Deck 18: Electric Potential
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Electric Potential
1
A free electron is in an electric field. With respect to the field, it experiences a force acting:
A) perpendicular.
B) along a constant potential line.
C) parallel.
D) anti-parallel (opposite in direction).
A) perpendicular.
B) along a constant potential line.
C) parallel.
D) anti-parallel (opposite in direction).
anti-parallel (opposite in direction).
2
The unit of electrical potential, the volt, is dimensionally equivalent to:
A) J/C.
B) J.C.
C) F.C.
D) C/J.
A) J/C.
B) J.C.
C) F.C.
D) C/J.
J/C.
3
Two protons, each of charge 1.60 *10 - 19 C, are 3.00 *10 - 5 m apart. What is the change in potential energy if they are brought 1.00 *10 - 5 m closer together? (ke = 8.99 *109 N·m2/C2)
A) 3.84 *10 - 24 J
B) 3.20 *10 - 16 J
C) 1.15 *10 - 23 J
D) 3.20 *10 - 19 J
A) 3.84 *10 - 24 J
B) 3.20 *10 - 16 J
C) 1.15 *10 - 23 J
D) 3.20 *10 - 19 J
3.84 *10 - 24 J
4
Which of the following characteristics are held in common by both gravitational and electrostatic forces when dealing with either point masses or charges?
A) potential energy is a function of distance of separation
B) forces are conservative
C) inverse square distance law applies
D) all of the above choices are valid
A) potential energy is a function of distance of separation
B) forces are conservative
C) inverse square distance law applies
D) all of the above choices are valid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A proton (+1.6 *10 - 19 C) moves 10 cm along the direction of an electric field of strength 4.0 N/C. The electrical potential difference between the proton's initial and ending points is:
A) 4.8 *10 - 19 V.
B) 0.40 V.
C) 0.044 V.
D) 6.4 *10 - 19 V.
A) 4.8 *10 - 19 V.
B) 0.40 V.
C) 0.044 V.
D) 6.4 *10 - 19 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A uniform electric field, with a magnitude of 600 N/C, is directed parallel to the positive x axis. If the potential at x = 4.0 m is 1000 V, what is the potential at x = 2.0 m?
A) "-800 V"
B) "2200 V"
C) "2800 V"
D) "1600 V"
A) "-800 V"
B) "2200 V"
C) "2800 V"
D) "1600 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Two point charges of values +3.4 C and +6.6 C, respectively, are separated by 0.20 m. What is the potential energy of this 2-charge system? (ke = 8.99* 109 N.m2/C2)
A) "+1.0 J"
B) "-5.0 J"
C) "-0.75 J"
D) "+0.50 J"
A) "+1.0 J"
B) "-5.0 J"
C) "-0.75 J"
D) "+0.50 J"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An electron and a proton are each released from rest in the same uniform electric field. The electron moves a distance delectron and the proton moves a distance dproton as each particle's kinetic energy increases by 1.6 eV. How do delectron and dproton compare?
A) delectron > dproton
B) delectron = dproton
C) delectron < dproton
D) The answer depends on the direction of the electric field.
A) delectron > dproton
B) delectron = dproton
C) delectron < dproton
D) The answer depends on the direction of the electric field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If an electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 300 V, find its approximate speed at the end of this process. (e = 1.6 * 10 - 19 C; me = 9.1 *10 - 31 kg)
A) 2.5 * 107 m/s
B) 2.1 * 107 m/s
C) 1.0 *107 m/s
D) 1.4 * 107 m/s
A) 2.5 * 107 m/s
B) 2.1 * 107 m/s
C) 1.0 *107 m/s
D) 1.4 * 107 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the distance between two isolated parallel plates that are oppositely charged is doubled, the electric field between the plates is essentially unchanged. However, the:
A) charge on each plate will double.
B) force on a charged particle halfway between the plates will get twice as small.
C) potential difference between the plates will double.
D) force on a charged particle halfway between the plates will get four times as small.
A) charge on each plate will double.
B) force on a charged particle halfway between the plates will get twice as small.
C) potential difference between the plates will double.
D) force on a charged particle halfway between the plates will get four times as small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An electron is released from rest at the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor. If the distance across the plates is 5.0 mm and the potential difference across the plates is 20 V, with what velocity does the electron hit the positive plate? (me = 9.1 * 10 - 31 kg, e = 1.6 *10 - 19 C)
A) 1.3 * 106 m/s
B) 1.0 * 106 m/s
C) 2.7 *106 m/s
D) 5.3 * 106 m/s
A) 1.3 * 106 m/s
B) 1.0 * 106 m/s
C) 2.7 *106 m/s
D) 5.3 * 106 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The quantity of electrical potential, the volt, is dimensionally equivalent to:
A) force/charge.
B) electric field/distance.
C) force * charge.
D) electric field * distance.
A) force/charge.
B) electric field/distance.
C) force * charge.
D) electric field * distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A uniform electric field, with a magnitude of 600 N/C, is directed parallel to the positive x axis. If the potential at x = 4.0 m is 1000 V, what is the change in potential energy of a proton as it moves from x = 4.0 m to x = 1.0 m? (qp = 1.6 *10 - 19 C)
A) 500 J
B) 2.9 *10 - 16 J
C) 1.9 *10 - 16 J
D) 8.0 *10 - 17 J
A) 500 J
B) 2.9 *10 - 16 J
C) 1.9 *10 - 16 J
D) 8.0 *10 - 17 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two particles each have the same mass but particle #1 has four times the charge of particle #2. Particle #1 is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 10 V and attains speed v. Particle #2 is accelerated from rest also through a potential difference of 10 V. What speed does particle #2 attain?
A) 2v
B) v/2
C) v/4
D)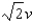
A) 2v
B) v/2
C) v/4
D)
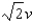

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Case 1: An electron is released from rest in a uniform electric field. Case 2: A proton is released from rest in a uniform electric field of the same magnitude as in case 1. How does the electric potential energy of the charge-field system behave in these cases?
A) In case 1 the potential energy increases, but in case 2 it decreases.
B) In both cases, the potential energy increases.
C) In case 1 the potential energy decreases, but in case 2 it increases.
D) In both cases, the potential energy decreases.
A) In case 1 the potential energy increases, but in case 2 it decreases.
B) In both cases, the potential energy increases.
C) In case 1 the potential energy decreases, but in case 2 it increases.
D) In both cases, the potential energy decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An electron in a cathode ray tube is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kV. What kinetic energy does the electron gain in the process? (e = 1.6 * 10 - 19 C)
A) 8.0 *10 - 16 J
B) 1.6 *10 - 15 J
C) 8.0 * 1022 J
D) 1.6 *10 - 16 J
A) 8.0 *10 - 16 J
B) 1.6 *10 - 15 J
C) 8.0 * 1022 J
D) 1.6 *10 - 16 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In which case does an electric field do positive work on a charged particle?
A) A negative charge moves opposite to the direction of the electric field.
B) A positive charge completes one circular path around a stationary positive charge.
C) A positive charge is moved to a point of higher potential energy.
D) A positive charge completes one elliptical path around a stationary positive charge.
A) A negative charge moves opposite to the direction of the electric field.
B) A positive charge completes one circular path around a stationary positive charge.
C) A positive charge is moved to a point of higher potential energy.
D) A positive charge completes one elliptical path around a stationary positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the distance between two negative point charges is increased by a factor of two, the resultant potential energy is what factor times the initial potential energy?
A) 2
B) 1/2
C) 1/4
D) 4
A) 2
B) 1/2
C) 1/4
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An electron (charge -1.6 *10 - 19 C) moves on a path perpendicular to the direction of a uniform electric field of strength 3.0 N/C. How much work is done on the electron as it moves 20 cm?
A) "1.6 * 10 - 20 J"
B) "-4.8 *10 - 20 J"
C) "4.8 *10 - 20 J"
D) "zero"
A) "1.6 * 10 - 20 J"
B) "-4.8 *10 - 20 J"
C) "4.8 *10 - 20 J"
D) "zero"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A proton (+1.6 *10 - 19 C) moves 10 cm on a path in the direction opposite to a uniform electric field of strength 3.0 N/C. How much work is done on the proton by the electrical field?
A) "4.8*10 - 20 J"
B) "1.6 * 10 - 20 J"
C) "zero"
D) "-4.8 *10 - 20 J"
A) "4.8*10 - 20 J"
B) "1.6 * 10 - 20 J"
C) "zero"
D) "-4.8 *10 - 20 J"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a doubly-ionized oxygen atom is accelerated from rest by going through a potential difference of 10 V, what will be the change in its kinetic energy?
A) 10 eV
B) 40 eV
C) 20 eV
D) none of the above
A) 10 eV
B) 40 eV
C) 20 eV
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A solid conducting sphere of 10 cm radius has a net charge of 40 nC. If the potential at infinity is taken as zero, what is the potential at the center of the sphere?
A) 360 V
B) 3.6 * 103 V
C) >3.6 * 104 V
D) 36 V
A) 360 V
B) 3.6 * 103 V
C) >3.6 * 104 V
D) 36 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An electron in a TV picture tube is accelerated through a potential difference of 20 kV before it hits the screen. What is the kinetic energy of the electron in electron volts? (1 eV = 1.6 * 10 - 19 J)
A) 6.25 * 1022 eV
B) 1.0 *104 eV
C) 2.0 * 104 eV
D) 3.2*10 - 22 eV
A) 6.25 * 1022 eV
B) 1.0 *104 eV
C) 2.0 * 104 eV
D) 3.2*10 - 22 eV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following were found from Millikan's oil drop experiment?
A) the weight, and hence the mass, of the electron
B) all of the above
C) that quarks have charges that are fractions of the electronic charge
D) the value of the electron's quantized charge
A) the weight, and hence the mass, of the electron
B) all of the above
C) that quarks have charges that are fractions of the electronic charge
D) the value of the electron's quantized charge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An ion is released from rest and moves due to the force from an electric field from a position in the field having a potential of 14 V to a position having a potential of 8 V. The ion:
A) can have either a positive or a negative charge.
B) must be neutral.
C) must have a positive charge.
D) must have a negative charge.
A) can have either a positive or a negative charge.
B) must be neutral.
C) must have a positive charge.
D) must have a negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Four point charges are on the rim of a circle. The charges are (in C) +0.50, +3.0, -1.0, -0.50. If the electrical potential at the circle's center due to the +0.5 charge alone is 4.5 * 104 V, what is the total potential at the center due to the four charges combined?
A) "18 * 104 V"
B) "4.5 * 104 V"
C) "zero"
D) "-4.5 *104 V"
A) "18 * 104 V"
B) "4.5 * 104 V"
C) "zero"
D) "-4.5 *104 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A point charge of +3.0 C is located at the origin of a coordinate system and a second point charge of -9.0 C is at x = 1.00 m. What is the electric potential at the x = 0.50 m point? (ke = 8.99 *109 N.m2/C2)
A) "-5.4 * 104 V"
B) "11 * 104 V"
C) "16 * 104 V"
D) "-11 * 104 V"
A) "-5.4 * 104 V"
B) "11 * 104 V"
C) "16 * 104 V"
D) "-11 * 104 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Two point charges of values +3.4 C and +6.6 C are separated by 0.20 m. What is the electrical potential at the point midway between the two charges? (ke = 8.99 * 109 N.m2/C2)
A) "+1.8 * 106 V"
B) "-0.90*106 V"
C) "+0.90 * 106 V"
D) "+3.6 *106 V"
A) "+1.8 * 106 V"
B) "-0.90*106 V"
C) "+0.90 * 106 V"
D) "+3.6 *106 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When charges qa, qb, and qc are placed respectively at the corners a, b, and c of a right triangle, the potential at the midpoint of the hypotenuse is 20 V. When the charge qa is removed, the potential at the midpoint becomes 15 V. When, instead, the charge qb is removed (qa and qc both in place), the potential at the midpoint becomes 13 V. What is the potential at the midpoint if only the charge qc is removed from the array of charges?
A) 12 V
B) 8 V
C) 7 V
D) 5 V
A) 12 V
B) 8 V
C) 7 V
D) 5 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the plane x = 4 m is an equipotential surface, in which of the following directions can the electric field be in the region immediately adjacent to this plane?
A) the positive y direction
B) both the positive and negative z directions
C) the positive x direction
D) more than one of these choices
A) the positive y direction
B) both the positive and negative z directions
C) the positive x direction
D) more than one of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
There is a hollow, conducting, uncharged sphere with a negative charge inside the sphere. Consider the electrical potential at the inner and outer surfaces of the sphere. Which of the following is true? 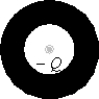
A) The potentials on both surfaces are equal but not zero.
B) The potentials on both surfaces are zero.
C) The potential on the inner surface is greater.
D) The potential on the outer surface is greater.

A) The potentials on both surfaces are equal but not zero.
B) The potentials on both surfaces are zero.
C) The potential on the inner surface is greater.
D) The potential on the outer surface is greater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Equipotential surfaces around a point charge are
A) spherical.
B) cylindrical.
C) planar.
D) none of these choices.
A) spherical.
B) cylindrical.
C) planar.
D) none of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A solid metal sphere of radius r is inside a metal concentric spherical shell of inner radius 2r and outer radius 3r. A charge is place on the solid metal sphere and it is found that the potential at its surface is 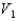 (at r) and that the potential at the outer surface of the spherical shell is
(at r) and that the potential at the outer surface of the spherical shell is 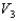 (at 3r). In terms of
(at 3r). In terms of 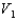 and
and 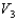 , what is the potential at the inner surface of the metal shell (at 2r)?
, what is the potential at the inner surface of the metal shell (at 2r)?
A)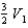
B)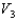
C)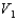
D)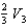
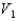 (at r) and that the potential at the outer surface of the spherical shell is
(at r) and that the potential at the outer surface of the spherical shell is 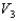 (at 3r). In terms of
(at 3r). In terms of 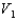 and
and 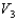 , what is the potential at the inner surface of the metal shell (at 2r)?
, what is the potential at the inner surface of the metal shell (at 2r)?A)
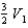
B)
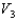
C)
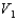
D)
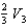

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At what distance from a point charge of 14 C would the electrical potential be 4.2 *104 V? (ke = 8.99 * 109 N.m2/C2)
A) 0.76 m
B) 0.58 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 1.7 m
A) 0.76 m
B) 0.58 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 1.7 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 9.0-V battery moves 200 mC of charge through a circuit running from its positive terminal to its negative terminal. How much energy was delivered to the circuit?
A) 4.5 x 103 J
B) 1.8 J
C) 2.2 mJ
D) 0.18 J
A) 4.5 x 103 J
B) 1.8 J
C) 2.2 mJ
D) 0.18 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When charges qa, qb, and qc are placed respectively at the corners a, b, and c of a right triangle, the potential at the midpoint of the hypotenuse is 20 V. When the charge qa is removed, the potential at the midpoint becomes 15 V. When, instead, the charge qb is removed (qa and qc both in place), the potential at the midpoint becomes 13 V. What is the potential at the midpoint if both charges qa and qc are removed?
A) 13 V
B) 7 V
C) 5 V
D) 8 V
A) 13 V
B) 7 V
C) 5 V
D) 8 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Find the electrical potential at 0.055 m from a point charge of 6.0 C. (ke = 8.99 *109 N.m2/C2)
A) 1.5 * 105 V
B) 1.2 * 107 V
C) 9.8 * 105 V
D) 3.6 *105 V
A) 1.5 * 105 V
B) 1.2 * 107 V
C) 9.8 * 105 V
D) 3.6 *105 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When charge Q1 is placed at point P1, the resulting potential at point P is V1. When Q2 is placed at point P2 after Q1 is in position at P1, the resulting potential at P becomes V2. What is the potential at point P if charge Q1 is then removed?
A) V1 - V2
B) (V1 + V2)/2
C) V1 + V2
D) V2 - V1
A) V1 - V2
B) (V1 + V2)/2
C) V1 + V2
D) V2 - V1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Electrons in an x-ray machine are accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 80,000 V. What is the kinetic energy of each of these electrons in eV?
A) 128 eV
B) 40 eV
C) 80 eV
D) 80 keV
A) 128 eV
B) 40 eV
C) 80 eV
D) 80 keV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A point charge of +3.0 C is located at the origin of a coordinate system and a second point charge of -9.0 C is at x = 1.0 m. At what point on the x axis is the electrical potential zero?
A) "+0.33 m"
B) "-0.25 m"
C) "+0.25 m"
D) "+0.75 m"
A) "+0.33 m"
B) "-0.25 m"
C) "+0.25 m"
D) "+0.75 m"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Increasing the separation of the two charged parallel plates of a capacitor, which are disconnected from a battery, will produce what effect on the capacitor?
A) increase charge
B) decrease charge
C) decrease capacitance
D) increase capacitance
A) increase charge
B) decrease charge
C) decrease capacitance
D) increase capacitance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Two capacitors with capacitances of 1.0 C and 0.50 F, respectively, are connected in series. The system is connected to a 150 V battery. What charge accumulates on the 1.0- F capacitor?
A) 50 C
B) 150 C
C) 100 C
D) 33 C
A) 50 C
B) 150 C
C) 100 C
D) 33 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If two parallel, conducting plates have equal positive charge, the electric field lines will:
A) leave one plate and go straight to the other plate.
B) enter both plates from infinity.
C) leave both plates and go to infinity.
D) none of the above.
A) leave one plate and go straight to the other plate.
B) enter both plates from infinity.
C) leave both plates and go to infinity.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
At which location will the electric field between the two parallel plates of a charged capacitor be the strongest in magnitude?
A) near the positive plate
B) near the negative plate
C) midway between the two plates nearest their center
D) midway between the two plates at their ends
A) near the positive plate
B) near the negative plate
C) midway between the two plates nearest their center
D) midway between the two plates at their ends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Three capacitors have capacitances C1 < C2 < C3. If these capacitors are connected in series, which of the following is true for the resulting equivalent capacitance?
A) Ceq < C1
B) Ceq > C3
C) Ceq = (C1 + C2 + C3)/3
D) None of the above is always correct.
A) Ceq < C1
B) Ceq > C3
C) Ceq = (C1 + C2 + C3)/3
D) None of the above is always correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Decreasing the voltage across the two plates of a capacitor will produce what effect on the capacitor?
A) decrease charge
B) increase capacitance
C) decrease capacitance
D) increase charge
A) decrease charge
B) increase capacitance
C) decrease capacitance
D) increase charge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A 20- F capacitor is attached across a 1000-V power supply. What is the net charge on the capacitor?
A) 20 mC
B) 40 mC
C) 10 mC
D) none of these choices
A) 20 mC
B) 40 mC
C) 10 mC
D) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The unit of capacitance, the farad, is dimensionally equivalent to which of the following?
A) J/V
B) C/V
C) V.C
D) V/C
A) J/V
B) C/V
C) V.C
D) V/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the equivalent capacitance between points a and b? All capacitors are 2.0 F. 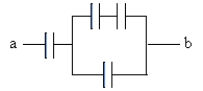
A) 1.2 µF
B) 0.25 µF
C) 4.0 µF
D) 0.60 µF

A) 1.2 µF
B) 0.25 µF
C) 4.0 µF
D) 0.60 µF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Doubling the voltage across a parallel-plate capacitor does not double which of the following?
A) the electric field between the plates
B) the charge
C) the energy stored
D) both a and b
A) the electric field between the plates
B) the charge
C) the energy stored
D) both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Two capacitors with capacitances of 1.5 C and 0.25 F, respectively, are connected in parallel. The system is connected to a 40-V battery. What charge accumulates on the 1.5- F capacitor?
A) 100 C
B) 75 C
C) 60 C
D) 33 C
A) 100 C
B) 75 C
C) 60 C
D) 33 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Three capacitors of 1.0, 1.5, and 3.0 F are connected in series. Find the combined capacitance.
A) 0.50 F
B) 1.0 F
C) 5.0 F
D) 5.5 F
A) 0.50 F
B) 1.0 F
C) 5.0 F
D) 5.5 F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Two capacitors with CA greater than CB, are connected in parallel with a battery. Which of the following is true?
A) There is the same charge stored on each capacitor.
B) There is the same potential difference across both capacitors.
C) There is more potential difference across CB.
D) There is more potential difference across CA.
A) There is the same charge stored on each capacitor.
B) There is the same potential difference across both capacitors.
C) There is more potential difference across CB.
D) There is more potential difference across CA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If C = 48 µF, determine the equivalent capacitance for the combination shown. 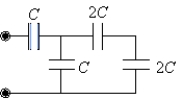
A) 32 µF
B) 48 µF
C) 24 µF
D) 28 µF

A) 32 µF
B) 48 µF
C) 24 µF
D) 28 µF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A parallel-plate capacitor has a capacitance of 20 µF. What potential difference across the plates is required to store 22 *10 - 5 C on this capacitor?
A) 2.2 * 10-2 V
B) 1.4 * 10 - 8 V
C) 11 V
D) 70 V
A) 2.2 * 10-2 V
B) 1.4 * 10 - 8 V
C) 11 V
D) 70 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A 0.50- F capacitor is connected to a 400 V battery. Find the charge on the capacitor.
A) 2.0 *10 - 4 C
B) 0.020 C
C) 1.0 *10 - 4 C
D) 1.2 * 10 - 12 C
A) 2.0 *10 - 4 C
B) 0.020 C
C) 1.0 *10 - 4 C
D) 1.2 * 10 - 12 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A capacitor is attached across a battery and charged. Then the battery is removed leaving the capacitor charged. The positive lead of the capacitor is then connected to one lead of a previously uncharged identical capacitor, and then the other lead of the charged capacitor is connected to the other lead of the second capacitor. How does the energy E0 stored in the originally charged capacitor compare to the energy Ef stored in the connected capacitors?
A) E0 = 2Ef
B) E0 < Ef
C) E0 = 4Ef
D) E0 = Ef
A) E0 = 2Ef
B) E0 < Ef
C) E0 = 4Ef
D) E0 = Ef

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose two equipotential surfaces are the planes x = 3 m and x = 5 m. If the potential at the x = 3 m surface is 10 V and the potential at the x = 5 m surface is 50 V, what is the magnitude of the electric field between the two surfaces?
A) 40 N/C
B) 20 N/C
C) 15 N/C
D) 10 N/C
A) 40 N/C
B) 20 N/C
C) 15 N/C
D) 10 N/C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Two capacitors, with CA greater than CB, are connected in series with a battery. Which of the following is true?
A) There is more charge stored on CB.
B) There is the same charge stored on each capacitor.
C) There is the same potential difference across both capacitors.
D) There is more charge stored on CA.
A) There is more charge stored on CB.
B) There is the same charge stored on each capacitor.
C) There is the same potential difference across both capacitors.
D) There is more charge stored on CA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If three 3.0-µF capacitors are connected in parallel, what is the combined capacitance?
A) 0.46 F
B) 1.0 F
C) 9.0 F
D) 0.75 F
A) 0.46 F
B) 1.0 F
C) 9.0 F
D) 0.75 F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Four identical 4-mF capacitors are connected together electrically. What is the greatest possible capacitance of the combination?
A) 16 mF
B) 8 mF
C) 4 mF
D) 1 mF
A) 16 mF
B) 8 mF
C) 4 mF
D) 1 mF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If C1 = 25 µF, C2 = 20 µF, C3 = 10 µF, and V0 = 42 V, determine the energy stored by C3. 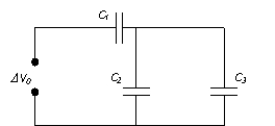
A) 3.6 mJ
B) 0.32 mJ
C) 1.8 mJ
D) 0.40 mJ

A) 3.6 mJ
B) 0.32 mJ
C) 1.8 mJ
D) 0.40 mJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown? 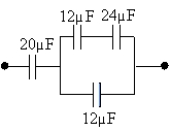
A) 25 µF
B) 10 µF
C) 29 µF
D) 40 µF

A) 25 µF
B) 10 µF
C) 29 µF
D) 40 µF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Four identical 4-mF capacitors are connected together electrically. What is the least possible capacitance of the combination?
A) 4 mF
B) 1 mF
C) 1/8 mF
D) 1/4 mF
A) 4 mF
B) 1 mF
C) 1/8 mF
D) 1/4 mF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How much charge can be placed on a capacitor of plate area 20 cm2 with air between the plates before it reaches "atmospheric breakdown" where E = 3.0 *106 V/m? ( 0 = 8.85 *10-12 C2/N.m2)
A) 6.6 *10-7 C
B) 2.7 * 10-8 C
C) 5.3 *10 - 8 C
D) 4.0 *10 - 7 C
A) 6.6 *10-7 C
B) 2.7 * 10-8 C
C) 5.3 *10 - 8 C
D) 4.0 *10 - 7 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Two capacitors with capacitances of 1.0 F and 0.50 F, respectively, are connected in series. The system is connected to a 50-V battery. What electrical potential energy is stored in the 1.0- F capacitor?
A) 5.6 * 10 - 4 J
B) 4.3 * 10 - 3 J
C) 0.065 *10 - 3 J
D) 1.4 *10 - 4 J
A) 5.6 * 10 - 4 J
B) 4.3 * 10 - 3 J
C) 0.065 *10 - 3 J
D) 1.4 *10 - 4 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Capacitor #1 has parallel plates of length L and width W, plate separation d, and is filled with dielectric with constant 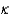 .Capacitor #2 has parallel plates of length 2L and width 2W, plate separation 2d, and is filled with dielectric with constant 2
.Capacitor #2 has parallel plates of length 2L and width 2W, plate separation 2d, and is filled with dielectric with constant 2 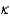 . If a voltage V is applied to capacitor #1 and a voltage 2V is applied to capacitor #2, which capacitor stores more energy and by what factor?
. If a voltage V is applied to capacitor #1 and a voltage 2V is applied to capacitor #2, which capacitor stores more energy and by what factor?
A) Capacitor #2 by a factor of 8
B) Capacitor #2 by a factor of 16
C) Capacitor #1 by a factor of 4
D) Both capacitors store the same energy.
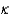 .Capacitor #2 has parallel plates of length 2L and width 2W, plate separation 2d, and is filled with dielectric with constant 2
.Capacitor #2 has parallel plates of length 2L and width 2W, plate separation 2d, and is filled with dielectric with constant 2 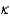 . If a voltage V is applied to capacitor #1 and a voltage 2V is applied to capacitor #2, which capacitor stores more energy and by what factor?
. If a voltage V is applied to capacitor #1 and a voltage 2V is applied to capacitor #2, which capacitor stores more energy and by what factor?A) Capacitor #2 by a factor of 8
B) Capacitor #2 by a factor of 16
C) Capacitor #1 by a factor of 4
D) Both capacitors store the same energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 6.0- F capacitor is attached to a 20-V power supply. How much energy is stored in the capacitor?
A) 2.0 *10 - 3 J
B) 5.2 * 10 - 4 J
C) 2.0 *10 - 4 J
D) 1.2 * 10 - 3 J
A) 2.0 *10 - 3 J
B) 5.2 * 10 - 4 J
C) 2.0 *10 - 4 J
D) 1.2 * 10 - 3 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown? 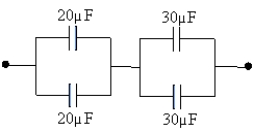
A) 4.6 µF
B) 100 µF
C) 12 µF
D) 24 µF

A) 4.6 µF
B) 100 µF
C) 12 µF
D) 24 µF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Two capacitors with capacitances of 1.5 F and 0.25 F, respectively, are connected in parallel. The system is connected to a 100-V battery. What electrical potential energy is stored in the 1.5- F capacitor?
A) 1.2 *10 - 3 J
B) 1.9 *10 - 3 J
C) 0.50 *10 - 3 J
D) 7.5 *10 - 3 J
A) 1.2 *10 - 3 J
B) 1.9 *10 - 3 J
C) 0.50 *10 - 3 J
D) 7.5 *10 - 3 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A parallel plate capacitor has the voltage applied to it doubled. Is the force between the plates attractive or repulsive, and what happens to the force between the plates when the voltage is doubled?
A) The force is attractive and it quadruples.
B) The force is attractive and it doubles.
C) The force is repulsive and it halves.
D) There is no force between the plates since the net charge is zero on the capacitor.
A) The force is attractive and it quadruples.
B) The force is attractive and it doubles.
C) The force is repulsive and it halves.
D) There is no force between the plates since the net charge is zero on the capacitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If C = 14 µF, what is the equivalent capacitance for the combination shown? 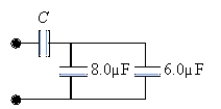
A) 5.8 µF
B) 6.5 µF
C) 8.2 µF
D) 7.0 µF

A) 5.8 µF
B) 6.5 µF
C) 8.2 µF
D) 7.0 µF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A pair of parallel plates, forming a capacitor, are charged. The plates are pulled apart to triple the original separation, the charges on the plates remaining the same. What is the ratio of the final energy stored to the original energy stored?
A) 1/9
B) 1.5
C) 1/3
D) 3
A) 1/9
B) 1.5
C) 1/3
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The dielectric strength of rutile is 6.0 *106 V/m, which corresponds to the maximum electric field that the dielectric can sustain before breakdown. What is the maximum charge that a 10 - 10-F capacitor with a 0.50-mm thickness of Rutile can hold?
A) 0.30 C
B) 6.0 C
C) 0.60 µC
D) 1.7 nC
A) 0.30 C
B) 6.0 C
C) 0.60 µC
D) 1.7 nC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A pair of parallel plates, forming a capacitor, are connected to a battery. While the capacitor is still connected to the battery maintaining a constant voltage, the plates are pulled apart to triple their original distance. What is the ratio of the final energy stored to the original energy stored?
A) 1/9
B) 1/3
C) 3
D) 1
A) 1/9
B) 1/3
C) 3
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Using a 1-mF capacitor, a 2-mF capacitor, and a 3-mF capacitor, which of the following capacitances cannot be made by a combination that uses all three? (Hint: At most only 2 combinations must be considered to determine the correct answer.)
A) 6/11 mF
B) 6 mF
C) 11/3 mF
D) 7 mF
A) 6/11 mF
B) 6 mF
C) 11/3 mF
D) 7 mF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A parallel-plate capacitor has dimensions 4.0 cm * 5.0 cm. The plates are separated by a 1.0-mm thickness of paper (dielectric constant = 3.7). What is the charge that can be stored on this capacitor, when connected to a 6.0-V battery? ( 0 = 8.85 * 10-12 C2/N.m2)
A) 4.8 *10 - 9 C
B) 4.8 *10 - 11 C
C) 9.8 *10 - 11 C
D) 3.9 *10 - 10 C
A) 4.8 *10 - 9 C
B) 4.8 *10 - 11 C
C) 9.8 *10 - 11 C
D) 3.9 *10 - 10 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A "sandwich" is constructed of two flat pieces of metal (2.00 cm on a side) with a 3.00-mm thick piece of a dielectric called rutile ( = 100) in between them. What is the capacitance? ( 0 = 8.85 * 10-12 C2/N.m2)
A) 177 pF
B) 118 pF
C) 100 µF
D) 8.85 µF
A) 177 pF
B) 118 pF
C) 100 µF
D) 8.85 µF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A 0.50- F capacitor is connected to a 400-V battery. What potential energy is stored in the capacitor?
A) 0.020 J
B) 0.040 J
C) 1.0 *10 - 4 J
D) 1.2 *10 - 12 J
A) 0.020 J
B) 0.040 J
C) 1.0 *10 - 4 J
D) 1.2 *10 - 12 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Inserting a dielectric material between two charged parallel conducting plates, originally separated by air and disconnected from a battery, will produce what effect on the capacitor?
A) increase voltage
B) increase charge
C) increase capacitance
D) decrease capacitance
A) increase voltage
B) increase charge
C) increase capacitance
D) decrease capacitance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



