A 41-year-old previously healthy man is admitted to the hospital with 3 days of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. He was found to have acute necrotizing pancreatitis due to alcohol use. His hospital course was complicated by hypotension requiring 8 L of intravenous fluids. He subsequently developed bilateral infiltrates and refractory hypoxemia requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation. While in the intensive care unit, he develops low-grade fevers and worsening hypoxemia requiring 100% FiO2 and positive end-expiratory pressure of 12. Cultures are obtained and antibiotic coverage is broadened. His blood and urine cultures show no growth 48 hours later. However, sputum culture grows Candida species.
Laboratory results are as follows: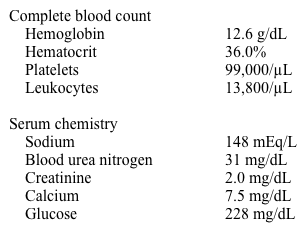
A repeat chest x-ray shows persistent bilateral infiltrates and new small bilateral pleural effusions.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in managing this patient's positive sputum culture?
A) Fluconazole
B) Micafungin
C) No antifungal drug treatment
D) Repeat respiratory cultures
E) Thoracentesis
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q105: A 47-year-old man is hospitalized due to
Q106: A 76-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Q107: A 65-year-old man is admitted to the
Q108: A 47-year-old man with known HIV infection
Q109: A 60-year-old woman is brought to the
Q111: A 58-year-old man with a history of
Q112: A 39-year-old man is admitted to the
Q113: A 64-year-old man with a moderate right-sided
Q114: A 35-year-old woman underwent ultrasound evaluation for
Q115: A 46-year-old man with known kyphoscoliosis complains
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents