
Integrated Advertising, Promotion and Marketing Communications 5th Edition by Kenneth Clow,Donald Baack
النسخة 5الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0132538961
Integrated Advertising, Promotion and Marketing Communications 5th Edition by Kenneth Clow,Donald Baack
النسخة 5الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0132538961 تمرين 28
Choosing A Phone Company: Options and Alternatives
The past two decades have witnessed a dramatic shift in the ways people can talk on the phone. Landline phones, while still in common use, are being challenged by new and different technologies. AT T, a major landline provider, has expanded to compete in areas such as mobile phones, texting, and Internet access using handheld devices.
Also, a new type of telephone technology has emerged, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). This new technology allows a customer to make voice calls using a broadband Internet connection instead of a regular (analog) phone line.
Some VoIP services allow users to make calls to people who use the same service. Others allow users to call anyone who has a telephone number, including local, long-distance, mobile phone, and international numbers. Some VoIP services only work over a computer or a special VoIP phone. Others can be used with a traditional phone connected to a VoIP adapter.

VoIP services can work with just a computer or with traditional phones.
Sources: HowStuffWorks, "Skype vs. Vonage" (http://electronics. howstuffworks.com/ skype-vonage2.htm, accessed November 24, 2009); Skype (www.skype.com/intl/en/ getconnected/, accessed November 24, 2009); FCC, "Voice-Over-Internet Protocol" (www.fcc.gov/voip/, accessed November 24, 2009); Vonage (vonage_works/ refer_id=WEBHO0706010001W lid=main_nav_how_works, accessed November 24, 2009).
In addition, wireless "hot spots" in locations such as airports, parks, and cafes allow callers to connect to the Internet and use VoIP service wirelessly.
A customer owning a special VoIP phone or a regular telephone connected to a VoIP adapter will have a phone that rings like a traditional telephone. If the person's VoIP service requires him to make calls using a computer, the software supplied by the service provider alerts the user when he has an incoming call.
VoIP services do have some disadvantages. First, some VoIP services do not work during power outages unless the service provider offers backup power. Second, not all VoIP services connect directly to emergency services through 911. Third, VoIP providers may not offer directory assistance or white page listings.
The two major VoIP providers are Skype and Vonage. Skype allows customers to make calls to other Skype members free of charge. The service includes free text messaging and video calls as well. Skype offers low rates for calls of other types. A customer can use Skype on a computer or on a mobile device. Skype works on a wide range of mobile phones, as well as on devices such as PlayStation Portable. Instant messages can be directed at individuals or group chat rooms. Skype users can also make conference calls. Skype offers customers pay-as-yougo or monthly payment options. No special equipment purchase is required in order to use Skype.
Vonage emphasizes that it provides lower-cost options when compared to AT T. The company features international calling at greatly reduced rate. Vonage does require users to install special hardware. After signing up for an account, Vonage ships an adapter or other equipment to the customer, who must then install it and set it up. Complete instructions are provided, and setup is relatively simple. Vonage service can be purchased at Best Buy, Wal-Mart, and Target. The systems offer unlimited local and long-distance calling, call waiting, call forwarding, automatic redial, and voice mail for a single monthly fee.
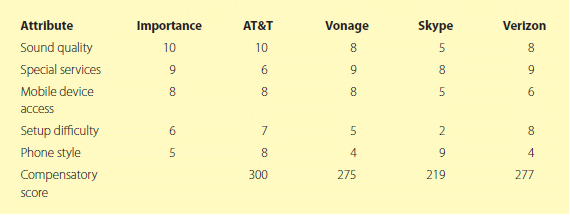
Kelli is evaluating the two VoIP services and two mobile phone services. Figure 1 provides the multiattribute evaluation approach she has developed. She is considering the attributes of sound quality, special services available, access to mobile devices, and difficulty in set up. Each attribute receives a score on a scale of 1 to 10 in terms of importance to Kelli, with 10 being the most important and 1 the least important. The four companies are then evaluated with a 10-point scale for each attribute, with 10 indicating the highest performance.
Using a compensatory heuristics method, Kelli assumes that no one single brand scores high on every attribute and that individual attributes vary in importance. With this model, Kelli will purchase the brand with the highest compensatory score, which is calculated by multiplying each attribute score by its importance, and then summing the total, as shown at the bottom of Figure 1.
Using the conjunctive heuristics method, a threshold or minimum rating is established. A brand is eliminated if an important attribute is rated lower than a certain number. For example, Kelli has rated "sound quality" as very important (rating of 10). She may decide any service with a rating lower than 8 will be eliminated. In her situation, Skype would be eliminated because it scored only a 5. This process is followed until one brand is left.
The phased heuristic approach combines the two methods. Any brand with a low score on any criterion is eliminated first. Then, if a tie exists, the conjunctive heuristics method is used to decide between the two remaining contenders.
Consumers make purchase decisions using one of these methods, or some other approach. Each competitor seeks to highlight the advantages of its approach in order to maintain current customers and attract new ones.
1. Use Figure 1 to explain the purchase decision Kelli will make using the following methods: (a) conjunctive heuristics, (2) compensatory heuristics, and (3) phased heuristics. Elaborate on which brand is chosen and which brands are not and explain why.
2. Create a similar table for two of the following products that you have recently purchased. Explain which method of evaluation could be used for each purchase decision.
a. An automobile
b. A dinner at a high-end restaurant
c. A life insurance policy
d. A new pair of jeans
3. How would the multiattribute model be expanded to include paging services
4. If a customer bases a purchase on affect referral rather than a multiattribute method for mobile phone service, which of the companies may have an advantage Why
Figure 1. Example of a Multiattribute Evaluation Approach for a Phone Service
The past two decades have witnessed a dramatic shift in the ways people can talk on the phone. Landline phones, while still in common use, are being challenged by new and different technologies. AT T, a major landline provider, has expanded to compete in areas such as mobile phones, texting, and Internet access using handheld devices.
Also, a new type of telephone technology has emerged, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). This new technology allows a customer to make voice calls using a broadband Internet connection instead of a regular (analog) phone line.
Some VoIP services allow users to make calls to people who use the same service. Others allow users to call anyone who has a telephone number, including local, long-distance, mobile phone, and international numbers. Some VoIP services only work over a computer or a special VoIP phone. Others can be used with a traditional phone connected to a VoIP adapter.

VoIP services can work with just a computer or with traditional phones.
Sources: HowStuffWorks, "Skype vs. Vonage" (http://electronics. howstuffworks.com/ skype-vonage2.htm, accessed November 24, 2009); Skype (www.skype.com/intl/en/ getconnected/, accessed November 24, 2009); FCC, "Voice-Over-Internet Protocol" (www.fcc.gov/voip/, accessed November 24, 2009); Vonage (vonage_works/ refer_id=WEBHO0706010001W lid=main_nav_how_works, accessed November 24, 2009).
In addition, wireless "hot spots" in locations such as airports, parks, and cafes allow callers to connect to the Internet and use VoIP service wirelessly.
A customer owning a special VoIP phone or a regular telephone connected to a VoIP adapter will have a phone that rings like a traditional telephone. If the person's VoIP service requires him to make calls using a computer, the software supplied by the service provider alerts the user when he has an incoming call.
VoIP services do have some disadvantages. First, some VoIP services do not work during power outages unless the service provider offers backup power. Second, not all VoIP services connect directly to emergency services through 911. Third, VoIP providers may not offer directory assistance or white page listings.
The two major VoIP providers are Skype and Vonage. Skype allows customers to make calls to other Skype members free of charge. The service includes free text messaging and video calls as well. Skype offers low rates for calls of other types. A customer can use Skype on a computer or on a mobile device. Skype works on a wide range of mobile phones, as well as on devices such as PlayStation Portable. Instant messages can be directed at individuals or group chat rooms. Skype users can also make conference calls. Skype offers customers pay-as-yougo or monthly payment options. No special equipment purchase is required in order to use Skype.
Vonage emphasizes that it provides lower-cost options when compared to AT T. The company features international calling at greatly reduced rate. Vonage does require users to install special hardware. After signing up for an account, Vonage ships an adapter or other equipment to the customer, who must then install it and set it up. Complete instructions are provided, and setup is relatively simple. Vonage service can be purchased at Best Buy, Wal-Mart, and Target. The systems offer unlimited local and long-distance calling, call waiting, call forwarding, automatic redial, and voice mail for a single monthly fee.
Kelli is evaluating the two VoIP services and two mobile phone services. Figure 1 provides the multiattribute evaluation approach she has developed. She is considering the attributes of sound quality, special services available, access to mobile devices, and difficulty in set up. Each attribute receives a score on a scale of 1 to 10 in terms of importance to Kelli, with 10 being the most important and 1 the least important. The four companies are then evaluated with a 10-point scale for each attribute, with 10 indicating the highest performance.
Using a compensatory heuristics method, Kelli assumes that no one single brand scores high on every attribute and that individual attributes vary in importance. With this model, Kelli will purchase the brand with the highest compensatory score, which is calculated by multiplying each attribute score by its importance, and then summing the total, as shown at the bottom of Figure 1.
Using the conjunctive heuristics method, a threshold or minimum rating is established. A brand is eliminated if an important attribute is rated lower than a certain number. For example, Kelli has rated "sound quality" as very important (rating of 10). She may decide any service with a rating lower than 8 will be eliminated. In her situation, Skype would be eliminated because it scored only a 5. This process is followed until one brand is left.
The phased heuristic approach combines the two methods. Any brand with a low score on any criterion is eliminated first. Then, if a tie exists, the conjunctive heuristics method is used to decide between the two remaining contenders.
Consumers make purchase decisions using one of these methods, or some other approach. Each competitor seeks to highlight the advantages of its approach in order to maintain current customers and attract new ones.
1. Use Figure 1 to explain the purchase decision Kelli will make using the following methods: (a) conjunctive heuristics, (2) compensatory heuristics, and (3) phased heuristics. Elaborate on which brand is chosen and which brands are not and explain why.
2. Create a similar table for two of the following products that you have recently purchased. Explain which method of evaluation could be used for each purchase decision.
a. An automobile
b. A dinner at a high-end restaurant
c. A life insurance policy
d. A new pair of jeans
3. How would the multiattribute model be expanded to include paging services
4. If a customer bases a purchase on affect referral rather than a multiattribute method for mobile phone service, which of the companies may have an advantage Why
Figure 1. Example of a Multiattribute Evaluation Approach for a Phone Service

التوضيح
Multi-Attribute Evaluation Approach in m...
Integrated Advertising, Promotion and Marketing Communications 5th Edition by Kenneth Clow,Donald Baack
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








