Two independent mutants are discovered in a strain of fruit flies. Both are due to the insertion of a transposable element into a gene that is required to produce red pigment in the eyes, but the eyes are yellow instead of red. When the transposon undergoes transposition to another location, the copy present in the original location is sometimes deleted. When the copy in the gene required for red pigment is deleted, the gene regains its ability to function, and the cell with the deletion and all its descendants can produce the red pigment. In one mutant, A shown below, the eyes have tiny red sectors scattered throughout, whereas in the other mutant, B, the eyes have larger blotches of color. What do these patterns tell you about the transposition of the transposons in the mutants A and B? 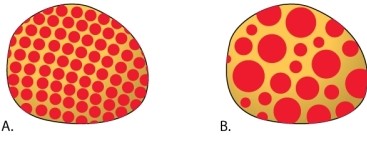
A) The transposons in A and B transpose at about the same time in development.
B) The transposon in A tends to transpose at an earlier time in development than that in B.
C) The transposon in A tends to transpose at a later time in development than that in B.
D) The transposon in A is likely a retrotransposon, which in B is a DNA transposon.
E) The transposon in A is likely a DNA transposon, which in B is a retrotransposon.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q102: The accompanying diagram shows three gene duplication
Q103: Genetic risk factors act independently of environment
Q104: A molecular clock allows differences among genomes
Q105: The human genome codes for a form
Q106: The tree below shows the estimated percent
Q108: The human genome contains a family of
Q109: The human genome contains a family of
Q110: Each curve in the graph below shows
Q111: The human genome contains a family of
Q112: In large genomes, MOST reciprocal translocations occur
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents