Deck 3: The Chemistry of Water
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Chemistry of Water
1
Sulfur is in the same column of the periodic table as oxygen but it is less electronegative than oxygen. Compared to water molecules, how will the H2S molecules behave?
A) have greater cohesion to other H2S molecules
B) have a greater tendency to form hydrogen bonds with each other
C) have a higher capacity to absorb heat for the same change in temperature
D) not be able to form hydrogen bonds with each other
A) have greater cohesion to other H2S molecules
B) have a greater tendency to form hydrogen bonds with each other
C) have a higher capacity to absorb heat for the same change in temperature
D) not be able to form hydrogen bonds with each other
D
2
Which of the following properties of water is responsible for the formation of raindrops?
A) cohesion property
B) adhesion property
C) high thermal energy
D) high kinetic energy
A) cohesion property
B) adhesion property
C) high thermal energy
D) high kinetic energy
A
3
Which answer best describes why does ice float in liquid water?
A) The high surface tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top.
B) The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C) Stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water.
D) The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.
A) The high surface tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top.
B) The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C) Stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water.
D) The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.
C
4
Which of the following statements is true for water in its liquid state?
A) It is less dense than ice.
B) It has a specific heat lower than most other substances.
C) It has a heat of vaporization higher than most other substances.
D) It is nonpolar.
A) It is less dense than ice.
B) It has a specific heat lower than most other substances.
C) It has a heat of vaporization higher than most other substances.
D) It is nonpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A) Water can form hydrogen bonds with compounds that form polar covalent bonds.
B) Water can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules.
C) Water can form intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
D) Water can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
A) Water can form hydrogen bonds with compounds that form polar covalent bonds.
B) Water can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules.
C) Water can form intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
D) Water can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How are the hydrogen bonds formed between water molecules?
A) by the attraction between the positive end of one water molecule with the negative end of the other
B) by sharing of electrons between two water molecules
C) by the transfer of electrons from one water molecule to the other
D) by sharing protons between two water molecules
A) by the attraction between the positive end of one water molecule with the negative end of the other
B) by sharing of electrons between two water molecules
C) by the transfer of electrons from one water molecule to the other
D) by sharing protons between two water molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following best defines 'one kilocalorie'?
A) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C
B) 10,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°F
C) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
D) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 100 g of water by 100°C
A) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C
B) 10,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°F
C) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
D) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 100 g of water by 100°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The nutritional label on a box of cookies says "150 kilocalories/cookie." How many joules of energy each cookie contains when 1 cal = 4.16 J?
A) 6.24 × 105 J
B) 6.24 × 106 J
C) 624 J
D) 150 J
A) 6.24 × 105 J
B) 6.24 × 106 J
C) 624 J
D) 150 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What kind of bond is formed between the two hydrogen atoms and the single oxygen atom?
A) hydrogen bonds
B) nonpolar covalent bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) ionic bonds
A) hydrogen bonds
B) nonpolar covalent bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) ionic bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following effects can occur because of the high surface tension of water?
A) Lakes cannot freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B) A raft spider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms can resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Sweat can evaporate from the skin, helping to keep people from overheating.
A) Lakes cannot freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B) A raft spider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms can resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Sweat can evaporate from the skin, helping to keep people from overheating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following can be attributed to water's high specific heat?
A) Oil and water do not mix well.
B) A lake heats up more slowly than the air around it.
C) Ice floats on water.
D) Sugar dissolves in hot tea faster than in iced tea.
A) Oil and water do not mix well.
B) A lake heats up more slowly than the air around it.
C) Ice floats on water.
D) Sugar dissolves in hot tea faster than in iced tea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements correctly describes the property of hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil?
A) nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
B) nonpolar substances that have an attraction for water molecules
C) polar substances that repel water molecules
D) polar substances that have an affinity for water
A) nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
B) nonpolar substances that have an attraction for water molecules
C) polar substances that repel water molecules
D) polar substances that have an affinity for water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When carbon dioxide in the atmosphere dissolves with the raindrops, what is the expected change in pH of the raindrops?
A) slightly acidic
B) slightly basic
C) same as pure water
D) depends on the altitude where rain drops are formed
A) slightly acidic
B) slightly basic
C) same as pure water
D) depends on the altitude where rain drops are formed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Rubbing alcohol swab on the skin feels cool because ________.
A) liquid alcohol transfers cold temperature to the skin
B) the density of alcohol is less than water
C) alcohol destroys skin microorganisms and they give off cold heat as they die
D) skin transfers heat to the liquid alcohol and the alcohol evaporates
A) liquid alcohol transfers cold temperature to the skin
B) the density of alcohol is less than water
C) alcohol destroys skin microorganisms and they give off cold heat as they die
D) skin transfers heat to the liquid alcohol and the alcohol evaporates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
To act as an effective coolant in a car's radiator, a substance has to have the capacity to absorb a great deal of heat. Which physical property is the best indicator for a good coolant?
A) pH
B) density at room temperature
C) heat of vaporization
D) specific heat
A) pH
B) density at room temperature
C) heat of vaporization
D) specific heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because ________.
A) the oxygen atom donates an electron to each of the hydrogen atoms
B) the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus
C) the oxygen atom has two pairs of electrons in its valence shell that are not neutralized by hydrogen atoms
D) one of the hydrogen atoms donates an electron to the oxygen atom
A) the oxygen atom donates an electron to each of the hydrogen atoms
B) the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus
C) the oxygen atom has two pairs of electrons in its valence shell that are not neutralized by hydrogen atoms
D) one of the hydrogen atoms donates an electron to the oxygen atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What kind of bonds are responsible for the unique cohesion, surface tension, and adhesion properties of water molecules?
A) hydrophobic bonding
B) ionic bonding
C) hydrogen bonding
D) polar covalent bonding
A) hydrophobic bonding
B) ionic bonding
C) hydrogen bonding
D) polar covalent bonding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following reasons explains why a steam burn is more severe than a hot water burn?
A) Burns caused by liquids are always milder.
B) Steam can penetrate the skin.
C) Steam contains more energy than water.
D) Water evaporates and leaves the surface faster and helps in cooling.
A) Burns caused by liquids are always milder.
B) Steam can penetrate the skin.
C) Steam contains more energy than water.
D) Water evaporates and leaves the surface faster and helps in cooling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why does a full bathtub have more thermal energy than a pot of freshly brewed coffee (even though the coffee has a higher temperature than the bathwater)?
A) higher; greater volume
B) higher; high kinetic energy
C) lower; low temperature
D) lower; low density
A) higher; greater volume
B) higher; high kinetic energy
C) lower; low temperature
D) lower; low density

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
On a hot day, temperature of land rises more quickly than that of sea. Which of the following statements best describe the process?
A) specific heat of soil is less than water
B) specific heat of soil is more than water
C) It rains more over the sea.
D) Dry soil soaks more water.
A) specific heat of soil is less than water
B) specific heat of soil is more than water
C) It rains more over the sea.
D) Dry soil soaks more water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a few drops of HCl is added to the buffer solution with the following equilibrium, ________.
NH4+(aq) + H2O(1) ⇔ H3O+(aq) + NH3(aq)
A) the concentrations of both NH3 and NH4+ decrease
B) the concentrations of both NH3 and NH4+ increase
C) the concentration of NH3 increases but NH4+ decreases
D) the concentration of NH3 decreases but NH4+ increases
NH4+(aq) + H2O(1) ⇔ H3O+(aq) + NH3(aq)
A) the concentrations of both NH3 and NH4+ decrease
B) the concentrations of both NH3 and NH4+ increase
C) the concentration of NH3 increases but NH4+ decreases
D) the concentration of NH3 decreases but NH4+ increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
One mole (mol) of glucose (molecular mass = 180 daltons) is ________.
A) 180 × 1023 molecules of glucose
B) 1 kilogram of glucose dissolved in 1 liter of solution
C) 180 mL of dissolved glucose
D) 180 grams of glucose
A) 180 × 1023 molecules of glucose
B) 1 kilogram of glucose dissolved in 1 liter of solution
C) 180 mL of dissolved glucose
D) 180 grams of glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How does 0.5 M sucrose (molecular mass 342) solution compare to 0.5 M glucose (molecular mass 180) solution?
A) Both have 6.02 × 1023 molecules.
B) Sucrose has 171 molecules, whereas glucose has 90.
C) Both have 3.01 × 1023 molecules.
D) Sucrose has 171 mg/L, whereas glucose has 90 mg/L.
A) Both have 6.02 × 1023 molecules.
B) Sucrose has 171 molecules, whereas glucose has 90.
C) Both have 3.01 × 1023 molecules.
D) Sucrose has 171 mg/L, whereas glucose has 90 mg/L.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How many grams of NaCl are required to prepare 50 mL of a solution of 1 M NaCl?
(MW of NaCl=58.44g)
A) 2.72g
B) 2.922g
C) 5.844g
D) 58.44g
(MW of NaCl=58.44g)
A) 2.72g
B) 2.922g
C) 5.844g
D) 58.44g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider two solutions: solution X has a pH of 4; solution Y has a pH of 7. From this information, we can reasonably conclude that ________.
A) solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H+)
B) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X
C) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y
D) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 1000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y
A) solution Y has no free hydrogen ions (H+)
B) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y is 1000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X
C) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 3 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y
D) the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution X is 1000 times as great as the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Assume that acid rain has lowered the pH of a lake to pH 5.0. What is the hydroxide ion concentration of this lake?
A) 1 × 10-9 mol of hydroxide ions per liter of lake water
B) 1 × 10-5 mol of hydroxide ions per liter of lake water
C) 5.0 M hydroxide ion
D) 5.0 × 10-5 mol of hydroxide ions per liter of lake water
A) 1 × 10-9 mol of hydroxide ions per liter of lake water
B) 1 × 10-5 mol of hydroxide ions per liter of lake water
C) 5.0 M hydroxide ion
D) 5.0 × 10-5 mol of hydroxide ions per liter of lake water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How many grams of the compound in the figure are required to make 1 liter of a 0.5 M solution? (Note: The atomic masses, in daltons, are approximately 12 for carbon, 1 for hydrogen.)
A) 39
B) 72
C) 78
D) 156
A) 39
B) 72
C) 78
D) 156

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion (OH-) concentration of 10-10 M?
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 10
D) pH 12
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 10
D) pH 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
0.660 moles of NaCl are dissolved in 95.0 mL of water. Calculate the molarity of the NaCl solution.
A) 62.7 M
B) 0.069 M
C) 0.0069 M
D) 6.95 M
A) 62.7 M
B) 0.069 M
C) 0.0069 M
D) 6.95 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl) is placed in water, the component atoms of the NaCl crystal dissociate into individual sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-). In contrast, the atoms of covalently bonded molecules (e.g., glucose, sucrose, glycerol) do not generally dissociate when placed in aqueous solution. Which of the following solutions would be expected to contain the greatest number of solute particles (molecules or ions)?
A) 1 liter of 0.5 M NaCl
B) 1 liter of 1.0 M NaCl
C) 1 liter of 1.0 M glucose
D) 1 liter of 1.0 M NaCl and 1 liter of 1.0 M glucose will contain equal numbers of solute particles.
A) 1 liter of 0.5 M NaCl
B) 1 liter of 1.0 M NaCl
C) 1 liter of 1.0 M glucose
D) 1 liter of 1.0 M NaCl and 1 liter of 1.0 M glucose will contain equal numbers of solute particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on two identical containers, one containing water and one methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
A)
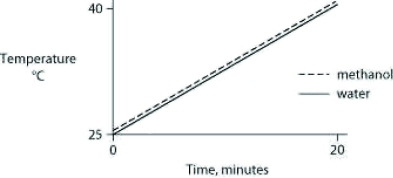
B)
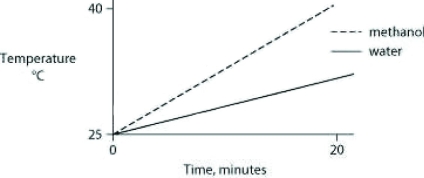
C)
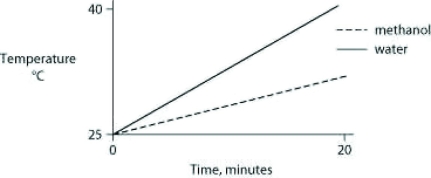
D)
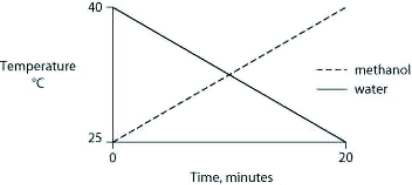
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What will be the most likely change in pH when the H+ ions in the solution is increased to twice its original concentration?
A) 1.6 to 1.3
B) 4.0 to 2.0
C) 5.0 to 2.5
D) 9.5 to 6.5
A) 1.6 to 1.3
B) 4.0 to 2.0
C) 5.0 to 2.5
D) 9.5 to 6.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Melting of ice and thus reduced feeding opportunities for polar bears is occurring because of the ________.
A) increase in phytoplankton population
B) drying up of lakes and streams
C) constant breaking and reforming of hydrogen bonds in water
D) increase in CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
A) increase in phytoplankton population
B) drying up of lakes and streams
C) constant breaking and reforming of hydrogen bonds in water
D) increase in CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: CO2 + H2O ⇔ H2CO3. What would be the effect of adding additional H2O?
A) It would drive the equilibrium dynamics to the right.
B) It would drive the equilibrium dynamics to the left.
C) Nothing would happen because the reactants and products are in equilibrium.
D) Reactions in both the directions will slow down.
A) It would drive the equilibrium dynamics to the right.
B) It would drive the equilibrium dynamics to the left.
C) Nothing would happen because the reactants and products are in equilibrium.
D) Reactions in both the directions will slow down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the concentration of hydroxide ions in a solution of pH 5?
A) 10-9 M
B) 10-5 M
C) 10-12 M
D) 10-10 M
A) 10-9 M
B) 10-5 M
C) 10-12 M
D) 10-10 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A solution contains 0.0000001 (10-7) moles of hydrogen ions [H+] per liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A) acidic: H+ acceptor
B) basic: H+ acceptor
C) acidic: H+ donor
D) neutral
A) acidic: H+ acceptor
B) basic: H+ acceptor
C) acidic: H+ donor
D) neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is considered to be a strong base (alkali)?
A) HCl → H+ + Cl-
B) NH3 + H+ ⇔ NH4+
C) H2CO3 ⇔ HCO3- + H+
D) NaOH → Na+ + OH-
A) HCl → H+ + Cl-
B) NH3 + H+ ⇔ NH4+
C) H2CO3 ⇔ HCO3- + H+
D) NaOH → Na+ + OH-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Rank, from low to high, the pH of blood, stomach acid, and urine.
A) blood, urine, and stomach acid
B) stomach acid, blood, and urine
C) urine, blood, stomach acid
D) stomach acid, urine, blood
A) blood, urine, and stomach acid
B) stomach acid, blood, and urine
C) urine, blood, stomach acid
D) stomach acid, urine, blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Three moles of the compound in the figure would weigh how many grams? (Note: The atomic masses, in daltons, are approximately 12 for carbon, 1 for hydrogen.)
A) 72
B) 78
C) 216
D) 234
A) 72
B) 78
C) 216
D) 234

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A solution of pH 7 is ________ than a solution of pH 8.
A) 100% less acidic
B) 100% more acidic
C) twice as acidic
D) ten times as acidic
A) 100% less acidic
B) 100% more acidic
C) twice as acidic
D) ten times as acidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
We can be sure that a mole of table sugar and a mole of vitamin C are equal in their ________.
A) mass
B) volume
C) number of atoms
D) number of molecules
A) mass
B) volume
C) number of atoms
D) number of molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of the lake?
A) 4.0M
B) 10-10M
C) 10-4M
D) 104M
A) 4.0M
B) 10-10M
C) 10-4M
D) 104M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A beaker contains 100 milliliters (mL) of NaOH solution at pH = 13. A technician carefully pours into the beaker 10 mL of HCl at pH = 1. Which of the following statements correctly describes the result of this mixing?
A) The concentration of Na+ ions will rise.
B) The pH of the beaker's contents will increase.
C) The pH of the beaker's contents will be neutral.
D) The pH of the beaker's contents will decrease.
A) The concentration of Na+ ions will rise.
B) The pH of the beaker's contents will increase.
C) The pH of the beaker's contents will be neutral.
D) The pH of the beaker's contents will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?
A)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_7d55_bc0b_89f8dd98b79e_TB8578_00.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_7d56_bc0b_bfd6308c26ad_TB8578_00.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_a467_bc0b_51fdc1cf1e63_TB8578_00.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_a468_bc0b_fd1311c38df9_TB8578_00.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_7d55_bc0b_89f8dd98b79e_TB8578_00.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_7d56_bc0b_bfd6308c26ad_TB8578_00.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_a467_bc0b_51fdc1cf1e63_TB8578_00.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Which of the following graphs describes the relationship between [H3O+] and pH?</strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8578/11eb7f0c_b014_a468_bc0b_fd1311c38df9_TB8578_00.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Dilution of a buffer solution with a small amount of water will ________ the pH of the solution.
A) raise
B) lower
C) not bring major change in
D) immediately raise then lower
A) raise
B) lower
C) not bring major change in
D) immediately raise then lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the reason why Hydrochloric acid is such a strong acid?
A) HCl dissociates completely to H+(aq) and Cl-(aq) in water
B) HCl does not dissociate at all when it is dissolved in water
C) HCl produces a gaseous product when it is neutralized
D) aqueous solutions of HCl contain equal concentrations of H+(aq) and OH-(aq)
A) HCl dissociates completely to H+(aq) and Cl-(aq) in water
B) HCl does not dissociate at all when it is dissolved in water
C) HCl produces a gaseous product when it is neutralized
D) aqueous solutions of HCl contain equal concentrations of H+(aq) and OH-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
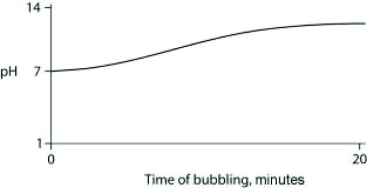
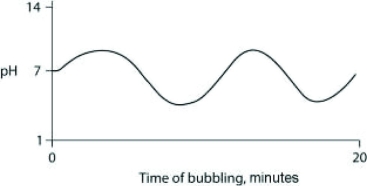
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is readily soluble in water, according to the equation CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3. Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is a weak acid. If CO2 is bubbled into a beaker containing pure, freshly distilled water, which of the following graphs correctly describes the results?
A)
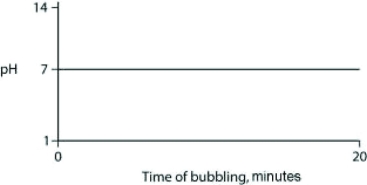
B)
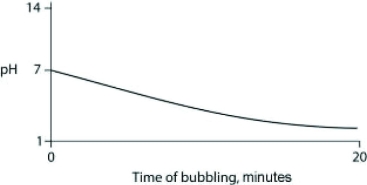
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A slice of pizza has 500 kcal. If we could burn the pizza and use all the heat to warm a 50-L container of cold water, what would be the approximate increase in the temperature of the water? (Note: A liter of cold water weighs about 1 kg.)
A) 50°C
B) 5°C
C) 100°C
D) 10°C
A) 50°C
B) 5°C
C) 100°C
D) 10°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How would you describe a buffer solution?
A) weak acid and its conjugate base
B) strong acid and its conjugate base
C) weak base and its conjugate acid
D) strong base and its conjugate acid
A) weak acid and its conjugate base
B) strong acid and its conjugate base
C) weak base and its conjugate acid
D) strong base and its conjugate acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As the [H3O+] of the solution decreases, the [OH-] ________.
A) increases and thus pH increases
B) increases and thus pH decreases
C) decreases and thus the pH decreases
D) decreases and thus the pH increases
A) increases and thus pH increases
B) increases and thus pH decreases
C) decreases and thus the pH decreases
D) decreases and thus the pH increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations might have what effect on seawater?
A) Seawater will become more alkaline, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
B) There will be no change in the pH of seawater, because carbonate will turn to bicarbonate.
C) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
D) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will increase.
A) Seawater will become more alkaline, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
B) There will be no change in the pH of seawater, because carbonate will turn to bicarbonate.
C) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will decrease.
D) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is a hydrophobic material?
A) paper
B) table salt
C) wax
D) sugar
A) paper
B) table salt
C) wax
D) sugar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How would acidification of seawater affect marine organisms?
A) It will increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
B) It will decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
C) It will increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
D) It will decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
A) It will increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
B) It will decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
C) It will increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
D) It will decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is NOT impacted by the acidification of ocean water?
A) Mollusk shells
B) Coral reef
C) Tiger shark teeth
D) Diatom shells
A) Mollusk shells
B) Coral reef
C) Tiger shark teeth
D) Diatom shells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the hydroxide ion concentration of the lake described in question 3?
A) 10-10M
B) 10-4M
C) 10-7M
D) 10.0M
A) 10-10M
B) 10-4M
C) 10-7M
D) 10.0M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



