Define the GLS estimator and discuss its properties when Ω is known.Why is this estimator sometimes called infeasible GLS? What happens when Ω is unknown? What would the Ω matrix look like for the case of independent sampling with heteroskedastic errors,where var(ui  Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2
Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2 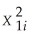 ? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into
? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into 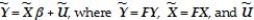 = FU,and
= FU,and 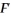 F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q29: Give several economic examples of how to
Q31: To prove that the OLS estimator is
Q33: An estimator of β is said to
Q35: The extended least squares assumptions in the
Q35: The presence of correlated error terms creates
Q36: The leading example of sampling schemes in
Q38: The homoskedasticity-only F-statistic is Q39: The OLS estimator for the multiple regression Q40: Consider the multiple regression model from Chapter Q41: Prove that under the extended least squares
A) ![]()
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents