Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that acts against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria by blocking peptidyl transfer, which inhibits protein synthesis by bacterial ribosomes. However, it tastes bitter, so most patients cannot tolerate it. As a result, synthesis of hydroxyl-substituted chloramphenicol analogues has become of interest because ester chloramphenicol analogues taste better than chloramphenicol. Substituents on the primary hydroxyl group of chloramphenicol analogues are typically hydrolyzed quickly in vivo to regenerate Compound 1. Compound 3, a chloramphenicol analogue, was synthesized by the transesterification of Compound 1 and vinyl propionate (Compound 2) , catalyzed by the enzyme LipBA lipase (Figure 1) .
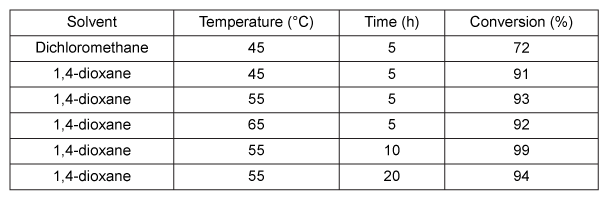
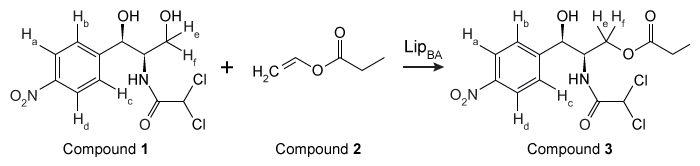 Figure 1 Transesterification of chloramphenicol catalyzed by LipBAAlthough enzyme catalysis allows for efficient regiospecific and stereospecific bond formation, the reaction conditions for the conversion efficiency of Compound 1 to Compound 3, as well as the purity of Compound 3, must also be optimized. The reaction solvent, temperature, and time were studied to find the conditions that gave the highest conversion rate and purity. Each parameter was altered individually while all others were kept constant, and the enzyme concentration was 4.5 g/L in each trial. The results of this study are shown in Table 1. The purity of Compound 3 was found to be over 90% when 1,4-dioxane was used and over 70% when dichloromethane was used.Table 1 Transesterification Conditions Optimization
Figure 1 Transesterification of chloramphenicol catalyzed by LipBAAlthough enzyme catalysis allows for efficient regiospecific and stereospecific bond formation, the reaction conditions for the conversion efficiency of Compound 1 to Compound 3, as well as the purity of Compound 3, must also be optimized. The reaction solvent, temperature, and time were studied to find the conditions that gave the highest conversion rate and purity. Each parameter was altered individually while all others were kept constant, and the enzyme concentration was 4.5 g/L in each trial. The results of this study are shown in Table 1. The purity of Compound 3 was found to be over 90% when 1,4-dioxane was used and over 70% when dichloromethane was used.Table 1 Transesterification Conditions Optimization
 The transesterification reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (Figure 2) , and the product was confirmed by 1H NMR. The 1H NMR spectra of Compounds 1 and 3 can be distinguished by the shift of He and Hf due to the addition of the electronegative ester functional group.
The transesterification reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (Figure 2) , and the product was confirmed by 1H NMR. The 1H NMR spectra of Compounds 1 and 3 can be distinguished by the shift of He and Hf due to the addition of the electronegative ester functional group.
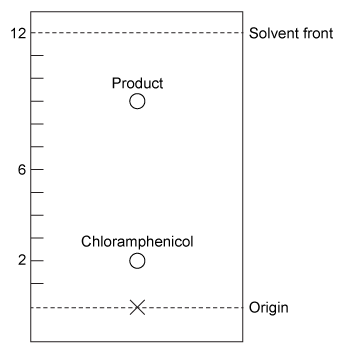 Figure 2 Thin-layer chromatography of reaction mixture
Figure 2 Thin-layer chromatography of reaction mixture
Adapted from F. Dong et al., "Transesterification Synthesis of Chloramphenicol." Molecules. ©2017 MDPI.
-Which of the following experimental conditions does NOT contribute to the highest conversion efficiency?
A) Use of 1,4-dioxane as the solvent
B) Reaction temperature of 55 °C
C) Reaction time of 20 hours
D) Enzyme concentration of 4.5 g/L
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q127: Passage
Fatty acids (FAs) are lipids that play
Q128: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q129: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q130: Passage
Malaria is caused by the parasite Plasmodium
Q131: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q133: Passage
Solid-phase peptide synthesis is normally carried out
Q134: Passage
Solid-phase peptide synthesis is normally carried out
Q135: Passage
Fatty acids (FAs) are lipids that play
Q136: Passage
Fatty acids (FAs) are lipids that play
Q137: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents