A 67-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to sudden-onset, severe low back pain that began when she was lifting her grandson. The pain does not radiate to the lower extremities; she has had no weakness or sensory loss in her legs or urinary incontinence. The patient has had back pain in the past but not of this severity. She has a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hypothyroidism, for which she takes lisinopril, atorvastatin, and levothyroxine. The patient was also found to have low bone mineral density during a screening test 2 years ago. She has been feeling more tired lately and has not been able to exercise as recommended but does take daily calcium and vitamin D supplements and weekly alendronate as prescribed. She also has not consumed dairy products regularly as in the past due to her poor appetite; she has lost about 4.5 kg (10 lb) over the past several months. The patient is a lifelong nonsmoker and drinks alcohol occasionally. Blood pressure is 148/86 mm Hg and pulse is 96/min. BMI is 21 kg/m2. Physical examination shows tenderness to percussion over the lower thoracic spine. Bilateral lower extremity muscle strength, sensation, and deep tendon reflexes are normal. Laboratory results are as follows: 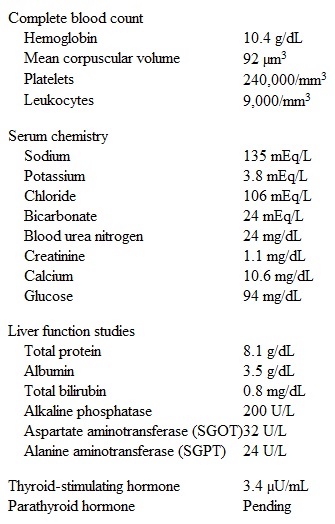 Spine radiography shows a T12 vertebral compression fracture. In addition to analgesics, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Spine radiography shows a T12 vertebral compression fracture. In addition to analgesics, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A) Add teriparatide to the medical regimen
B) Change oral alendronate to intravenous ibandronate
C) Obtain parathyroid sestamibi scintigraphy
D) Perform serum and urine protein electrophoresis
E) Test for IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase antibody
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q458: A 29-year-old woman with chronic anemia comes
Q459: A 24-month-old boy is brought to the
Q460: A 6-year-old boy is brought to the
Q461: A 58-year-old man is brought to the
Q462: A 4-year-old girl is brought to the
Q464: A 70-year-old woman comes to the office
Q465: A 52-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the
Q466: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the
Q467: A 64-year-old man admitted to a rehabilitation
Q468: A 70-year-old woman comes to the office
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents