A 65-year-old man comes to the physician to discuss chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. His medications include budesonide/formoterol, tiotropium, and as-needed albuterol. He has dyspnea on exertion after walking 100 yards or up a flight of stairs. The patient has never had an exacerbation requiring hospitalization. He quit smoking 7 years ago and has a 45-pack-year history. SaO2 is 88% on room air at rest. He has a barrel chest, and the lung examination shows decreased air entry bilaterally but is otherwise clear to auscultation. Heart examination is significant for a holosystolic murmur at the left lower sternal border and a loud P2. There is 1+ bilateral pretibial edema. Pulmonary function results are as follows: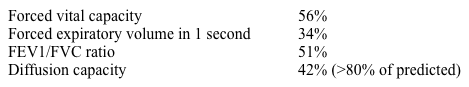
An echocardiogram demonstrates normal left ventricular function, normal right ventricular size and function, and moderate tricuspid regurgitation. Estimated pulmonary artery systolic pressure is 50 mm Hg, and mean pulmonary artery pressure is 29 mm Hg.
In addition to starting home oxygen, which of the following would be recommended in this patient?
A) No additional therapy
B) Right heart catheterization followed by bosentan
C) Right heart catheterization followed by inhaled iloprost
D) Sildenafil
E) Warfarin
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q709: A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician
Q710: A 38-year-old man comes to the office
Q711: A 20-year-old man with known cystic fibrosis
Q712: A 60-year-old man comes to the physician
Q713: A 43-year-old construction worker comes to the
Q715: A 65-year-old man is evaluated for progressively
Q716: A 60-year-old man comes to the physician
Q717: A 20-year-old man with a history of
Q718: A 68-year-old man comes to the office
Q719: A 24-year-old woman with a history of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents