Hendricks Ltd. of Calgary manufactures and sells computers. The Manufacturing Division is located in China and transfers 75% of its output to the Assembly Division in the Philippines. The balance of the product is sold in the local market at 2,100 yuan/unit. The Philippines division sells 20% of its output in the local market at 31,500 pesos/unit, with the balance shipped to Calgary. The Calgary operation packages the units and sells the final product at $1,900 Canadian per unit.
The following budget data are available:
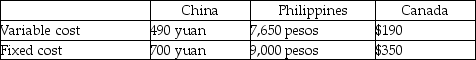
Exchange rates are: $1 Canadian = 7 yuan and $1 Canadian = 45 pesos
Tax rates are 45% in China, 20% in the Philippines and 40% in Canada. Income taxes are not included in the calculation of cost-based transfer prices. Assume that Hendricks does not pay Canadian tax on amounts already taxed in foreign jurisdictions. Take each calculation to 2 decimal places.
Required:
The company has determined that it may transfer units at 250% of variable cost or at market and comply with all existing tax legislation. Which transfer pricing method should the company pursue? Support your recommendation with appropriate calculations.
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q35: Walton Industries has two divisions: Machining and
Q36: Payne Ltd. has two divisions. The Compound
Q37: The Micro Division of Silicon Computers produces
Q38: The Assembly Division of Canadian Car Company
Q39: River Road Paint Company has two divisions.
Q40: Sonora Manufacturing Inc. designs and builds off-road
Q41: Global Giant, a multinational corporation, has a
Q42: Empire Ltd. has two divisions. Division C
Q43: Stavanger Ltd. is a Canadian company with
Q45: Clark Industries Ltd. manufactures monochromators that are
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents