Refer to Figure 9.1 to answer the following questions.
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions.
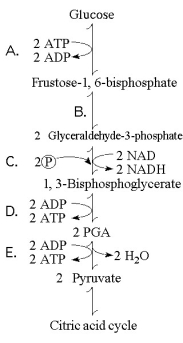
-The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and water is -686 kcal/mole and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mole. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
A) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
B) Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
C) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
D) There is no CO₂ or water produced as products of glycolysis.
E) Glycolysis consists of many enzymatic reactions, each of which extracts some energy from the glucose molecule.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q15: In addition to ATP, what are the
Q21: During cellular respiration, acetyl CoA accumulates in
Q24: Carbon dioxide (CO₂)is released during which of
Q31: Why is glycolysis described as having an
Q31: Use the following information to answer the
Q33: Use the following information to answer the
Q37: Which kind of metabolic poison would most
Q37: Refer to Figure 9.2, showing the citric
Q41: Refer to Figure 9.2, showing the citric
Q91: In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents