Deck 18: Urinary System and Body Fluids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Urinary System and Body Fluids
1
The renal medulla contains the
A) glomerulus and glomerular capsule
B) proximal and distal convoluted tubules
C) distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
D) nephron loops and collecting ducts
E) renal corpuscles and proximal convoluted tubules
A) glomerulus and glomerular capsule
B) proximal and distal convoluted tubules
C) distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
D) nephron loops and collecting ducts
E) renal corpuscles and proximal convoluted tubules
D
2
The functional unit of the kidney is the
A) glomerulus
B) pyramid
C) papilla
D) nephron
E) nephron loop
A) glomerulus
B) pyramid
C) papilla
D) nephron
E) nephron loop
D
3
The predominant solutes in urine are glucose and sodium.
False
The predominant solute is urea.
The predominant solute is urea.
4
The structures that receive the filtrate from the nephrons and take it to the minor calyces is the
A) collecting duct
B) descending limb of the nephron loop
C) renal pelvis
D) ureter
E) peritubular capillary
A) collecting duct
B) descending limb of the nephron loop
C) renal pelvis
D) ureter
E) peritubular capillary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The portion of the nephron that is between the proximal and distal convoluted tubules is the
A) glomerular capsule
B) collecting duct
C) nephron loop
D) glomerulus
E) juxtaglomerular apparatus
A) glomerular capsule
B) collecting duct
C) nephron loop
D) glomerulus
E) juxtaglomerular apparatus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Water is reabsorbed by osmosis from all parts of the renal tubule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The triangular,striated regions that make up the renal medulla are the renal
A) columns
B) pyramids
C) papillae
D) pelvises
E) calyces
A) columns
B) pyramids
C) papillae
D) pelvises
E) calyces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Urine volume increases as a result of increased ADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An increase in pH above normal is termed acidosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A nephron consists of a renal
A) pyramid and a renal column
B) corpuscle and a renal tubule
C) capsule and a renal pelvis
D) calyx and a renal pelvis
E) tubule and nephron loop
A) pyramid and a renal column
B) corpuscle and a renal tubule
C) capsule and a renal pelvis
D) calyx and a renal pelvis
E) tubule and nephron loop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The cortical material between the renal pyramids makes up the renal
A) cortex
B) pelvis
C) columns
D) papillae
E) calyces
A) cortex
B) pelvis
C) columns
D) papillae
E) calyces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The respiratory system compensates for deviations in pH by adjusting the amount of carbon dioxide that is exhaled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Blood plasma accounts for most of the extracellular fluid volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The maintenance of the volume and composition of body fluids is the basic function of the _____ system.
A) cardiovascular
B) digestive
C) nervous
D) urinary
E) respiratory
A) cardiovascular
B) digestive
C) nervous
D) urinary
E) respiratory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The kidneys are
A) retroperitoneal and between twelfth thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae
B) retroperitoneal and between the second and fifth lumbar vertebrae
C) retroperitoneal and in the lower right and left quadrants of the abdomen
D) surrounded by peritoneum and attached to the posterior abdominal wall by a mesentery near the first lumbar vertebra
E) surrounded by peritoneum and attached to the posterior abdominal wall by a mesentery near the third lumbar vertebra
A) retroperitoneal and between twelfth thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae
B) retroperitoneal and between the second and fifth lumbar vertebrae
C) retroperitoneal and in the lower right and left quadrants of the abdomen
D) surrounded by peritoneum and attached to the posterior abdominal wall by a mesentery near the first lumbar vertebra
E) surrounded by peritoneum and attached to the posterior abdominal wall by a mesentery near the third lumbar vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Glucose normally passes freely from the blood into the glomerular capsule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The capillary complex within the renal corpuscle is the
A) glomerular capsule
B) glomerulus
C) nephron loop
D) peritubular capillary
E) renal papilla
A) glomerular capsule
B) glomerulus
C) nephron loop
D) peritubular capillary
E) renal papilla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Buffers adjust deviations in pH by removing hydrogen ions from the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Potassium and phosphates are the major intracellular ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
About 40 percent of the body weight is fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Afferent arterioles are branches of the
A) interlobar artery
B) arcuate artery
C) segmental artery
D) peritubular capillary
E) interlobular artery
A) interlobar artery
B) arcuate artery
C) segmental artery
D) peritubular capillary
E) interlobular artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The volume of filtrate formed in a 24 hour period is about
A) 180 gallons
B) 2 liters
C) 125 gallons
D) 180 liters
E) 125 liters
A) 180 gallons
B) 2 liters
C) 125 gallons
D) 180 liters
E) 125 liters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In tubular reabsorption,substances move from the
A) proximal convoluted tubule into the nephron loop
B) peritubular capillaries into the renal tubule
C) proximal convoluted tubule into the glomerular capsule
D) renal tubules into the peritubular capillaries
E) peritubular capillaries into the nephron loop
A) proximal convoluted tubule into the nephron loop
B) peritubular capillaries into the renal tubule
C) proximal convoluted tubule into the glomerular capsule
D) renal tubules into the peritubular capillaries
E) peritubular capillaries into the nephron loop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The formation of urine involves three basic steps.These are
A) secretion, excretion, and urination
B) filtration, osmosis, and transport
C) filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
D) osmosis, active transport, facilitated diffusion
E) tubular filtration, capsular reabsorption, capillary secretion
A) secretion, excretion, and urination
B) filtration, osmosis, and transport
C) filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
D) osmosis, active transport, facilitated diffusion
E) tubular filtration, capsular reabsorption, capillary secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If glomerular hydrostatic pressure is 60 mm Hg,glomerular osmotic pressure is 32 mm Hg,and capsular hydrostatic pressure is 18 mm Hg,the net filtration pressure is _____ mm Hg.
A) 64
B) 10
C) 20
D) 46
E) 28
A) 64
B) 10
C) 20
D) 46
E) 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In glomerular filtration,fluid passes from the
A) glomerulus into the glomerular capsule
B) glomerular capsule into the proximal tubule
C) afferent arteriole into the glomerulus
D) glomerular capsule into the glomerulus
E) glomerulus into the efferent arteriole
A) glomerulus into the glomerular capsule
B) glomerular capsule into the proximal tubule
C) afferent arteriole into the glomerulus
D) glomerular capsule into the glomerulus
E) glomerulus into the efferent arteriole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The female urethra is _____ than in the male and opens _____ to the opening for the vagina.
A) shorter; posterior
B) shorter; anterior
C) longer; posterior
D) longer; anterior
A) shorter; posterior
B) shorter; anterior
C) longer; posterior
D) longer; anterior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The smooth muscle in the wall of the urinary bladder is the _____ muscle.
A) sphincter
B) detrusor
C) cremaster
D) dartos
A) sphincter
B) detrusor
C) cremaster
D) dartos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The openings for the ureters and urethra form a triangular area on the floor of the bladder that is called the
A) pyramid
B) detrusor area
C) prostatic area
D) trigone
E) transurethral area
A) pyramid
B) detrusor area
C) prostatic area
D) trigone
E) transurethral area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The act of expelling urine from the bladder is called
A) urination
B) voiding
C) micturition
D) both a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) urination
B) voiding
C) micturition
D) both a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The urinary bladder is located _____ the peritoneum.
A) posterior to the symphysis pubis and below
B) posterior to the symphysis pubis and above
C) anterior to the symphysis pubis and below
D) anterior to the symphysis pubis and above
E) in the midline of the abdominal cavity and above
A) posterior to the symphysis pubis and below
B) posterior to the symphysis pubis and above
C) anterior to the symphysis pubis and below
D) anterior to the symphysis pubis and above
E) in the midline of the abdominal cavity and above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Urine is transported away from the kidney in the
A) renal pelvis
B) renal sinus
C) ureter
D) collecting tubule
E) urethra
A) renal pelvis
B) renal sinus
C) ureter
D) collecting tubule
E) urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which is true concerning the internal and external urethral sphincters?
A) The internal sphincter is involuntary smooth muscle and the external is voluntary striated muscle.
B) The internal sphincter is voluntary striated muscle and the external is involuntary smooth muscle.
C) Both are involuntary smooth muscle.
D) Both are voluntary striated muscle.
A) The internal sphincter is involuntary smooth muscle and the external is voluntary striated muscle.
B) The internal sphincter is voluntary striated muscle and the external is involuntary smooth muscle.
C) Both are involuntary smooth muscle.
D) Both are voluntary striated muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Most of the tubular reabsorption occurs in the
A) glomerular capsule
B) proximal tubule
C) nephron loop
D) distal tubule
E) collecting duct
A) glomerular capsule
B) proximal tubule
C) nephron loop
D) distal tubule
E) collecting duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Some substances,such as glucose,are reabsorbed by facilitated diffusion.This means that reabsorption is limited by the
A) amount of ATP available
B) number of carrier molecules present
C) permeability of the tubular cells
D) hydrostatic pressure in the tubule
E) osmotic pressure in the tubule
A) amount of ATP available
B) number of carrier molecules present
C) permeability of the tubular cells
D) hydrostatic pressure in the tubule
E) osmotic pressure in the tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The juxtaglomerular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus are specialized cells in the
A) ascending limb of the nephron loop
B) macula densa
C) afferent arteriole
D) efferent arteriole
E) proximal convoluted tubule
A) ascending limb of the nephron loop
B) macula densa
C) afferent arteriole
D) efferent arteriole
E) proximal convoluted tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The vessel that returns blood from the kidney directly into the IVC is the _____ vein.
A) interlobar
B) renal
C) splenic
D) hepatic
E) segmental
A) interlobar
B) renal
C) splenic
D) hepatic
E) segmental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Water reabsorption is the result of
A) hydrostatic pressure
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport
D) osmosis
E) pinocytosis
A) hydrostatic pressure
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport
D) osmosis
E) pinocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The portion of the nephron tubule that is not permeable to water is the
A) proximal convoluted tubule
B) descending limb of the nephron loop
C) ascending limb of the nephron loop
D) distal convoluted tubule
E) collecting duct
A) proximal convoluted tubule
B) descending limb of the nephron loop
C) ascending limb of the nephron loop
D) distal convoluted tubule
E) collecting duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All of the following affect net filtration pressure EXCEPT
A) blood pressure in the glomerulus
B) hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capsule
C) blood pressure in the peritubular capillaries
D) osmotic pressure in the blood of the glomerulus
A) blood pressure in the glomerulus
B) hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capsule
C) blood pressure in the peritubular capillaries
D) osmotic pressure in the blood of the glomerulus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Excess hydrogen ions are removed from the blood by
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular osmosis
D) tubular secretion
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular osmosis
D) tubular secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which substance is present in the blood and filtrate but normally is not present in the urine?
A) plasma proteins
B) glucose
C) sodium
D) hydrogen ions
E) urea
A) plasma proteins
B) glucose
C) sodium
D) hydrogen ions
E) urea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Urethratresia means
A) inflammation of the urethra
B) inflammation of the ureter
C) lack of an opening in the urethra
D) obstruction of the urethra
E) suture of the urinary bladder
A) inflammation of the urethra
B) inflammation of the ureter
C) lack of an opening in the urethra
D) obstruction of the urethra
E) suture of the urinary bladder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The predominant solute in urine is
A) glucose
B) urea
C) sodium
D) bicarbonate ions
E) chloride ions
A) glucose
B) urea
C) sodium
D) bicarbonate ions
E) chloride ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The predominant extracellular cation is
A) chloride
B) sodium
C) phosphate
D) hydrogen
E) potassium
A) chloride
B) sodium
C) phosphate
D) hydrogen
E) potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Substances in body fluids that help prevent significant changes in pH are
A) bicarbonate ions
B) buffers
C) weak acids
D) water molecules
E) salts
A) bicarbonate ions
B) buffers
C) weak acids
D) water molecules
E) salts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The primary hormone that regulates electrolyte concentration is
A) antidiuretic hormone
B) angiotensin
C) aldosterone
D) atrial natriuretic hormone
E) adrenocorticotropic hormone
A) antidiuretic hormone
B) angiotensin
C) aldosterone
D) atrial natriuretic hormone
E) adrenocorticotropic hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which one of the following is normally present in the urine?
A) urochrome
B) albumin
C) glucose
D) ketone bodies
E) bilirubin
A) urochrome
B) albumin
C) glucose
D) ketone bodies
E) bilirubin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A pH of 7.3 indicates
A) normal blood pH
B) acidosis
C) alkalosis
D) less than normal hydrogen ions
A) normal blood pH
B) acidosis
C) alkalosis
D) less than normal hydrogen ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An enzyme produced by the kidneys is
A) angiotensin
B) catalase
C) renin
D) erythropoietin
E) atriopeptin
A) angiotensin
B) catalase
C) renin
D) erythropoietin
E) atriopeptin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All of the following are avenues of fluid loss from the body EXCEPT
A) urine
B) perspiration
C) air that is exhaled
D) feces
E) utilization of nutrients
A) urine
B) perspiration
C) air that is exhaled
D) feces
E) utilization of nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following represents a normal pH for urine?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 9
E) 10
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 9
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Three-fourths of the extracellular fluid in the body is
A) intravascular fluid
B) plasma
C) cerebrospinal fluid
D) interstitial fluid
E) fluid inside the cells
A) intravascular fluid
B) plasma
C) cerebrospinal fluid
D) interstitial fluid
E) fluid inside the cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Angiotensin II increases blood pressure by
A) vasoconstriction of systemic arteries and stimulation of aldosterone
B) vasodilation of systemic arteries and stimulation of aldosterone
C) vasoconstriction of systemic arteries and stimulation of antidiuretic hormone
D) vasodilation of systemic arteries and stimulation of antidiuretic hormone
A) vasoconstriction of systemic arteries and stimulation of aldosterone
B) vasodilation of systemic arteries and stimulation of aldosterone
C) vasoconstriction of systemic arteries and stimulation of antidiuretic hormone
D) vasodilation of systemic arteries and stimulation of antidiuretic hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which substance is present in the blood but not normally present in the filtrate or the urine?
A) plasma proteins
B) glucose
C) sodium
D) hydrogen ions
E) urea
A) plasma proteins
B) glucose
C) sodium
D) hydrogen ions
E) urea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Aldosterone causes the reabsorption of sodium.This action triggers the passive reabsorption of _____ and _____ urine output.
A) proteins; increases
B) glucose; increases
C) glucose; decreases
D) water; decreases
E) water; increases
A) proteins; increases
B) glucose; increases
C) glucose; decreases
D) water; decreases
E) water; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The pituitary hormone that increases the permeability of collecting ducts to water is
A) oxytocin
B) antidiuretic hormone
C) luteinizing hormone
D) adrenocorticotropic hormone
E) aldosterone
A) oxytocin
B) antidiuretic hormone
C) luteinizing hormone
D) adrenocorticotropic hormone
E) aldosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The movement of substances from the blood in the peritubular capillary into the renal tubule is known as
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular osmosis
D) tubular secretion
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular osmosis
D) tubular secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The surgical removal of a stone from the renal pelvis is
A) nephrolithiasis
B) urethratresia
C) cystectasy
D) pyelolithotomy
E) periureteritis
A) nephrolithiasis
B) urethratresia
C) cystectasy
D) pyelolithotomy
E) periureteritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Under normal conditions,which of the following accounts for most fluid intake?
A) water-containing foods
B) water produced as a result of metabolism
C) water from beverages
A) water-containing foods
B) water produced as a result of metabolism
C) water from beverages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the term for the tubular structure that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the exterior?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What are two hormones that have a direct influence urine concentration and volume?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is another term for urination or voiding?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the term for the cluster of capillaries in the renal corpuscle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the term for the structure that forms where the ascending limb touches the afferent arteriole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the term for the process in the renal corpuscle by which plasma components leave the blood and enter the renal tubules?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the term for the presence of red blood cells in the urine?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the term for the central collecting structure in the kidney that is continuous with the ureter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the term for the specific region where most of the tubular reabsorption occurs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the term for the portion of renal tubule adjacent to the glomerular capsule?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the term for the arteries that are located in the renal columns?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the term for the striated appearing structures that make up the medulla of the kidney?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is the collective term for the muscle in the wall of the urinary bladder?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the term for the fluid compartment that contains 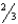 of the total body fluid volume?
of the total body fluid volume?
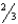 of the total body fluid volume?
of the total body fluid volume?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the term for the enzyme produced by the kidneys that promotes the production of angiotensin II?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



