Passage
Obesity is a condition that affects over 30% of adults in the United States and is associated with comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, heart disease, and cancer. For individuals with clinically severe obesity, defined as having a body mass index above 40 kg/m2, lifestyle interventions may produce insufficient weight reduction. Weight loss surgery, such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) , has proved to be the most effective clinical intervention for facilitating massive and immediate weight loss in clinically obese patients.In RYGB, the stomach is first divided into a small gastric pouch and a distal gastric remnant, which remains attached to the duodenum. Next, the jejunum is transected and its lower section is connected to the newly created gastric pouch to form the alimentary limb. This connection is typically created with surgical staples. The formation of the alimentary limb allows ingested food to bypass the region composed of the distal gastric remnant, the duodenum, and the upper jejunum; collectively termed the biliopancreatic limb. Finally, the lumen of the upper jejunum is reconnected to the lumen of the lower jejunum to allow enzymes and compounds to flow freely from the biliopancreatic limb into the alimentary limb.
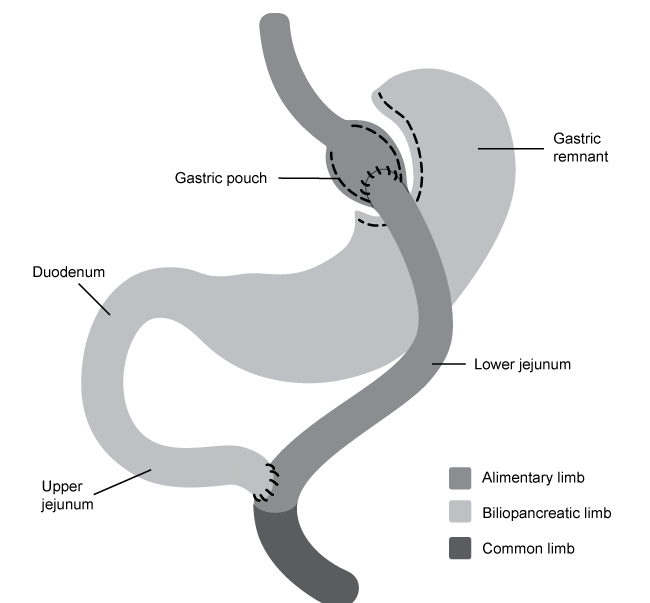 Figure 1 RYGB surgically divides the digestive tract into the alimentary limb and the biliopancreatic limb, which then merge into the common limb.RYGB facilitates weight loss by reducing the functional volume of the stomach and altering intestinal anatomy to induce nutrient malabsorption. However, the procedure is associated with several complications, such as steatorrhea, or fatty stools, due to disruption of lipid digestion. Animal studies also suggest that RYGB promotes the growth of weight loss-inducing gut bacteria. Researchers have found that transplanting gut microbiota of obese postoperative RYGB mice into nonoperated, obese mice lacking gut flora may reproduce the therapeutic effects of RYGB in transplant-recipient mice.
Figure 1 RYGB surgically divides the digestive tract into the alimentary limb and the biliopancreatic limb, which then merge into the common limb.RYGB facilitates weight loss by reducing the functional volume of the stomach and altering intestinal anatomy to induce nutrient malabsorption. However, the procedure is associated with several complications, such as steatorrhea, or fatty stools, due to disruption of lipid digestion. Animal studies also suggest that RYGB promotes the growth of weight loss-inducing gut bacteria. Researchers have found that transplanting gut microbiota of obese postoperative RYGB mice into nonoperated, obese mice lacking gut flora may reproduce the therapeutic effects of RYGB in transplant-recipient mice.
Adapted from Bächler T, Le roux CW, Bueter M. How do patients' clinical phenotype and the physiological mechanisms of the operations impact the choice of bariatric procedure?. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2016;9:181-9.
-Which organ synthesizes a compound that facilitates the mechanical digestion of lipids?
A) Pancreas
B) Salivary glands
C) Gallbladder
D) Liver
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q94: Passage
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is
Q95: Passage
Eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts
Q96: Passage
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease
Q97: Passage
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease
Q98: Passage
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is
Q100: Passage
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease
Q101: Passage
Skin grafting is a procedure in which
Q102: Passage
Renal reabsorption of glucose is facilitated by
Q103: Passage
Skin grafting is a procedure in which
Q104: Passage
Renal reabsorption of glucose is facilitated by
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents