Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive family of metals occupying Group 2 (IIA) of the periodic table. In their elemental form, the alkaline-earth metals have a shiny, silvery-white to slightly yellowish appearance. The alkaline-earth metals exhibit some similarities to the chemistry of the alkali metals (Group 1) but are a little less reactive.Atoms of the alkaline-earth metals (M) have only two valence electrons and a low first and second ionization energy. Consequently, these metals readily lose both electrons to produce cations with a +2 charge (M+2) during reactions with nonmetals. As a result, the alkaline-earth metals do not exist in their elemental metallic form in nature. Instead, the Group 2 elements are found primarily as metal oxides, which form by reacting oxygen (Reaction 1) .
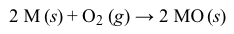
Similarly, elemental samples of alkaline-earth metals will react with elemental halogens (X2) to form metal halides (Reaction 2) , all of which are ionic except for BeCl2.
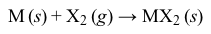
Except for beryllium, the alkaline-earth metals react with water to produce very basic metal hydroxide solutions and hydrogen gas (Reaction 3) .
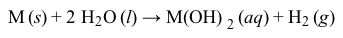
The most difficult alkaline-earth metal to study is radium, because it is a rare radioactive element that is produced from the nuclear decay of uranium. The most common natural isotope, radium-226, has a half-life of 1,600 years and decays by alpha emission into radon-222 (Reaction 4) .
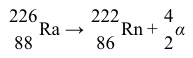
-What is the mass of water necessary to generate 11.2 L of hydrogen gas if calcium metal reacts with water at standard temperature and pressure (STP) ?
A) 2.0 g
B) 4.5 g
C) 9.0 g
D) 18.0 g
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q147: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q148: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q149: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q150: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q151: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q153: Which gas would occupy more volume at
Q154: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q155: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q156: Passage
The alkaline-earth metals are a highly reactive
Q157: Passage
The alkali metals are a highly reactive
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents