Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps are PEG 150 distearate and ethylhexyl glycerin. Both can be synthesized from glyceryl tristearate (Figure 1) .
 Figure 1 Formation of PEG 150 distearate and ethylhexyl glycerin from glyceryl tristearateThe first step in this process requires the saponification of glyceryl tristearate. The resulting stearate molecules can then react with PEG 150 in an acid-catalyzed Fischer esterification to form PEG 150 distearate. The glycerol produced during saponification is used as a nucleophile to form ethylhexyl glycerin through a base-catalyzed SN2 reaction with an ethylhexyl halide.Studies have shown that hand washing with soap can substantially reduce the number of germs present on hands and that washing hands before preparing food is particularly effective in reducing illness. Researchers examined the effect of washing for 20 seconds with different amounts of soap containing PEG 150 distearate and ethylhexyl glycerin and found an inverse correlation between the volume of soap used and the amount of bacteria recovered from the hands. The data are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1 Formation of PEG 150 distearate and ethylhexyl glycerin from glyceryl tristearateThe first step in this process requires the saponification of glyceryl tristearate. The resulting stearate molecules can then react with PEG 150 in an acid-catalyzed Fischer esterification to form PEG 150 distearate. The glycerol produced during saponification is used as a nucleophile to form ethylhexyl glycerin through a base-catalyzed SN2 reaction with an ethylhexyl halide.Studies have shown that hand washing with soap can substantially reduce the number of germs present on hands and that washing hands before preparing food is particularly effective in reducing illness. Researchers examined the effect of washing for 20 seconds with different amounts of soap containing PEG 150 distearate and ethylhexyl glycerin and found an inverse correlation between the volume of soap used and the amount of bacteria recovered from the hands. The data are shown in Figure 2.
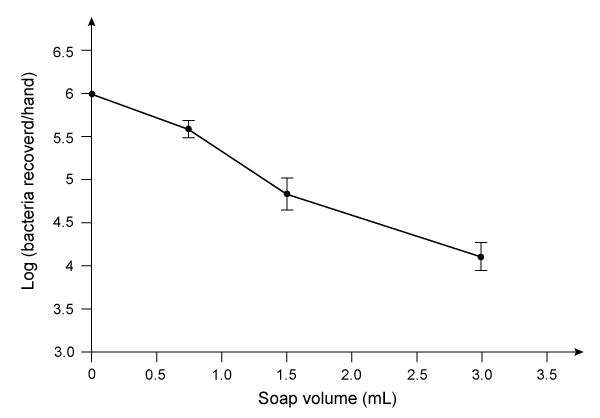 Figure 2 Bacteria recovered from hands after washing with varying amounts of soapThe researchers then investigated the effect of hand washing with different kinds of soap on the transfer of bacteria from hands to objects. Volunteers washed with a fixed volume of soap for 30 seconds, then handled sterilized plastic spheres for 30 seconds. Bacteria were then recovered from the spheres. The results are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Bacteria Recovered from Objects
Figure 2 Bacteria recovered from hands after washing with varying amounts of soapThe researchers then investigated the effect of hand washing with different kinds of soap on the transfer of bacteria from hands to objects. Volunteers washed with a fixed volume of soap for 30 seconds, then handled sterilized plastic spheres for 30 seconds. Bacteria were then recovered from the spheres. The results are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Bacteria Recovered from Objects
 Adapted from Fuls JL, Rodgers ND, Fischler GE, et al. Alternative hand contamination technique to compare the activities of antimicrobial and nonantimicrobial soaps under different test conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008.
Adapted from Fuls JL, Rodgers ND, Fischler GE, et al. Alternative hand contamination technique to compare the activities of antimicrobial and nonantimicrobial soaps under different test conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008.
-A reaction between a long-chain anhydride and phenylethylamine is done to produce a long-chain amide and a carboxylic acid. Which of the following aqueous solutions can separate the products of this reaction in an extraction?
A) NaHSO4
B) HNO3
C) LiOH
D) HClO4
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q48: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q49: Passage
The β-lactam scaffold is an important feature
Q50: Passage
The β-lactam scaffold is an important feature
Q51: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q52: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Q54: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Q55: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Q56: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Q57: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q58: Which structure is the product of the
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents