The two figures represent an asexual and a sexual population. The letters indicate beneficial mutations. The shaded areas represent the frequency of particular combinations of mutations in the population over time. Why does it take longer for the beneficial allele combination of ABC to go to fixation in the asexual population than in the sexual population? 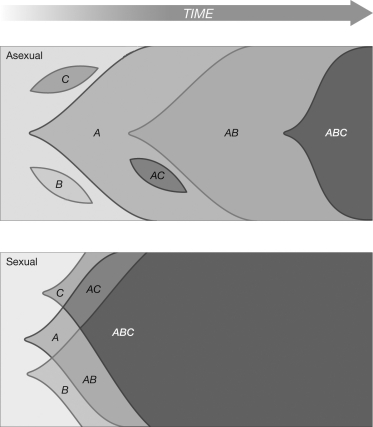
A) In the asexual population, new allelic combinations have to arise via de novo mutations.
B) There is no principal difference between asexual and sexual populations. In the sexual population shown, the favorable mutations just happen to be on different chromosomes.
C) The effective population size of both populations is the same.
D) Sexual populations tend to have higher mutation rates.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q15: In a population that is polymorphic for
Q16: During bacterial conjugation, small circular chromosomes of
Q17: The Amazon molly, Poecillia formosa, is a
Q18: The figure shown illustrates the proportion of
Q19: What is the consequence of a deleterious
Q21: Why are transduction, conjugation, and transformation sometimes
Q22: Birds of paradise are a family of
Q23: Which step of the process of amphimixis
Q24: In the crustacean genus Hyalella, females mate
Q25: How could the number of gametes produced
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents