Patients with recurrent infections of Neisseria meningitidis, an extracellular bacterial pathogen that causes meningitis, were examined to determine the underlying cause of their immunodeficiency. A subset of these patients were found to have defects in complement activation on the bacterial surface, a process that for this bacterium is dominated by alternative complement activation leading to C3b deposition on the pathogen surface. When neutrophils from these patients were examined in vitro, the results in Figure were obtained. 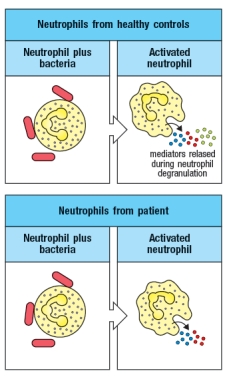
Based on these data, the identity of the green neutrophil mediator in Figure is likely to be:
A) Complement factor B
B) The C3 convertase
C) Factor P (properdin)
D) C3b
E) Mannose-binding lectin (MBL)
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q11: Pathogenic infections induce damage to the host
Q12: Infants and young children with deficiencies in
Q13: Epithelial surfaces provide the first line of
Q14: One form of anemia results when individuals
Q15: Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacterium that
Q17: The classical complement pathway is initiated by
Q18: Our environment contains masses of microorganisms, many
Q19: Mannose binding lectins (MBL) and ficolins are
Q20: The alternative pathway of complement activation has
Q21: Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacterium that
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents