T-bet and GATA-3 are transcription factors known to regulate the development of polarized subsets of CD4 T cells. To investigate the effects of altering the cytokines produced by CD4 effector T cells during chronic airway inflammation, transgenic mice were generated that constitutively express either T-bet or GATA-3 in all T cells. These strains of mice are referred to as T-bet-tg or GATA-3-tg, respectively. Wild-type, T-bet-tg and GATA-3-tg mice were then sensitized by intraperitoneal injection of chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) in a TH2-inducing adjuvant. Three weeks later, mice were challenged daily by intranasal administration of OVA protein in saline for 8 weeks. Control mice were immunized and challenged with saline alone. One day following the final intranasal challenge with OVA or saline, the mice were euthanized, and their lungs were examined by histological analysis for the percentages of mucus-positive cells and for thickening of airway walls as a measure of airway remodeling. These data were quantified, and are shown in Figure Q25)A. Note that the airway remodeling is scored on a relative scale in arbitrary units (AU). 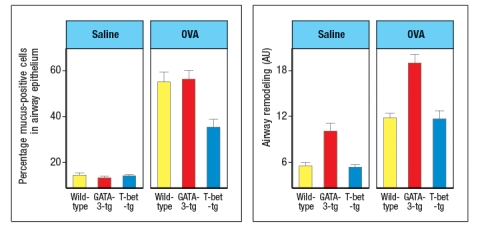
a) What is the effect of GATA-3-expressing T cells on the numbers of mucus-producing cells compared to its effect on airway remodeling?
b) What is the effect of enforcing T-bet expression in T cells on the numbers of mucus-producing cells compared to its effect on airway remodeling?
One day after the final challenge with intranasal OVA or saline, mice were also examined for the numbers of eosinophils in their lungs. Lung homogenates were also tested for cytokine levels by ELISA. These data are shown in Figure .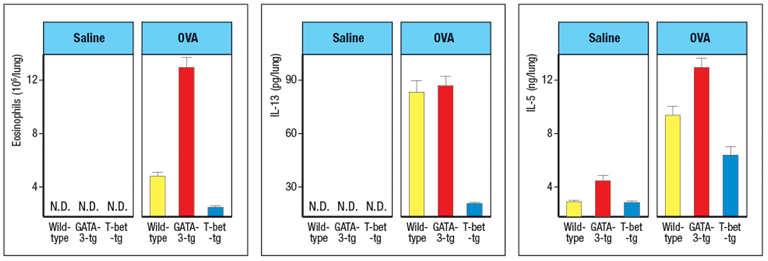
c) What is the effect of enforced expression of GATA-3 or T-bet in T cells on the numbers of eosinophils in the lung? Based on the cytokine data, which cytokine is likely contributing to this effect?
In a final experiment, mice are euthanized one day after the final saline or OVA administration, and lymphocytes are isolated from the lungs. The isolated lymphocytes are stimulated through their T-cell receptors to induce cytokine production from effector T cells. During this 5-hour in vitro stimulation to elicit cytokine production, the cells are also incubated with a protein secretion inhibitor. After the 5-hour incubation, the cells are stained with antibodies to CD3 and CD4, then the cells are fixed and permeabilized, and stained with antibodies to IFN- For IL-4. The percentages of CD4 T cells expressing each cytokine are shown in Figure .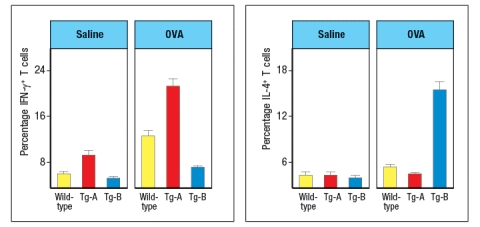
d) Based on these data, deduce whether Tg-A is the GATA-3-tg line or the T-bet-tg line, and similarly, deduce the identity of Tg-B. Explain your reasoning.
IL-12 is an important cytokine that induces T-bet up-regulation in CD4 T cells. If one discovered that polymorphisms in the IL-12 locus were linked to increased susceptibility to allergies and asthma based on GWAS (genome-wide association studies) data derived from human population cohorts, what difference would be expected when comparing the allele in healthy controls versus the allele found more frequently in asthma patients?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q16: Genetic studies have identified more than 40
Q17: Genetic variations in proteins involved in immune
Q18: Red blood cells are common targets
Q19: Individuals with allergic responses to inhaled antigens
Q20: In mice, an allergic response in the
Q21: Celiac disease occurs when an individual
Q23: IL-33 is a cytokine known
Q24: On occasion, individuals on antibiotics such
Q25: The response of most individuals to
Q26: Hypersensitivity responses to divalent cations such as
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents