Passage
Cable theory is a mathematical model used to calculate currents and voltages along and across axon membranes. The model treats small sections of the membrane as the resistor-capacitor circuit shown in Figure 1. An electric neuronal signal enters the circuit through the input node. A portion of the signal remains inside the axon and continues to the next section of membrane via Output 1, and the rest of the signal exits to the extracellular fluid via Output 2.
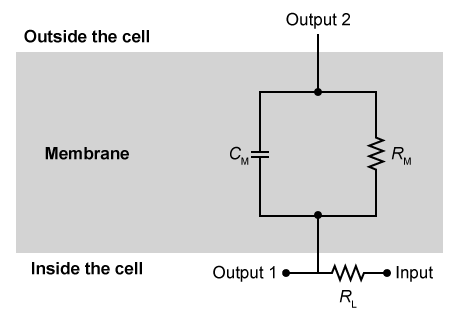 Figure 1 Circuit unit used to model axon membranesResearchers studied cable theory by recreating the circuit in Figure 1 using a 2 μF capacitor for CM, a 200 Ω resistor for RM, and a 1,000 Ω resistor for RL. The researchers sent an electrical signal through the input and discovered that the capacitor acted as a resistor whose resistance varied with the signal's frequency, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1 Circuit unit used to model axon membranesResearchers studied cable theory by recreating the circuit in Figure 1 using a 2 μF capacitor for CM, a 200 Ω resistor for RM, and a 1,000 Ω resistor for RL. The researchers sent an electrical signal through the input and discovered that the capacitor acted as a resistor whose resistance varied with the signal's frequency, as shown in Figure 2.
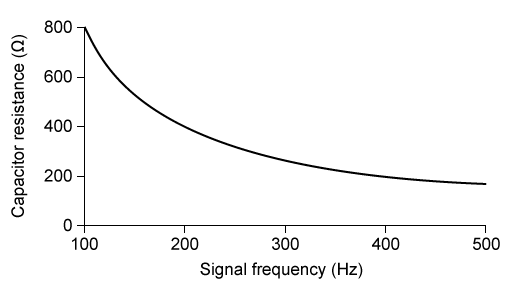 Figure 2 Capacitor equivalent resistance vs. signal frequency for CM
Figure 2 Capacitor equivalent resistance vs. signal frequency for CM
Adapted from Tuckwell H, Introduction to Theoretical Neurobiology 2006 SIAM.
-A voltmeter is placed across RL. If a charge of 0.1 C flows into the input node every 2 s, what will be the reading on the voltmeter?
A) 0 V
B) 50 V
C) 100 V
D) 200 V
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q78: Passage
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a medical
Q79: Passage
Ultrasound is a technique that uses the
Q80: Passage
Ultrasound is a technique that uses the
Q81: Passage
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure
Q82: Passage
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure
Q84: Passage
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure
Q85: Passage
Sound waves propagate through many conducting structures
Q86: Passage
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure
Q87: Passage
Cable theory is a mathematical model used
Q88: Passage
Cable theory is a mathematical model used
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents