Passage
Black holes have played an important part in astrophysics for the last half-century. A black hole is a region of space where the force of gravity is especially strong and gravitational potential energy U is very large. Analogous to the electrostatic potential energy associated with electrical charges, U is defined as the work required to move an object of mass m from an infinite distance to a point at radial distance r within the gravitational field of a second mass M as given by
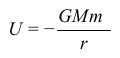 Equation 1where G is the gravitational constant. Near a black hole, the gravitational potential energy can become so negative that not even light has enough energy to escape the black hole's gravity.Escape velocity can be determined by launching an object of mass m with velocity v to an infinite radial distance from the surface of a central mass M (eg, a star or a planet) with radius R. For a black hole to exist, the escape velocity must be equal to the speed of light.Scientists have thoroughly studied the physics of black holes. Stars near the center of our galaxy have been observed to orbit an extremely massive, invisible object (millions of times more massive than our Sun) that is almost certainly a black hole. The orbital angular velocity ω of a star is defined as
Equation 1where G is the gravitational constant. Near a black hole, the gravitational potential energy can become so negative that not even light has enough energy to escape the black hole's gravity.Escape velocity can be determined by launching an object of mass m with velocity v to an infinite radial distance from the surface of a central mass M (eg, a star or a planet) with radius R. For a black hole to exist, the escape velocity must be equal to the speed of light.Scientists have thoroughly studied the physics of black holes. Stars near the center of our galaxy have been observed to orbit an extremely massive, invisible object (millions of times more massive than our Sun) that is almost certainly a black hole. The orbital angular velocity ω of a star is defined as
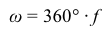 ω=360°⋅fEquation 2where f is the frequency of rotation in hertz (Hz) . Likewise, black holes are not merely static masses but are often observed to rotate about their own axis. The interaction between the rotation of a black hole and matter falling into the hole is suspected to form powerful beams (jets) of ionized matter that project away from the black hole along its axis of rotation. Nevertheless, many aspects of how these jets are formed remains a mystery. Black holes will remain a fruitful area for research far into the future.
ω=360°⋅fEquation 2where f is the frequency of rotation in hertz (Hz) . Likewise, black holes are not merely static masses but are often observed to rotate about their own axis. The interaction between the rotation of a black hole and matter falling into the hole is suspected to form powerful beams (jets) of ionized matter that project away from the black hole along its axis of rotation. Nevertheless, many aspects of how these jets are formed remains a mystery. Black holes will remain a fruitful area for research far into the future.
-Which of the following graphs best illustrates how the gravitational potential energy for a black hole varies with radial distance r ?
A) 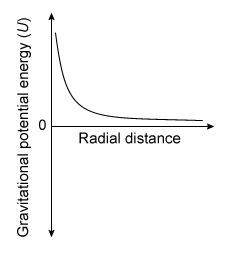
B) 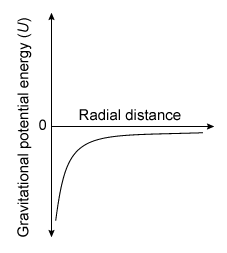
C) 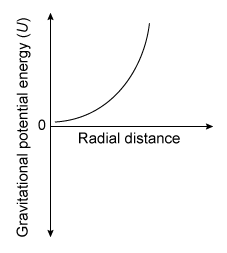
D) 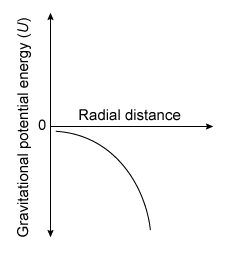
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q190: An observer perceives a sound to be
Q191: Passage
Black holes have played an important part
Q192: A spring is extended 15 cm from
Q193: Different substances have different thermal conductivities k,
Q194: Passage
The flow of blood through the human
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents