Passage
Copper plays a vital role as a trace mineral for biological processes. The amount of dietary copper needed by an adult each day is about 30 μg/kg of body weight, and blood plasma normally has a copper concentration of 1 mg/L.Copper is an essential element, and toxic effects are not common. However, given sufficient exposure to high levels by inhalation, absorption, or ingestion from sources such as industrial hazards or contaminated groundwater, copper toxicity can occur.Salts that are more soluble tend to exhibit higher toxicity when ingested, but the solubilities of copper salts vary and are also temperature-dependent, as shown by selected examples in Figure 1.
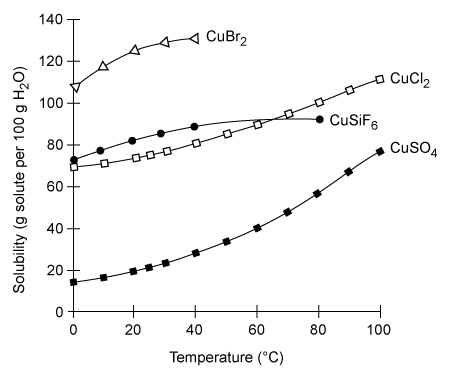 Figure 1 The solubility of selected copper salts in distilled water with increasing temperatureSome copper salts have solubilities much lower than those shown in Figure 1. For example, CuF2 has a solubility of only 0.075 g per 100 g of water (at 25 °C) . This indicates that CuF2 dissociates in water only to a small extent (Reaction 1) and that the equilibrium favors the undissociated salt, giving CuF2 a solubility product constant of Ksp = 1.6 × 10−6.
Figure 1 The solubility of selected copper salts in distilled water with increasing temperatureSome copper salts have solubilities much lower than those shown in Figure 1. For example, CuF2 has a solubility of only 0.075 g per 100 g of water (at 25 °C) . This indicates that CuF2 dissociates in water only to a small extent (Reaction 1) and that the equilibrium favors the undissociated salt, giving CuF2 a solubility product constant of Ksp = 1.6 × 10−6.
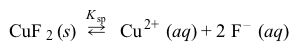 Reaction 1Compound-specific properties can also impact solubility. In CuF2, the dissociated F− ion is mildly basic (pKb = 10.8) , causing the equilibrium to be influenced by the pH of the solution.Specific characteristics of copper can also play a role. For example, copper ions in solution express an affinity to form coordinate bonds with available lone-pair electrons of nitrogen atoms in amines (Reaction 2) .
Reaction 1Compound-specific properties can also impact solubility. In CuF2, the dissociated F− ion is mildly basic (pKb = 10.8) , causing the equilibrium to be influenced by the pH of the solution.Specific characteristics of copper can also play a role. For example, copper ions in solution express an affinity to form coordinate bonds with available lone-pair electrons of nitrogen atoms in amines (Reaction 2) .
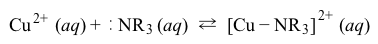 Reaction 2If excess amine ligands are present, coordinate bonds like that shown in Reaction 2 will continue to form until each Cu2+ ion in solution is coordinated with four nitrogen atoms. This acquisition of copper ions by ligands in solution can also impact the solubility equilibrium of copper salts by forming soluble coordination complexes.
Reaction 2If excess amine ligands are present, coordinate bonds like that shown in Reaction 2 will continue to form until each Cu2+ ion in solution is coordinated with four nitrogen atoms. This acquisition of copper ions by ligands in solution can also impact the solubility equilibrium of copper salts by forming soluble coordination complexes.
-For the separation of a saturated aqueous mixture of CuF2 (Ksp = 1.6 × 10−6) and BaF2 (Ksp = 3.0 × 10−6) , a lab technician chose to use the common ion effect to precipitate CuF2 from the solution rather than BaF2. Which of the following statements does NOT explain why precipitating CuF2 is the better choice for the separation procedure?
A) CuF2 is less soluble and more responsive to small changes in common ion concentrations.
B) Adding F− as the common ion would cause CuF2 to precipitate.
C) There are fewer moles of CuF2 to remove from the solution than moles of BaF2.
D) Precipitating BaF2 would require a greater number of common ions to be added to the solution.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q212: Passage
Copper plays a vital role as a
Q213: Passage
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy involves placing a patient
Q214: Passage
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy involves placing a patient
Q215: The reversible reaction Q216: Passage Q218: Passage Q219: When ammonia burns in air, nitrogen dioxide Q220: Passage Q221: Passage Q222: Based on the Pauli exclusion principle, which![]()
Copper plays a vital role as a
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy involves placing a patient
Amino acids and copper both serve vital
Within the renal system, two buffers operate
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents