Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon and Nile, must make their pricing decisions simultaneously. Amazon (A) and Nile (N) face the following demand and long-run cost conditions, which are common knowledge to the managers: 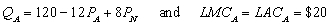
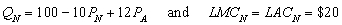 The prices,
The prices, 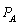 and
and 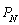 , are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities,
, are the prices charged by Amazon and Nile, respectively. The quantities, 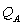 and
and 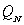 , are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve,
, are the respective daily quantities sold by each firm. The figure below shows Nile's best-response curve, 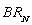 . Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
. Only one point on Amazon's best-response curve, point K, is shown in the figure.
-Point C is not likely to be the decision outcome because it is not _______________ _____________, and either firm could unilaterally ___________ (increase, decrease) its price and earn greater daily profit. 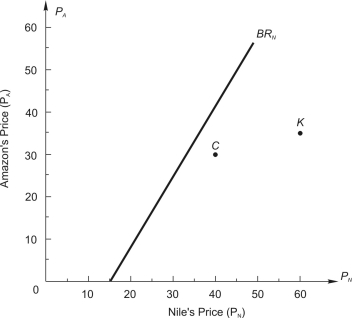
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q27: Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon
Q28: Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon
Q29: Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon
Q30: Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon
Q31: Managers of two competing oligopoly firms, Amazon
Q33: Sony and Zenith must each decide which
Q34: Sony and Zenith must each decide which
Q35: Sony and Zenith must each decide which
Q36: Sony and Zenith must each decide which
Q37: Sony and Zenith must each decide which
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents