Passage Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli (EHEC) O157:H7 Is a Bacterium Responsible for for Causing
Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a bacterium responsible for causing foodborne illnesses. EHEC virulence, or the ability to cause disease, is acquired through quorum sensing, a form of bacterial cell-cell communication dependent on population density. EHEC O157:H7 bacteria monitor population density by detecting changes in the concentration of autoinducer-3 (AI-3) , an extracellular signaling molecule secreted by many bacterial species. AI-3 generally acts on neighboring bacteria to activate the genes on the enterocyte effacement (LEE) locus. These genes code for type III secretion proteins (EspA, EspB, EspD, Tir) , which promote entry of Shiga-like toxins secreted by EHEC into host intestinal epithelial cells. This ultimately leads to cell death, lesions, and symptoms such as bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramps.It has been reported that a mutation in S-ribosylhomocysteine lyase (LuxS) , an enzyme involved in quorum sensing, may result in diminished production of AI-3. However, researchers predict that certain peptide hormones can activate LEE gene transcription in the LuxS. To test this hypothesis, mutant EHEC bacteria deficient in LuxS (LuxS−) were cultured and separately exposed to the hormones epinephrine (E) , norepinephrine (NE) , gastrin (G) , and secretin (S) at 37°C. Total RNA was extracted from the treated bacterial cultures, and LEE mRNA was quantified (Figure 1) .
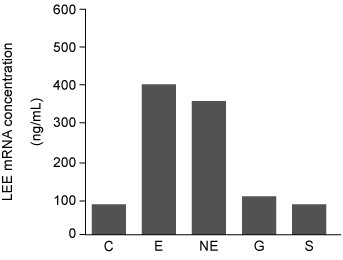 Figure 1 Concentration of LEE mRNA in mutant LuxS− bacteria supplemented with purified peptide hormones (Note: C = control.) Western blot was performed to compare the presence and concentration of type III secretion proteins from wild-type (WT) , LuxS−, and LuxS− cultured in preconditioned media (PCM) . PCM was generated by culturing uninfected intestinal epithelial cells in growth media for 24 hours. After 24 hours, the cells were removed and the PCM was used to supplement the growth of LuxS− bacteria.
Figure 1 Concentration of LEE mRNA in mutant LuxS− bacteria supplemented with purified peptide hormones (Note: C = control.) Western blot was performed to compare the presence and concentration of type III secretion proteins from wild-type (WT) , LuxS−, and LuxS− cultured in preconditioned media (PCM) . PCM was generated by culturing uninfected intestinal epithelial cells in growth media for 24 hours. After 24 hours, the cells were removed and the PCM was used to supplement the growth of LuxS− bacteria.
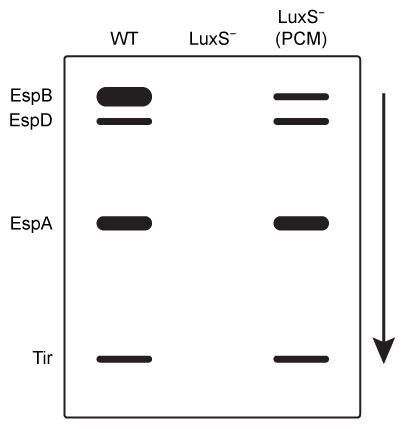 Figure 2 Western blot results of type III secretion proteins isolated from WT, mutant LuxS−, and LuxS− in PCM
Figure 2 Western blot results of type III secretion proteins isolated from WT, mutant LuxS−, and LuxS− in PCM
-Which of the following is most likely to be found within the cell membranes of intestinal epithelial cells?
A) Peptidoglycan
B) Cholesterol
C) Cytoskeletal filaments
D) Cellulose
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q31: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q32: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q33: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Q34: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q35: Passage
The Bloom syndrome helicase (BLM) transcript is
Q37: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Q38: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q39: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q40: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Q41: Passage
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a progressive condition
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents