A family of six (mother, father, and four children) had two children with a history of chronic illness. Both children had repetitive infections of the sinuses, middle ears, and lungs due to a variety of respiratory viruses. Their other siblings were generally healthy and showed no signs of persistent or recurrent virus infections.
The two affected children had normal numbers of B cells, T cells, and NK cells in their blood. They also showed no defects in neutrophil function or in complement protein levels. The two children also had normal antibody levels to vaccine protein antigens, such as tetanus toxoid, and had normal T cell responses to antigens from the vaccine strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis after being vaccinated.
Blood cells from one parent, one healthy child and the two affected children were examined for surface MHC protein expression by flow cytometry using two antibodies, one that recognizes all HLA class I proteins, and one that recognizes all HLA class II proteins. The results are shown in Figure
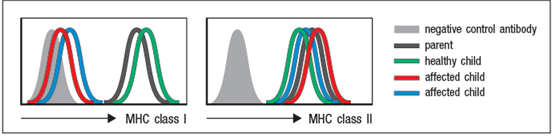
a) Analysis of HLA genotypes from the two affected children showed that they shared one haplotype of this locus. This haplotype encodes a common HLA-A allele, HLA-A2. Based on these data, is it likely that the two affected children have a point mutation (or mutations) in the coding sequence for HLA-A2? Why or why not?
b) Name two proteins that could be candidates for the defective gene in the two affected children.
To address which gene defect might be present in the affected children, peripheral blood cells were isolated from one healthy child and one affected child, and mRNA was isolated from the cells. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to assess the levels of mRNA for the three HLA class I heavy chain genes (HLA-A, -B, and –C) and for the β2-microglobulin gene. The results are shown in Figure .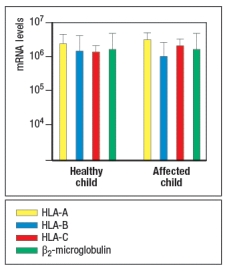
In a second experiment, Western blots were performed, confirming that cell lysates from both affected children contained normal levels of all three HLA class I heavy chain proteins and the β2-microglobulin protein.
c) Do these data eliminate any of your answers to part (b)?
In a final experiment, peripheral blood cells from the two affected children and one HLA-A2+ parent were transfected with a construct encoding the Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HepBsAg), a protein that is currently used in the vaccine against Hepatitis B. This protein is normally synthesized and transported to the cell surface. In addition to the full length HepBsAg construct, cells were also transfected with a mini-gene, encoding just a single HLA-A2-binding peptide derived from Hepatitis B, amino acids 338–347. Using a cytolytic CD8 T cell clone specific for HepBsAg(338–347) peptide bound to HLA-A2, the transfected cells were tested for recognition by the CD8 T cell clone using an assay that measures target cell killing. Figure Q6.29C shows the results of this experiment.
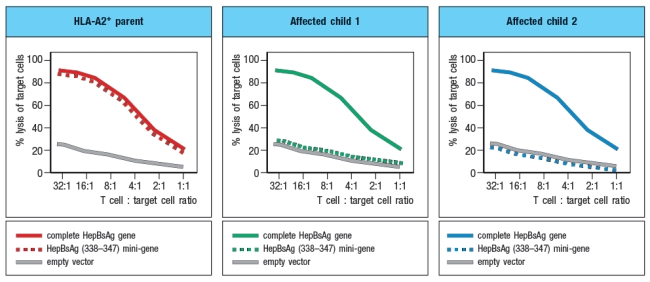
d) What is the most likely gene that is defective in the affected children?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q17: During MHC class I synthesis and folding
Q18: A cell line carrying a mutation in
Q19: Peptide editing is an important component of
Q20: The genes encoding MHC proteins are closely
Q21: Alloreactivity refers to the ability of T
Q23: Some CD1 molecules bind to glycosphingolipids,
Q24: The extensive polymorphism of MHC genes in
Q25: In the 1980s, a mutant strain
Q26: NKG2D is an activating receptor expressed
Q27: The MHC locus encodes a large number
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents