Deck 29: Development and Inheritance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Development and Inheritance
1
What connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava in infants?
A)Ductus venosus
B)Ductus arteriosus
C)Anteriosum
D)Patent ductus arteriosus
E)Superior vena cava
A)Ductus venosus
B)Ductus arteriosus
C)Anteriosum
D)Patent ductus arteriosus
E)Superior vena cava
A
2
How many pairs of pharyngeal arches are there?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
E)6
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
E)6
D
3
CVS is taking cells from where?
A)Amnion
B)Chorion
C)Placenta
D)Umbilical cord
E)Uterus
A)Amnion
B)Chorion
C)Placenta
D)Umbilical cord
E)Uterus
B
4
Which hormone is secreted by nonpregnant women from neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus?
A)GnRH
B)hCG
C)CRH
D)AFP
E)ATP
A)GnRH
B)hCG
C)CRH
D)AFP
E)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following develops from the epiblast and carries a protective fluid?
A)Cytotrophoblast
B)Yolk sac
C)Exocoelomic membrane
D)Amnion
E)Lacunae
A)Cytotrophoblast
B)Yolk sac
C)Exocoelomic membrane
D)Amnion
E)Lacunae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Each somite may differentiate into a
A)Sertoli cell
B)Dermatome
C)Ovary
D)Myogenic cells
E)Ductus deferens
A)Sertoli cell
B)Dermatome
C)Ovary
D)Myogenic cells
E)Ductus deferens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What exam is performed between 14-16 weeks gestation and is used to detect genetic abnormalities?
A)Sonogram
B)Amniocentesis
C)CVS
D)AFP test
E)CBC
A)Sonogram
B)Amniocentesis
C)CVS
D)AFP test
E)CBC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Involution is
A)When the placenta is expelled
B)When the umbilical cord is cut
C)When the uterus decreases in size
D)When the cervix dilates
E)None of these choices
A)When the placenta is expelled
B)When the umbilical cord is cut
C)When the uterus decreases in size
D)When the cervix dilates
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is the portion of the endometrium that lies between the embryo and the stratum basalis?
A)Decidua basalis
B)Decidua capsularis
C)Decidua parietalis
D)Lamina propria
E)Adventitia
A)Decidua basalis
B)Decidua capsularis
C)Decidua parietalis
D)Lamina propria
E)Adventitia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following will become the primary structure for exchange of material between the mother and the fetus?
A)Chorionic villi of the placenta
B)Amnion
C)Amnionic fluid
D)Embryonic disc
E)Endoderm
A)Chorionic villi of the placenta
B)Amnion
C)Amnionic fluid
D)Embryonic disc
E)Endoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The fusion of the male pronucleus and the female pronucleus results in which developmental stage?
A)Female pronucleus
B)Male pronucleus
C)Zygote
D)Blastomeres
E)Morula
A)Female pronucleus
B)Male pronucleus
C)Zygote
D)Blastomeres
E)Morula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a principle hormone that releases milk into the mammary ducts?
A)Prolactin
B)PIH
C)PRH
D)Oxytocin
E)GnRH
A)Prolactin
B)PIH
C)PRH
D)Oxytocin
E)GnRH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Labor cannot take place until all of which hormone's effects are diminished?
A)Estrogen
B)Progesterone
C)Testosterone
D)Relaxin
E)Inhibin
A)Estrogen
B)Progesterone
C)Testosterone
D)Relaxin
E)Inhibin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the connection between the placenta and the embryo?
A)Amnion
B)Chorion
C)Umbilical cord
D)Placenta
E)Capillary beds
A)Amnion
B)Chorion
C)Umbilical cord
D)Placenta
E)Capillary beds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a series of functional changes that sperm go through when they are in the female reproductive tract?
A)Acrosomal reaction
B)Maturation
C)Fertilization
D)Capacitation
E)Polyspermy
A)Acrosomal reaction
B)Maturation
C)Fertilization
D)Capacitation
E)Polyspermy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Fertilization normally occurs within which structure?
A)Ovary
B)Fallopian tube
C)Ovarian ligament
D)Body of uterus
E)Vagina
A)Ovary
B)Fallopian tube
C)Ovarian ligament
D)Body of uterus
E)Vagina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an agent or influence that causes developmental defects in an embryo?
A)Carcinogen
B)Toxin
C)Nicotine
D)Radiation
E)Teratogen
A)Carcinogen
B)Toxin
C)Nicotine
D)Radiation
E)Teratogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the time from the onset of labor to the complete dilation of the cervix?
A)Stage of dilation
B)Stage of expulsion
C)Placental stage
D)Gestation
E)Effacement
A)Stage of dilation
B)Stage of expulsion
C)Placental stage
D)Gestation
E)Effacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the part of the blastocyst that promotes implantation and produces hCG?
A)Blastocyte
B)Blastosphere
C)Trophoblast
D)Blastocyst cavity
E)Uterine cavity
A)Blastocyte
B)Blastosphere
C)Trophoblast
D)Blastocyst cavity
E)Uterine cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
During pregnancy stroke volume can increase by
A)10%
B)20%
C)30%
D)40%
E)50%
A)10%
B)20%
C)30%
D)40%
E)50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
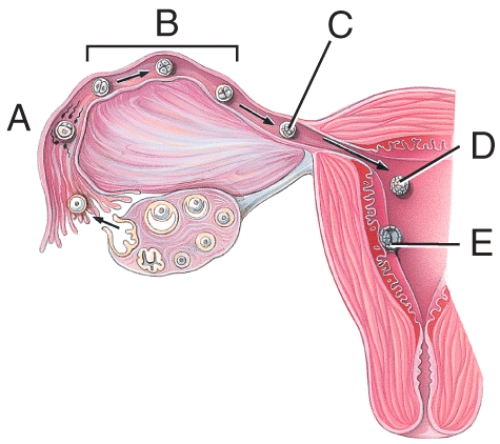
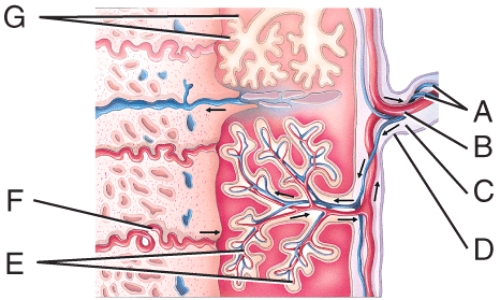
Which cells are derived from the yolk sac and form a connective tissue layer?
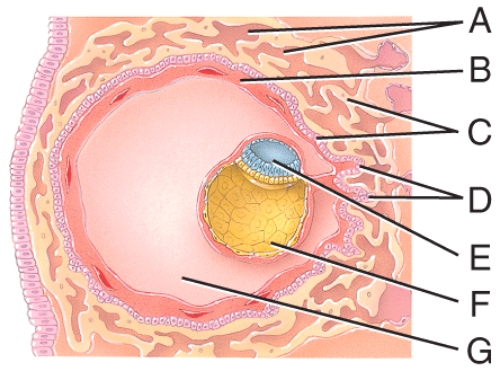
A)A
B)B
C)E
D)F
E)G

A)A
B)B
C)E
D)F
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which structure was formerly called the blastocyst cavity?
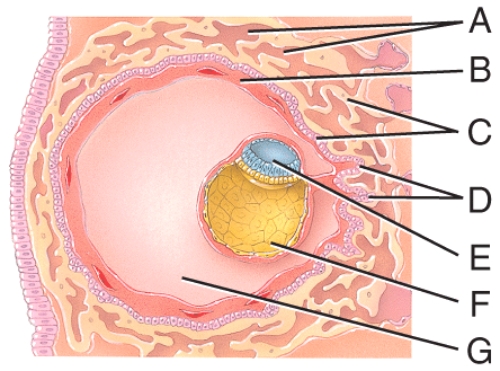
A)C
B)D
C)E
D)F
E)G

A)C
B)D
C)E
D)F
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is line "G" pointing to?
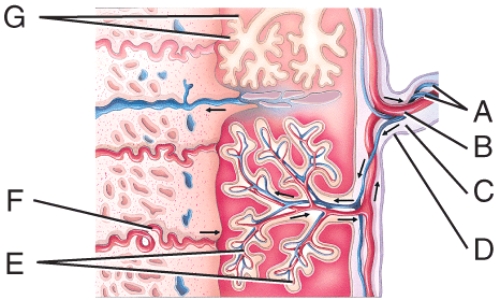
A)Chorionic villi
B)Amnion
C)Umbilical vein
D)Umbilical artery
E)Amnionic capillary bed

A)Chorionic villi
B)Amnion
C)Umbilical vein
D)Umbilical artery
E)Amnionic capillary bed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Chromosome #15 is considered
A)A sex chromosome
B)An autosome
C)The SRY chromosome
D)A linked gene
E)A transposon
A)A sex chromosome
B)An autosome
C)The SRY chromosome
D)A linked gene
E)A transposon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
This is composed of the syncytiotrophoblast and the cytotrophoblast.
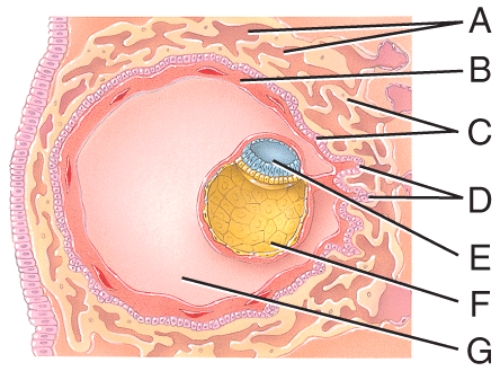
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Where are the fetal blood vessels?
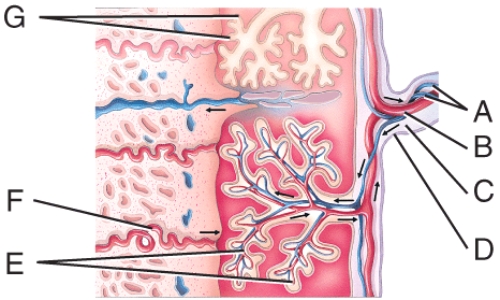
A)C
B)D
C)E
D)F
E)G

A)C
B)D
C)E
D)F
E)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What stage happens 3-4 days after fertilization?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
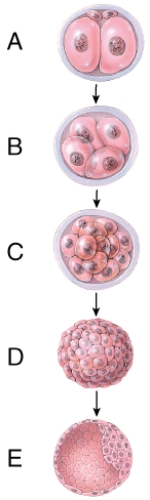
What does diagram "A" represent?
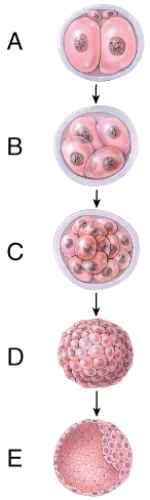
A)Cleavage of embryo
B)Cleavage of zygote
C)Cleavage of morula
D)Cleavage of blastocyst
E)Cleavage of fetus

A)Cleavage of embryo
B)Cleavage of zygote
C)Cleavage of morula
D)Cleavage of blastocyst
E)Cleavage of fetus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is line "A" pointing to?
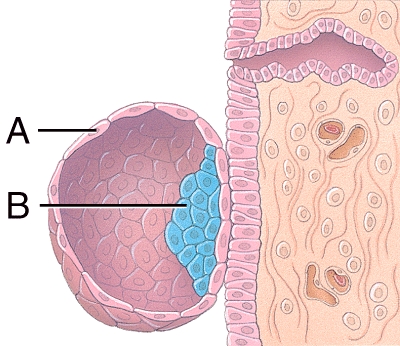
A)Endometrial gland
B)Trophoblast
C)Embryoblast
D)Blastocyst
E)Dermatome

A)Endometrial gland
B)Trophoblast
C)Embryoblast
D)Blastocyst
E)Dermatome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a permanent change in an allele?
A)Mutation
B)Phenotype
C)Genotype
D)Dominant
E)Recessive
A)Mutation
B)Phenotype
C)Genotype
D)Dominant
E)Recessive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is line "G" pointing to?
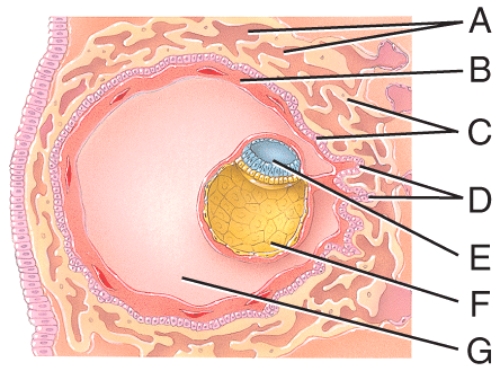
A)Chorion
B)Chorionic villi
C)Sinusoid
D)Extraembryonic mesoderm
E)None of these choices

A)Chorion
B)Chorionic villi
C)Sinusoid
D)Extraembryonic mesoderm
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What stage happens 6 days after fertilization?
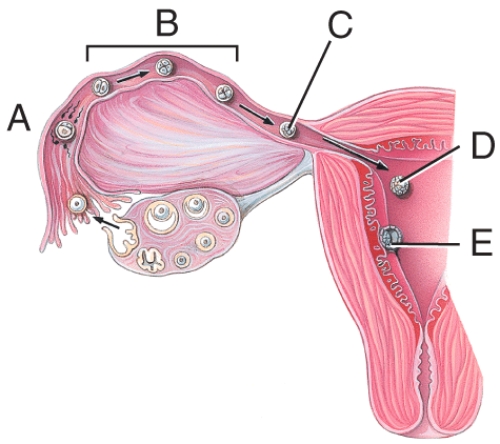
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a child has B blood,and the mother has B blood,what is the possible genotype of the father?
A)B
B)O
C)AB
D)B or O
E)B,O or AB
A)B
B)O
C)AB
D)B or O
E)B,O or AB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A Barr body
A)Is an inactivated X chromosome
B)Cannot be stained
C)Are transcribed and translated
D)Is seen in males
E)Is only found in humans
A)Is an inactivated X chromosome
B)Cannot be stained
C)Are transcribed and translated
D)Is seen in males
E)Is only found in humans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which one represents the morula stage?
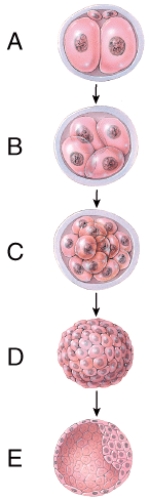
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If one parent has type A blood and one parent has type B blood,what blood type is possible for their child?
A)AB
B)A
C)B
D)O
E)All of these choices
A)AB
B)A
C)B
D)O
E)All of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Where is the amniotic cavity?
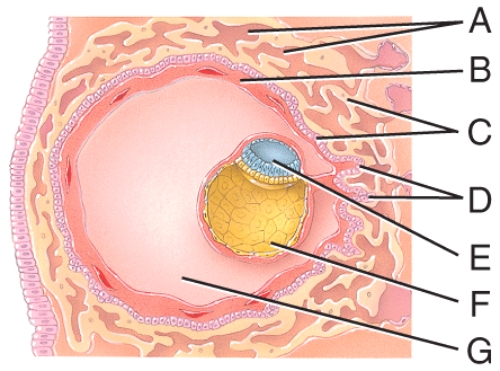
A)E
B)D
C)C
D)B
E)A

A)E
B)D
C)C
D)B
E)A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An example of incomplete dominance is
A)ABO blood groups
B)Sickle-cell disease
C)Angelman Syndrome
D)Prader-Willi Syndrome
E)PKU
A)ABO blood groups
B)Sickle-cell disease
C)Angelman Syndrome
D)Prader-Willi Syndrome
E)PKU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When phenotype can be drastically different depending on parental origin it is called:
A)Mutation
B)Translocation
C)Genomic imprinting
D)Incomplete dominance
E)Codominance
A)Mutation
B)Translocation
C)Genomic imprinting
D)Incomplete dominance
E)Codominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which one represents the blastocyst stage?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Clubfeet is an example of which condition listed?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is line "F" pointing to?
A)Umbilical arteries
B)Umbilical vein
C)Fetal blood vessels
D)Maternal endometrial arteriole
E)Chorionic villi

A)Umbilical arteries
B)Umbilical vein
C)Fetal blood vessels
D)Maternal endometrial arteriole
E)Chorionic villi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which condition listed is a malpresentation in which the fetal buttocks or lower limbs present into the maternal pelvis?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the products of the three primary germ layers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Describe the process and purpose of amniocentesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the terms below describes the development of an organism from an undifferentiated cell?
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Karyotype
E)Fertilization age
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Karyotype
E)Fertilization age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which condition listed is a sex chromosome aneuploidy,caused by the presence of a single X chromosome designated XO?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which condition listed is an infectious disease of childbirth resulting from an infection originating in the birth canal and affecting the mother's endometrium?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Puerperal fever
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Fetal alcohol syndrome
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Puerperal fever
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Fetal alcohol syndrome
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Describe the hormonal events surrounding parturition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the terms below describes the beginning or first discernable indication of the development of an organ or structure?
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Karyotype
E)Fertilization age
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Karyotype
E)Fertilization age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which condition listed is a sex chromosome aneuploidy,usually due to trisomy XXY?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which condition listed is a developmental abnormality due to mechanical forces that mold a part of the fetus over a prolonged period of time?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which condition listed is a sex chromosome aneuploidy characterized by at least 3 X chromosomes (XXX)?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Metafemale syndrome
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Lethal gene
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Metafemale syndrome
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Lethal gene
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which condition listed is also called morning sickness?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which condition listed is one of the most common causes of mental retardation and the most common preventable cause of birth defects in the United States?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Metafemale syndrome
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Fetal alcohol syndrome
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Metafemale syndrome
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Fetal alcohol syndrome
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Red-green color blindness is a recessive,X-linked trait represented as Xc.(Normal color vision is represented as XC. )If a daughter has red-green color blindness,what must the genotypes of her parents be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which condition listed gives rise to sterile females with virtually no ovaries and limited development of secondary sex characteristics?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the terms below includes all structures that develop from a zygote: the embryo,the embryonic placenta and its associated membranes?
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Gestational age
E)Karyotype
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Gestational age
E)Karyotype

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which condition listed gives rise to individuals that are: somewhat mentally disadvantaged,sterile males with undeveloped testes,scant body hair,and enlarged breasts?
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome
A)Emesis gravidarum
B)Deformation
C)Turner's syndrome
D)Breech presentation
E)Klinefelter's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Distinguish between genotype and phenotype and explain how the environment may affect each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the terms below describes the chromosomal characteristic of an individual presented as a systematic arrangement of pairs of metaphase chromosomes arranged by size?
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Karyotype
E)Fertilization age
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Karyotype
E)Fertilization age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In a heterozygous individual for a certain trait,the dominant allele gives normal skin pigmentation.What is the masked,recessive trait in this individual?
A)Normal vision
B)Albinism
C)Normal nervous system
D)Polydactyly
E)Cystic fibrosis
A)Normal vision
B)Albinism
C)Normal nervous system
D)Polydactyly
E)Cystic fibrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following structures is NOT produced from the mesoderm?
A)Melanocytes
B)All skeletal muscle
C)All cardiac muscle
D)Blood vessels
E)Lymphatic tissue
A)Melanocytes
B)All skeletal muscle
C)All cardiac muscle
D)Blood vessels
E)Lymphatic tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In a heterozygous individual for a certain trait,the dominant allele gives polydactyly.What is the masked,recessive trait in this individual?
A)Normal vision
B)Brachydactyly
C)Normal digits
D)Syndactylism
E)Straight thumb
A)Normal vision
B)Brachydactyly
C)Normal digits
D)Syndactylism
E)Straight thumb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In a heterozygous individual for a certain trait,the dominant allele gives Huntington's disease.What is the masked,recessive trait in this individual?
A)Normal vision
B)Normal digits
C)Normal nervous system
D)Polydactyly
E)Straight thumb
A)Normal vision
B)Normal digits
C)Normal nervous system
D)Polydactyly
E)Straight thumb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the term used to describe the age of an embryo or fetus calculated from the presumed first day of the last normal menstrual period?
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Gestational age
E)Fertilization age
A)Conceptus
B)Primordium
C)Epigenesis
D)Gestational age
E)Fertilization age

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following structures is(are)produced from the endoderm?
A)Adrenal cortex
B)Gonads
C)Epithelium of the oral cavity
D)Epithelial lining of the pharynx
E)Arachnoid mater
A)Adrenal cortex
B)Gonads
C)Epithelium of the oral cavity
D)Epithelial lining of the pharynx
E)Arachnoid mater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is a noninvasive prenatal test?
A)AFP
B)CVS
C)Amniocentesis
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)AFP
B)CVS
C)Amniocentesis
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is a function of the hormone corticotropin-releasing hormone?
A)Maintain endometrium of uterus during pregnancy
B)Help prepare mammary glands for lactation
C)Establish the timing of birth
D)Increase flexibility of the pubic symphysis
E)All of these are functions of CRH
A)Maintain endometrium of uterus during pregnancy
B)Help prepare mammary glands for lactation
C)Establish the timing of birth
D)Increase flexibility of the pubic symphysis
E)All of these are functions of CRH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When are the three primary germ layers established during pregnancy?
A)First week of development
B)Second week of development
C)Third week of development
D)Fourth week of development
E)Second month of development
A)First week of development
B)Second week of development
C)Third week of development
D)Fourth week of development
E)Second month of development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a breast-feeding benefit for infants?
A)Beneficial cells
B)Beneficial molecules
C)Decreased incidence of diseases later in life
D)Enhancement of intellectual and neurological development
E)All of these are breast-feeding benefits
A)Beneficial cells
B)Beneficial molecules
C)Decreased incidence of diseases later in life
D)Enhancement of intellectual and neurological development
E)All of these are breast-feeding benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following structures is(are)produced from the endoderm?
A)Cartilage
B)Dermis of the skin
C)Kidneys and ureters
D)Internal and external ear
E)Gametes
A)Cartilage
B)Dermis of the skin
C)Kidneys and ureters
D)Internal and external ear
E)Gametes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which hormone causes release of milk into the mammary ducts via the milk ejection reflex?
A)Prolactin
B)Oxytocin
C)Estrogen
D)Progesterone
E)Aldosterone
A)Prolactin
B)Oxytocin
C)Estrogen
D)Progesterone
E)Aldosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In a heterozygous individual for a certain trait,the dominant allele gives syndactylism.What is the masked,recessive trait in this individual?
A)Normal vision
B)Brachydactyly
C)Normal digits
D)Polydactyly
E)Straight thumb
A)Normal vision
B)Brachydactyly
C)Normal digits
D)Polydactyly
E)Straight thumb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following are major potential teratogens that affect embryonic development?
A)Alcohol
B)Cigarette smoke
C)Various prescription drugs
D)Irradiation
E)All of these
A)Alcohol
B)Cigarette smoke
C)Various prescription drugs
D)Irradiation
E)All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



