The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes the transmission of two genes in the X chromosome. The male parent has mutant alleles for both the white gene (w-) and the crossveinless gene (cv-) . The female parent has nonmutant forms of these genes (w+ and cw+) . A cross between siblings of the F1 generation-a red-eyed, crossveined female and a red-eyed, crossveined male-generates F2 progeny. Examine the genotype of the F2 male progeny. Notice that the progeny fall into two groups. Refer to the figure below when answering the following question. Which of the statements below does NOT explain why the male progeny from the F1 cross are used for linkage analysis? 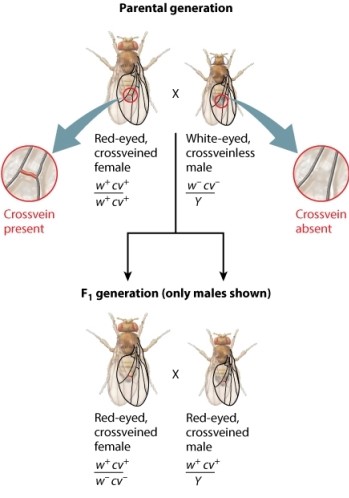
A) The phenotype of F2 males reveals the genotype of the X chromosome they inherited from their mother.
B) All four possible classes of maternal gametes are observed in the F2 male progeny in a 1:1:1:1 ratio, which indicates that the two genes undergo independent assortment.
C) The lack of independent assortment indicates that the two genes are linked in the X chromosome.
D) The Y chromosome in the male offspring allows the genotype of each X chromosome inherited from the mother to be observed in the male phenotype.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q133: The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes
Q134: The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes
Q135: Physical exchange between homologous chromosomes (crossover) occurs
Q136: The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes
Q137: Recombination frequency is used to measure the
Q139: The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes
Q140: Two genes, A and B, are found
Q141: Which of the following BEST describes the
Q142: If a pedigree involves a Y-linked trait,
Q143: An XXY person inherited three sex chromosomes
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents