from equilibrium than is achieved by the ETC alone.
D) causing a decrease in ETC activity, resulting in fewer available protons for ATP synthase.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q213: Passage
The sirtuins are a class of enzymes
Q214: Passage
The influenza A virus is an enveloped
Q215: Passage
The influenza A virus is an enveloped
Q216: Passage
The influenza A virus is an enveloped
Q217: Passage
The influenza A virus is an enveloped
Q219: Passage
Interactions between positively charged histones and negatively
Q220: Which of the following steps in the
Q221: Passage
The sirtuins are a class of enzymes
Q222: Passage
Physical activity produces an increased energy requirement
Q223: Passage
Physical activity produces an increased energy requirement
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents