Deck 24: The Adaptive Immune Response
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: The Adaptive Immune Response
1
Anti-HIV antibodies are best at binding to viral proteins when the virus is
A) within the cytoplasm of an infected T cell.
B) within the nucleus of an infected T cell.
C) within the cytoplasm of an infected macrophage.
D) within the nucleus of an infected macrophage.
E) extracellular within the bloodstream.
A) within the cytoplasm of an infected T cell.
B) within the nucleus of an infected T cell.
C) within the cytoplasm of an infected macrophage.
D) within the nucleus of an infected macrophage.
E) extracellular within the bloodstream.
E
2
To which superfamily do antibodies belong?
A) interleukins
B) heat shock
C) immunoglobulin
D) major histocompatibility complex
E) homeobox
A) interleukins
B) heat shock
C) immunoglobulin
D) major histocompatibility complex
E) homeobox
C
3
The chickenpox vaccine is created with an attenuated virus, and the rabies vaccine with an inactivated virus. This means that the chickenpox virus is a ________, and the rabies virus is ________.
A) subunit vaccine; a genetic vaccine
B) genetic vaccine; a subunit vaccine
C) nonfunctional form; living but weakened
D) subunit vaccine; nonfunctional
E) living weakened form; nonfunctional
A) subunit vaccine; a genetic vaccine
B) genetic vaccine; a subunit vaccine
C) nonfunctional form; living but weakened
D) subunit vaccine; nonfunctional
E) living weakened form; nonfunctional
E
4
The immune response elicited from each individual antigenic determinant found within an antigen is best described as
A) monoclonal.
B) multiclonal.
C) biclonal.
D) polyclonal.
E) triclonal.
A) monoclonal.
B) multiclonal.
C) biclonal.
D) polyclonal.
E) triclonal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following could be categorized as an example of humoral immunity?
A) T regulatory cells
B) T helper cells
C) antimalaria antibodies
D) T cytotoxic cells
E) macrophages
A) T regulatory cells
B) T helper cells
C) antimalaria antibodies
D) T cytotoxic cells
E) macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is most likely to elicit the strongest antigen-specific immune response if injected intravenously into a mouse?
A) a sterile glucose solution
B) equine serum albumin
C) complement proteins from another mouse
D) red blood cells from a transfusion-compatible species
E) mouse antigoat antibodies
A) a sterile glucose solution
B) equine serum albumin
C) complement proteins from another mouse
D) red blood cells from a transfusion-compatible species
E) mouse antigoat antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The small segment of antigen that is capable of eliciting an immune response is called a(n)
A) hapten.
B) clonotope.
C) aggretope.
D) epitope.
E) naïve antigen.
A) hapten.
B) clonotope.
C) aggretope.
D) epitope.
E) naïve antigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Of the following cells, which could be considered a "professional" antigen-presenting cell?
A) neutrophil
B) T lymphocyte
C) natural killer cell
D) dendritic cell
E) fibroblast
A) neutrophil
B) T lymphocyte
C) natural killer cell
D) dendritic cell
E) fibroblast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a radial immunodiffusion assay, immunoprecipitation rings will be created within the agar dish based on
A) equivalence point.
B) antibody isotype.
C) antibody allotype.
D) polyclonal antigen preparation.
E) Fc binding of antigens.
A) equivalence point.
B) antibody isotype.
C) antibody allotype.
D) polyclonal antigen preparation.
E) Fc binding of antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The five classes of antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD) that can be produced during an immune response are based on differences in ________ chain regions.
A) CL
B) VH
C) CH
D) VL
E) all constant and variable
A) CL
B) VH
C) CH
D) VL
E) all constant and variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Laboratory isolation of an anti-Streptococcus antibody was found to bind to ten Streptococcus pyogenes at one time. The antibody isolated was
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.
A) IgG.
B) IgM.
C) IgA.
D) IgD.
E) IgE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is most likely to elicit the strongest antigen-specific immune response within a human?
A) an outer membrane protein from Plasmodium falciparium
B) an RNA genome from HIV
C) a DNA genome from herpes
D) a capsular polysaccharide coating from Streptococcus mutans
E) a plasma membrane from Escherichia coli
A) an outer membrane protein from Plasmodium falciparium
B) an RNA genome from HIV
C) a DNA genome from herpes
D) a capsular polysaccharide coating from Streptococcus mutans
E) a plasma membrane from Escherichia coli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure B below displays a 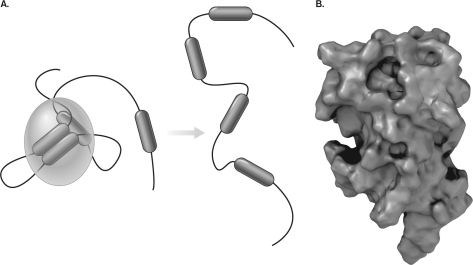
A) denatured antigen.
B) antigen-presenting cell.
C) mast cell.
D) native antigen.
E) conformational epitope.

A) denatured antigen.
B) antigen-presenting cell.
C) mast cell.
D) native antigen.
E) conformational epitope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Severe combined immunodeficiency is most commonly caused by
A) chromosome 22 trisomy.
B) Y-linked inherited hypermetabolism.
C) X-linked inherited enzyme or receptor deficiency.
D) chromosome 7 deletion.
E) XXY inheritance.
A) chromosome 22 trisomy.
B) Y-linked inherited hypermetabolism.
C) X-linked inherited enzyme or receptor deficiency.
D) chromosome 7 deletion.
E) XXY inheritance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A threshold dose of antigen is best described as the dose needed to
A) generate an optimal immune response.
B) activate only a few immune cells.
C) generate only a T-cell response.
D) induce immune complement response.
E) induce immunological tolerance.
A) generate an optimal immune response.
B) activate only a few immune cells.
C) generate only a T-cell response.
D) induce immune complement response.
E) induce immunological tolerance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Edward Jenner was able to demonstrate the first example of immunological cross-protection because
A) the smallpox virus was nonpathogenic.
B) the cowpox virus only affected milkmaids.
C) cowpox and smallpox viruses were metabolically different.
D) cowpox virus was structurally similar to the smallpox virus.
E) plague survivors were immune to smallpox.
A) the smallpox virus was nonpathogenic.
B) the cowpox virus only affected milkmaids.
C) cowpox and smallpox viruses were metabolically different.
D) cowpox virus was structurally similar to the smallpox virus.
E) plague survivors were immune to smallpox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What process is shown in the figure below? 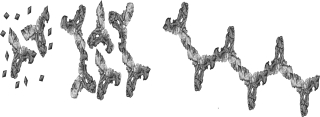
A) elicitation of an immune response
B) haptens
C) immunoprecipitation
D) antibodies preventing attachment
E) basic antibody structure

A) elicitation of an immune response
B) haptens
C) immunoprecipitation
D) antibodies preventing attachment
E) basic antibody structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The difference between antibody allotypes and isotypes is that isotypes are ________ and allotypes are ________.
A) the differences in constant regions; differences within isotypes
B) differences within allotypes; the differences in constant regions
C) the differences in constant regions; alternations in the hypervariable regions
D) alternations in the hypervariable regions; differences within isotypes
E) alternations in the hypervariable regions of one person; alternations in the hypervariable regions among a species
A) the differences in constant regions; differences within isotypes
B) differences within allotypes; the differences in constant regions
C) the differences in constant regions; alternations in the hypervariable regions
D) alternations in the hypervariable regions; differences within isotypes
E) alternations in the hypervariable regions of one person; alternations in the hypervariable regions among a species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
People who survived infection with Yersinia pestis during the fourteenth-century European epidemic found themselves immune when reexposed to
A) influenza.
B) syphilis.
C) smallpox.
D) plague.
E) pneumonia.
A) influenza.
B) syphilis.
C) smallpox.
D) plague.
E) pneumonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following would be considered an aspect of the adaptive immune response?
A) interferons
B) lymphocytes
C) defensins
D) natural killer cells
E) neutrophils
A) interferons
B) lymphocytes
C) defensins
D) natural killer cells
E) neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Complement molecule, C1 complex, will bind to an IgG antibody at the
A) VL portion.
B) F(ab')2 portion.
C) CL portion.
D) Fc portion.
E) J-chain region.
A) VL portion.
B) F(ab')2 portion.
C) CL portion.
D) Fc portion.
E) J-chain region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A complete T-cell receptor on a helper T cell contains both the antigen-binding receptor molecule and a ________ protein for signal transduction.
A) CD8
B) CD3 complex
C) MHC I
D) MHC II
E) CD28
A) CD8
B) CD3 complex
C) MHC I
D) MHC II
E) CD28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The secondary signal needed for TH0 helper cells to differentiate into either TH1 cells or TH2 cells is the cross-link between ________ (on TH0 helper cells) and ________ (on APC cell).
A) CD154; CD40
B) MHC I; B7
C) CD4; MHC II
D) CD8; MHC I
E) CD28; B7
A) CD154; CD40
B) MHC I; B7
C) CD4; MHC II
D) CD8; MHC I
E) CD28; B7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A typical antibody molecule has ________ antigen-binding sites.
A) one
B) four
C) five
D) two
E) three
A) one
B) four
C) five
D) two
E) three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
RAG1 and RAG2 are enzymes that control gene splicing on B-cell antibody genes. Which order are segments worked on in the creation of the heavy-chain gene segment?
A) VD spliced together, then J, then C
B) DJ spliced together, then V
C) VJ spliced together, then D
D) VC spliced together, then D, then J
E) VDJ segments are all spliced together simultaneously.
A) VD spliced together, then J, then C
B) DJ spliced together, then V
C) VJ spliced together, then D
D) VC spliced together, then D, then J
E) VDJ segments are all spliced together simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Anti-Streptococcus antibodies found in the serum of a patient during a primary antibody response differ from the antibodies produced during a secondary response to the same antigen because of
A) VDJ recombination.
B) affinity maturation.
C) class switching.
D) MHC processing.
E) antigen adaptation.
A) VDJ recombination.
B) affinity maturation.
C) class switching.
D) MHC processing.
E) antigen adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An example of an antigen that could stimulate naïve B-cell proliferation and differentiation without the help of a T cell would be a(n) ________ molecule from ________.
A) lipopolysaccharide; Proteus vulgaris
B) plasmid DNA; Yersinia pestis
C) protein A; Staphylococcus aureus
D) anthrax toxin; Bacillus anthracis
E) porin protein; Escherichia coli
A) lipopolysaccharide; Proteus vulgaris
B) plasmid DNA; Yersinia pestis
C) protein A; Staphylococcus aureus
D) anthrax toxin; Bacillus anthracis
E) porin protein; Escherichia coli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
There are ________ polypeptide chains in the typical antibody.
A) 2
B) 12
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
A) 2
B) 12
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The antigen-binding receptor expressing hepatitis antigen in an infected liver cell would be
A) TCR.
B) MHC II.
C) MHC I.
D) CD4.
E) CD8.
A) TCR.
B) MHC II.
C) MHC I.
D) CD4.
E) CD8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Positive selection in T-cell education refers to
A) T-cell receptors that can bind strongly to self MHC proteins.
B) CD8 receptors that can bind strongly to self MHC proteins.
C) T-cell receptors that can bind weakly to self MHC proteins.
D) CD4 that can bind weakly to self MHC proteins.
E) B-cell receptors that bind weakly to T-cell receptors.
A) T-cell receptors that can bind strongly to self MHC proteins.
B) CD8 receptors that can bind strongly to self MHC proteins.
C) T-cell receptors that can bind weakly to self MHC proteins.
D) CD4 that can bind weakly to self MHC proteins.
E) B-cell receptors that bind weakly to T-cell receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A baby will receive ________ class of antibodies from his or her mother before birth through the umbilical cord, and then ________ class of antibodies through the breast milk after birth.
A) IgG; IgA
B) IgM; IgD
C) IgG; IgM
D) IgM; IgA
E) IgE; IgG
A) IgG; IgA
B) IgM; IgD
C) IgG; IgM
D) IgM; IgA
E) IgE; IgG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Mycobacteria spp. have evolved a mechanism to evade adaptive immunity by
A) creating autoantibodies against activated T-cell populations.
B) triggering T- and B-cell apoptosis.
C) hiding within red blood cells of the body (similar to malarial infection).
D) inducing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-10).
E) producing phagocytic chemorepellants and paralyzing neutrophils.
A) creating autoantibodies against activated T-cell populations.
B) triggering T- and B-cell apoptosis.
C) hiding within red blood cells of the body (similar to malarial infection).
D) inducing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-10).
E) producing phagocytic chemorepellants and paralyzing neutrophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Bacteremia is a condition in which live bacteria enter the bloodstream, but not the cells of the body. Which form of processing would occur to stimulate a cell-mediated immune response?
A) bacterial peptide transported from cytoplasm to rER for presentation on MHC I
B) endocytosis by APC followed by presentation on MHC II
C) neutrophil phagocytosis with presentation on Fc receptor
D) cytotoxic T-cell endocytosis for presentation on CD8 receptor
E) B-cell capping for presentation on the B-cell receptor
A) bacterial peptide transported from cytoplasm to rER for presentation on MHC I
B) endocytosis by APC followed by presentation on MHC II
C) neutrophil phagocytosis with presentation on Fc receptor
D) cytotoxic T-cell endocytosis for presentation on CD8 receptor
E) B-cell capping for presentation on the B-cell receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Chlamydia trachomatis is a bacterial STD that lives intracellularly within human host cells. What immune response would most likely prevail in this infection?
A) more TH2 cells than TH1 cells
B) more TH1 cells than TH2 cells
C) equal ratio of TH1 cells to TH2 cells
D) more B cells than CD8 cells
E) mostly antibodies
A) more TH2 cells than TH1 cells
B) more TH1 cells than TH2 cells
C) equal ratio of TH1 cells to TH2 cells
D) more B cells than CD8 cells
E) mostly antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The inflammatory antibody of someone undergoing an allergic reaction to cat dander would be found primarily
A) in the lymph nodes.
B) free-floating in the bloodstream.
C) bound to mast cells and basophils.
D) in mucus secretions.
E) attached to T cells.
A) in the lymph nodes.
B) free-floating in the bloodstream.
C) bound to mast cells and basophils.
D) in mucus secretions.
E) attached to T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease characterized by weakness of the skeletal muscles due to antiacetylcholine receptor antibodies. Thymectomy is a successful treatment for this condition in some patients because it
A) removes all autoreactive B cells from the body.
B) primes antigen-presenting cells to reverse their response to self tissue.
C) neutralizes the autoantibodies from the body.
D) produces proteins to bind the autoantibodies before reaching their target.
E) prevents further miseducation of T-cell populations.
A) removes all autoreactive B cells from the body.
B) primes antigen-presenting cells to reverse their response to self tissue.
C) neutralizes the autoantibodies from the body.
D) produces proteins to bind the autoantibodies before reaching their target.
E) prevents further miseducation of T-cell populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Immunization with the childhood DPT (diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus) vaccine protects against subsequent exposure to tetanus by
A) stopping isotype switching of B cells from IgM to IgA.
B) preloading antigen-presenting cells.
C) stimulating quick inflammation upon future exposure.
D) producing life-spanning antitetanus IgE antibodies.
E) generating tetanus-specific memory B cells.
A) stopping isotype switching of B cells from IgM to IgA.
B) preloading antigen-presenting cells.
C) stimulating quick inflammation upon future exposure.
D) producing life-spanning antitetanus IgE antibodies.
E) generating tetanus-specific memory B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During the course of an intestinal infection with Salmonella enteritidis, the B cells undergo class switching. ________ switching is most likely to occur, which is caused by ________ cytokines.
A) IgD to IgE; B-cell
B) IgM to IgA; T-cell
C) IgG to IgM; B-cell
D) IgA to IgG; T-cell
E) IgD to IgM; T-cell
A) IgD to IgE; B-cell
B) IgM to IgA; T-cell
C) IgG to IgM; B-cell
D) IgA to IgG; T-cell
E) IgD to IgM; T-cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Capping of B-cell receptors on the surface of an antigen-exposed B cell immediately causes
A) VDJ gene switching, recombination, and hypermutation.
B) neutrophil phagocytosis of the antigen.
C) complement cascade signaling and antigen destruction.
D) cell-signaling cascade, inducing cell proliferation and differentiation.
E) helper T-cell proliferation and regulatory T-cell differentiation.
A) VDJ gene switching, recombination, and hypermutation.
B) neutrophil phagocytosis of the antigen.
C) complement cascade signaling and antigen destruction.
D) cell-signaling cascade, inducing cell proliferation and differentiation.
E) helper T-cell proliferation and regulatory T-cell differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The cells involved in shutting down immune responses that help prevent autoimmunity are
A) B cells.
B) TH17.
C) cytokines.
D) Treg cells.
E) mast cells.
A) B cells.
B) TH17.
C) cytokines.
D) Treg cells.
E) mast cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In 2004, doctors successfully used gene therapy with a severely defective leukemia virus to insert a cytokine receptor gene needed for T-cell development into the bone marrow of four children with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). What is SCID, and how did doing this procedure address the disease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a person is infected with the cold virus one year, why can he or she still catch a cold again the next year, even if his or her immune system is working properly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why is type AB blood considered to be the "universal recipient"? Explain what this means in terms of the antigens and antibodies present in blood types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Why are macrophages, monocytes, mast cells, and dendritic cells considered "professional" antigen-presenting cells, whereas fibroblasts are considered "nonprofessional" antigen-presenting cells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Innate lymphoid cells in the gut can be stimulated by
A) Treg cells.
B) cytotoxic T cells.
C) hormones.
D) IgA.
E) SIgA.
A) Treg cells.
B) cytotoxic T cells.
C) hormones.
D) IgA.
E) SIgA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which antibodies help compartmentalize the gut system?
A) IgM
B) IgE
C) IgA
D) IgG
E) IgD
A) IgM
B) IgE
C) IgA
D) IgG
E) IgD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A mutation that caused a person to have an ineffective complement C6 protein would have a direct effect on formation of
A) complement-antibody complex.
B) C3 convertase.
C) C3b opsonins for phagocytosis.
D) membrane attack complex.
E) C5 convertase.
A) complement-antibody complex.
B) C3 convertase.
C) C3b opsonins for phagocytosis.
D) membrane attack complex.
E) C5 convertase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe the structure of a typical IgG antibody, including the F(ab')₂ and Fc portions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A surgical patient infected with a blood-borne Staphylococcus would initially produce an anti-staphylococcal antibody of the IgM class. Why is that?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Omenn syndrome is an immune disorder associated with mutations in the recombination-activating genes (RAG1 and RAG2) needed for gene switching in lymphocytes. What effect would this mutation have on B cells, T cells, and the overall health of the adaptive immune response?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The gut is able to distinguish between indigenous microbiota and pathogens by using which part of epithelial cells?
A) TLRs and NLRs
B) SIgA
C) cytokines
D) IL-22
E) ILCs
A) TLRs and NLRs
B) SIgA
C) cytokines
D) IL-22
E) ILCs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If infections are spread by person-to-person contact, what percentage of the population will be protected against herd immunity if people are not vaccinated?
A) 66%
B) 25%
C) 10%
D) 100%
E) 40%
A) 66%
B) 25%
C) 10%
D) 100%
E) 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What cells are NOT associated with the gut epithelia?
A) columnar epithelial cells
B) intestinal epithelial cells
C) goblet cells
D) B cells
E) helper T cells
A) columnar epithelial cells
B) intestinal epithelial cells
C) goblet cells
D) B cells
E) helper T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The ________ vaccine stimulates cell-mediated immunity.
A) Sabin live polio
B) influenza
C) inactivated polio
D) acellular pertussis
E) PCV
A) Sabin live polio
B) influenza
C) inactivated polio
D) acellular pertussis
E) PCV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ________ vaccine is inactivated.
A) influenza
B) DTap
C) hepatitis B
D) HPV
E) MMR
A) influenza
B) DTap
C) hepatitis B
D) HPV
E) MMR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How can a person who has taken penicillin for a childhood ear infection later develop an allergy to penicillin when prescribed that drug again?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is NOT associated with overall human health?
A) introduction of Treg cell production
B) encounters with TLRs
C) antigen interactions with dendritic cells
D) encounters with NLRs
E) fecal transplant
A) introduction of Treg cell production
B) encounters with TLRs
C) antigen interactions with dendritic cells
D) encounters with NLRs
E) fecal transplant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Regulation of complement destruction of normal body cells is controlled by
A) CD8, serum factor C3b, and serum albumin.
B) CD58, serum factor H, and decay-accelerating factor.
C) CD4, serum factor Bb, and decay-accelerating factor.
D) MHC I, serum factor C5a, and serum lipoprotein.
E) MHC II, serum albumin, and T regulatory cells.
A) CD8, serum factor C3b, and serum albumin.
B) CD58, serum factor H, and decay-accelerating factor.
C) CD4, serum factor Bb, and decay-accelerating factor.
D) MHC I, serum factor C5a, and serum lipoprotein.
E) MHC II, serum albumin, and T regulatory cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Some patients suffering from bare lymphocyte syndrome (BLS), a rare immunodeficiency, have a genetic mutation in their TAP1/TAP2 genes causing the production of a defective TAP transporter. Describe what effect this has on antigen processing and in what cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Using the figure below, interpret what is occurring at stage 3.
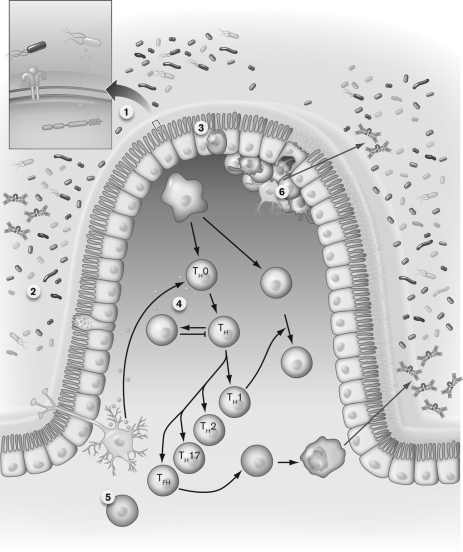


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
X-linked hyper IgM syndrome (XHIM) is an immunodeficiency disorder caused by mutations of the gene encoding CD154. Why is this disease characterized by recurrent infections (starting in childhood) and elevated serum levels of IgM?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Would taking probiotic health supplements be good for the average person's immunity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disorder affecting the skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs. A hallmark of lupus is the production of an array of autoantibodies. Some scientists believe that the autoantibody formation seen in lupus is a result of Epstein-Barr virus molecular mimicry. What do these scientists believe has happened in the case of lupus? Give one example as evidential support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Detail the benefits and predict possible risks of vaccinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why are antihistamines good for allergic rhinitis but not for atopic asthma?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Would treating a person infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who has recently developed acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) using a helper T-cell transfusion work? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Using the information presented in the table below, discuss why most vaccines are given between birth and 24 months.
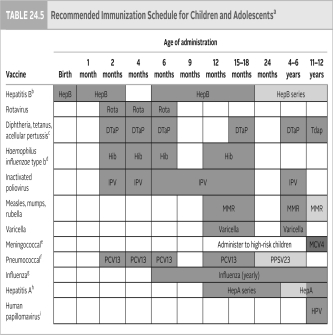


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a person was unable to undergo negative selection during T-cell education, what is T-cell education, and why would this be a severe immune problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
List the steps for the classical complement cascade. Discuss two ways this cascade results in microbial destruction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A patient presents in the emergency room with large red lesions up and down his arms. His case history reveals that he works for a gardening company, and that this rash most likely developed after clearing a weedy bank two days prior. The resident on duty concludes that the rash is a result of poison ivy exposure. Immunologically speaking, what is going on in this man's body, and what type of immune response is he experiencing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



