
The following table from the Venter et al.paper presents the numbers of different types of genes discovered in this study.
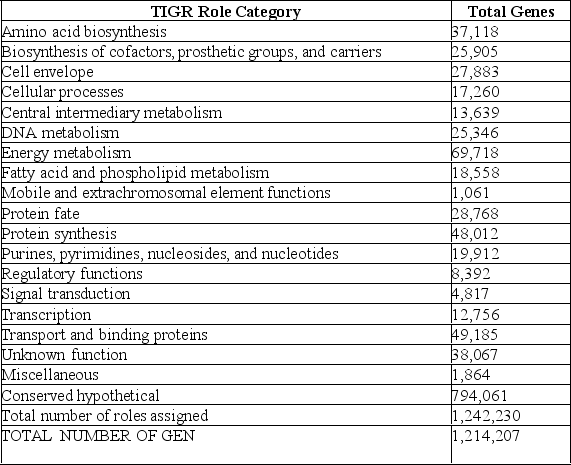
-Refer to the paragraph on the Venter et al.paper and Table 20.1 Because DNAs for sequencing were chosen at random with no way of knowing which organism they came from,how could genes be identified?
A) by searching for ORFs,especially those with translation start and stop sites
B) by searching for similarity between predicted ORFs and those in existing databases
C) by searching for exons bounded by consensus donor and acceptor splice sites (those that mark exon/intron boundaries)
D) by searching for ORFs,particularly those with translation start and stop sites,as well as for similarity between predicted ORFs and those in existing databases
E) by searching for ORFs,particularly those with translation start and stop sites;for similarity between predicted ORFs and those in existing databases;and for exons bounded by consensus donor and acceptor splice sites (those that mark exon/intron boundaries)
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q19: LINES transposable elements are closely related to
Q20: Forensic DNA fingerprinting often involves recovery of
Q21: The following table from the Venter et
Q22: Mutations that occur in one member of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents