Passage
Malaria is caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum and is transmitted through a female mosquito bite. Although there are antimalarial treatments available, P. falciparum has become resistant to many of these drugs. P. falciparum cells contain a respiratory organelle called the apicoplast that is necessary for the parasite's survival but is not found in humans. Therefore, a new drug that targets this organelle could be useful in the treatment of malaria.A portion of the apicoplast protein ferredoxin (PfFd) is shown in Figure 1, with certain amino acid residues labeled. In the apicoplast, ferredoxin NADP+ reductase (PfFNR) interacts electrostatically with PfFd and catalyzes an electron transfer reaction. A compound that selectively inhibits this interaction could be a beneficial antimalarial agent.
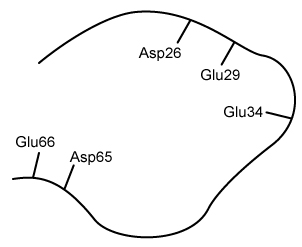 Figure 1 Structure of a portion of PfFdChalcone (Compound 3) is a compound that interacts with PfFd and exhibits antimalarial properties. A series of chalcone derivatives (Compounds 4-8) were synthesized via the aldol condensation shown in Scheme 1, where nucleophilic addition of Compound 1 to Compound 2 is followed by elimination to yield α,β-unsaturated carbonyl molecules, Compounds 3-8.
Figure 1 Structure of a portion of PfFdChalcone (Compound 3) is a compound that interacts with PfFd and exhibits antimalarial properties. A series of chalcone derivatives (Compounds 4-8) were synthesized via the aldol condensation shown in Scheme 1, where nucleophilic addition of Compound 1 to Compound 2 is followed by elimination to yield α,β-unsaturated carbonyl molecules, Compounds 3-8.
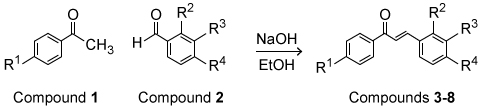 Scheme 1An inhibition assay was performed to compare chalcone (Compound 3) and its derivatives by determining the extent to which these compounds inhibited electron transfer between PfFNR and PfFd (Table 1) .Table 1 Inhibition of electron transfer assay results
Scheme 1An inhibition assay was performed to compare chalcone (Compound 3) and its derivatives by determining the extent to which these compounds inhibited electron transfer between PfFNR and PfFd (Table 1) .Table 1 Inhibition of electron transfer assay results
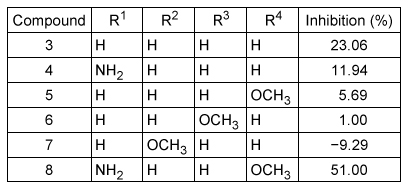 Adapted from H. Suwito et al. "Design and synthesis of chalcone derivatives as inhibitors of the ferredoxin - ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase interaction of Plasmodium falciparum: pursuing new antimalarial agents." Molecules. ©2014 MDPI.
Adapted from H. Suwito et al. "Design and synthesis of chalcone derivatives as inhibitors of the ferredoxin - ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase interaction of Plasmodium falciparum: pursuing new antimalarial agents." Molecules. ©2014 MDPI.
-Which amino acid residue on PfFNR most likely interacts with the residues of PfFd shown in Figure 1?
A) 
B) 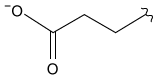
C) 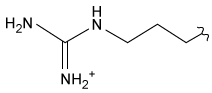
D) 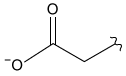
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q125: Passage
Solid-phase peptide synthesis is normally carried out
Q126: Passage
Fatty acids (FAs) are lipids that play
Q127: Passage
Fatty acids (FAs) are lipids that play
Q128: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q129: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q131: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q132: Passage
Chloramphenicol (Compound 1) is an antibiotic that
Q133: Passage
Solid-phase peptide synthesis is normally carried out
Q134: Passage
Solid-phase peptide synthesis is normally carried out
Q135: Passage
Fatty acids (FAs) are lipids that play
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents