For a continuous random variable x and constant a, P(x 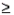 a) = P(x >a) and P(x
a) = P(x >a) and P(x 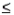 a) = P(x < a).
a) = P(x < a).
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q68: One difference between a binomial random variable
Q72: The normal probability distribution is one of
Q77: Examples of continuous probability distributions include the
Q107: For any random variable x and constant
Q108: In the standard normal curve, the z-score
Q111: The area between z = 0 and
Q113: In the standard normal curve, the probability
Q114: The normal probability distribution is right-skewed for
Q115: For a continuous random variable x and
Q117: Let ![]()
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents