Correct bond calculations in the United States usually involve semiannual periods because bond interest is typically paid twice a year.
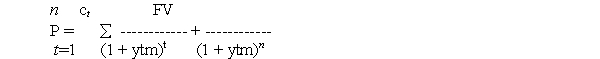 where
where
P = the current market price of the bond
n = the number of semiannual periods to maturity
ytm = the semiannual yield to maturity to be solved for
c = the semiannual coupon in dollars
FV = the face value (or maturity value or par value)which in this discussion is always $1,000
What does this formula imply about the term structure of interest rates? How would real-world bond investors price bonds to correct for this?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q20: Why is duration important for investing in
Q21: Yield spreads vary inversely with the: _.
Q25: If interest rates rise, then price risk
Q26: The vast majority of corporate bonds pay
Q27: Three theories have been proposed to explain
Q27: As interest rates increase,long bonds will decrease
Q30: Risk premiums,or yield spreads,refer to the issue
Q31: The term structure of interest rates denotes
Q36: Reinvestment risk represents the possibility that future
Q39: A financial crisis or an accounting scandal
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents