A recently discovered bacterium carries out ATP synthesis coupled to the flow of electrons through a chain of carriers to some electron acceptor. The components of its electron transfer chain differ from those found in mitochondria; they are listed below with their standard reduction potentials. 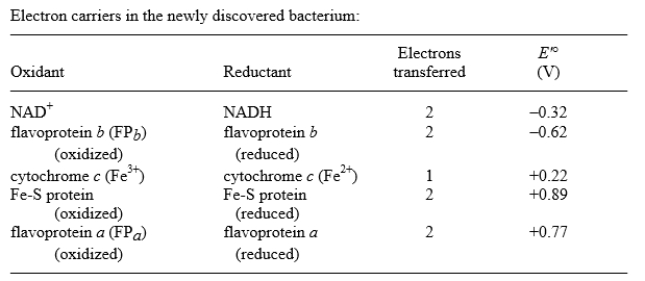 (a) Place the electron carriers in the order in which they are most likely to act in carrying electrons. (b) Is it likely that O2 (for which E'° = 0.82 V) is the final electron acceptor in this organism? Why or why not? (c) How would you calculate the maximum number of ATP molecules that could theoretically be synthesized, under standard conditions, per pair of electrons transfered through this chain of carriers? (The Faraday constant,
(a) Place the electron carriers in the order in which they are most likely to act in carrying electrons. (b) Is it likely that O2 (for which E'° = 0.82 V) is the final electron acceptor in this organism? Why or why not? (c) How would you calculate the maximum number of ATP molecules that could theoretically be synthesized, under standard conditions, per pair of electrons transfered through this chain of carriers? (The Faraday constant, 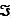 , is 96.48 kJ/V · mol.) G'° for ATP synthesis is +30.5 kJ/mol.
, is 96.48 kJ/V · mol.) G'° for ATP synthesis is +30.5 kJ/mol.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q58: Antimycin A blocks electron transfer between cytochromes
Q59: Which statement is NOT a feature of
Q60: Which statement is NOT true of the
Q61: Cytochrome c interacts with multiple different proteins
Q62: Which factor is NOT controlled by hypoxia-inducible
Q64: Under standard conditions, NADH reoxidation by the
Q65: How do the cytosolic and mitochondrial isozymes
Q66: Which phrase BEST describes the role
Q67: Bovine ATP synthase contains 8 c subunits
Q68: Which statement about human mitochondria is TRUE?
A)
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents