Why is calcium fluoride, Ca 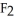 , a high melting point crystalline solid while tin (IV) chloride,
, a high melting point crystalline solid while tin (IV) chloride, 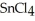 , is a volatile liquid?
, is a volatile liquid?
A) There is no theory to predict the physical property of melting point. Melting point temperatures are empirically determined.
B) Actually, we would predict these results to be the opposite. Since each metal is combined with a group 17 halogen, the heavier metal (tin) combination should have the higher melting point.
C) Ca 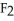 is a small, linear, non-polar molecule, while
is a small, linear, non-polar molecule, while 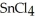 is a huge tetrahedral structure. Therefore the bonds in calcium fluoride tend to give it a higher melting point temperature.
is a huge tetrahedral structure. Therefore the bonds in calcium fluoride tend to give it a higher melting point temperature.
D) Ionic compounds formed by elements on opposite sides of the periodic table, like 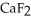 , tend to have higher melting points than more covalently bonded structures, like
, tend to have higher melting points than more covalently bonded structures, like 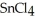 .
.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q26: In a solution of 77 percent nitrogen
Q35: Friends on a crowded ice skating rink
Q36: Which of the following would have the
Q41: Two chemical structures are shown, one of
Q56: Which has the most atoms?
A)a mole of
Q124: Which of the following intermolecular forces best
Q126: Which of the following would have the
Q129: Which of the following intermolecular forces best
Q139: Which of the following would have the
Q142: Why is the surface area of a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents