Deck 3: Why Are There Wars
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Why Are There Wars
1
Crisis bargaining is also known as:
A)credible commitment.
B)rejecting ideal points.
C)interstate war.
D)coercive diplomacy.
A)credible commitment.
B)rejecting ideal points.
C)interstate war.
D)coercive diplomacy.
D
2
In the figure,what do the words "Bargaining Range" represent?
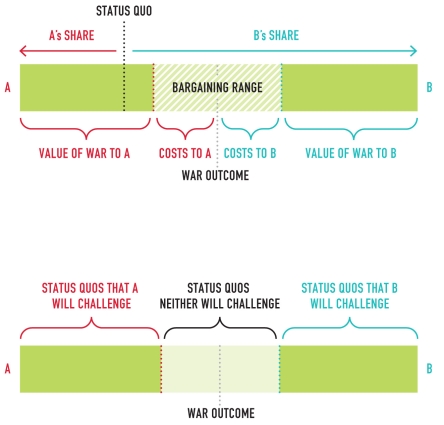
A)The value of war to both A and B
B)The set of deals to which State A will agree
C)The set of deals to which both states will agree
D)The set of deals to which State B will agree

A)The value of war to both A and B
B)The set of deals to which State A will agree
C)The set of deals to which both states will agree
D)The set of deals to which State B will agree
C
3
A state's preferred outcome or settlement of a dispute is known as:
A)an ideal point.
B)a crisis.
C)a bargain.
D)diplomacy.
A)an ideal point.
B)a crisis.
C)a bargain.
D)diplomacy.
A
4
Which of the following describes a crisis?
A)A state rejects an international agreement that most other states have ratified.
B)A state threatens military force to achieve its bargaining goals.
C)Two states decide to bargain over territory that both claim.
D)A weaker state has to bargain with a stronger state.
A)A state rejects an international agreement that most other states have ratified.
B)A state threatens military force to achieve its bargaining goals.
C)Two states decide to bargain over territory that both claim.
D)A weaker state has to bargain with a stronger state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which is true of World War I?
A)Leaders expected the war to be the longest in history.
B)Leaders thought the war would be an average length and prepared for it.
C)Leaders expected the war to be short.
D)Leaders had fairly realistic expectations for the war.
A)Leaders expected the war to be the longest in history.
B)Leaders thought the war would be an average length and prepared for it.
C)Leaders expected the war to be short.
D)Leaders had fairly realistic expectations for the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When two states decide to bargain:
A)they agree to divide the disputed good equally.
B)both agree to reject taking intransigent,all-or-nothing positions while negotiating.
C)both agree to reject the option of going to war over the conflict.
D)one state might end up giving in to all of the demands of the other.
A)they agree to divide the disputed good equally.
B)both agree to reject taking intransigent,all-or-nothing positions while negotiating.
C)both agree to reject the option of going to war over the conflict.
D)one state might end up giving in to all of the demands of the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why does anarchy cause war?
A)Men have evil inclinations that cause them to go to war.
B)No authority exists to stop a state from using force to advance its own interests.
C)Only a few states are strong enough to protect themselves.
D)Bargaining is impossible without a central authority.
A)Men have evil inclinations that cause them to go to war.
B)No authority exists to stop a state from using force to advance its own interests.
C)Only a few states are strong enough to protect themselves.
D)Bargaining is impossible without a central authority.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is an example of a civil war?
A)The United States' war against Al-Qaeda and radical Islamic terrorist groups
B)Armed conflict between FARC (Revolutionary Armed Forces of Columbia)guerrillas and the Colombian national army
C)World War I
D)The UN-sanctioned intervention to stop Iraq from taking over Kuwait
A)The United States' war against Al-Qaeda and radical Islamic terrorist groups
B)Armed conflict between FARC (Revolutionary Armed Forces of Columbia)guerrillas and the Colombian national army
C)World War I
D)The UN-sanctioned intervention to stop Iraq from taking over Kuwait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the strict definition of war,which of the following conflicts is a war?
A)A militarized conflict between Rwanda and Congo,in which 500 soldiers are killed
B)A skirmish between a Chinese and an American vessel in the South China sea,in which no soldiers are killed
C)An American drone strike against Pakistani militants,in which 50 people are killed
D)A conflict between India and Pakistan,in which 2,000 soldiers are killed
A)A militarized conflict between Rwanda and Congo,in which 500 soldiers are killed
B)A skirmish between a Chinese and an American vessel in the South China sea,in which no soldiers are killed
C)An American drone strike against Pakistani militants,in which 50 people are killed
D)A conflict between India and Pakistan,in which 2,000 soldiers are killed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why do states fight wars?
A)Most states are inherently aggressive.
B)They value something more than the cost of war and cannot come to an agreement.
C)They have too much information about other states and realize they could win.
D)They disagree over the rules of war.
A)Most states are inherently aggressive.
B)They value something more than the cost of war and cannot come to an agreement.
C)They have too much information about other states and realize they could win.
D)They disagree over the rules of war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What do states hope to achieve by engaging in coercive diplomacy?
A)To make an adversary reveal information about their preferences
B)To force concessions by threatening to use force if no agreement is reached
C)To make their threats appear credible
D)To alter an opponent's ideal point
A)To make an adversary reveal information about their preferences
B)To force concessions by threatening to use force if no agreement is reached
C)To make their threats appear credible
D)To alter an opponent's ideal point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why would a state go to war to change another state's regime?
A)International law allows states to attack another state whose government makes threats against its neighbors.
B)War is the only way that democratic states can change authoritarian regimes into representative governments.
C)States will use war,when possible,to remove a regime in another country that is hostile to it.
D)A state would change a regime that refuses to trade with other states.
A)International law allows states to attack another state whose government makes threats against its neighbors.
B)War is the only way that democratic states can change authoritarian regimes into representative governments.
C)States will use war,when possible,to remove a regime in another country that is hostile to it.
D)A state would change a regime that refuses to trade with other states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Why might states decide not to go to war over a disputed good?
A)The opposing side also has a legitimate claim.
B)The costs of war are higher than the expected benefits from war.
C)States always prefer to strike a deal rather than fight wars.
D)To be unpredictable.
A)The opposing side also has a legitimate claim.
B)The costs of war are higher than the expected benefits from war.
C)States always prefer to strike a deal rather than fight wars.
D)To be unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following accurately describes the "bargaining range"?
A)The possible outcomes to which states can agree without going to war over a dispute
B)The amount of territory states claim in a dispute
C)The types of demands a state makes in a crisis
D)The number of actors involved in a dispute
A)The possible outcomes to which states can agree without going to war over a dispute
B)The amount of territory states claim in a dispute
C)The types of demands a state makes in a crisis
D)The number of actors involved in a dispute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A state that provokes a crisis would most prefer:
A)to go to war to achieve its goals.
B)that the other state capitulate completely.
C)that the other side agree to negotiations over the dispute.
D)that a more powerful country intervene in the dispute.
A)to go to war to achieve its goals.
B)that the other state capitulate completely.
C)that the other side agree to negotiations over the dispute.
D)that a more powerful country intervene in the dispute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Despite American threats,Afghanistan did not believe that the United States would be willing to engage in a lengthy war to remove its Taliban government from power.By disregarding such threats,Afghanistan doubted:
A)American capabilities.
B)American interests.
C)American resolve.
D)American honesty.
A)American capabilities.
B)American interests.
C)American resolve.
D)American honesty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which is an example of interstate war?
A)A government committing acts of genocide against an ethnic group,where several thousand civilians are killed
B)A government fighting a well-armed rebel group within its territory,where several thousand soldiers have died on the battlefield
C)Two governments fighting each other,where several thousand soldiers have died on the battlefield
D)A government engaged in counterinsurgency activity against an international group that employs terrorism,in which several thousand people on both sides of the conflict have died
A)A government committing acts of genocide against an ethnic group,where several thousand civilians are killed
B)A government fighting a well-armed rebel group within its territory,where several thousand soldiers have died on the battlefield
C)Two governments fighting each other,where several thousand soldiers have died on the battlefield
D)A government engaged in counterinsurgency activity against an international group that employs terrorism,in which several thousand people on both sides of the conflict have died

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is an explanation for the occurrence of war?
A)The outbreak of war is always random; therefore,it cannot be explained.
B)Misperceptions and mistakes by actors can lead to war between states.
C)Insufficient resolve on both sides leads to war.
D)States fight wars because they are generally costless.
A)The outbreak of war is always random; therefore,it cannot be explained.
B)Misperceptions and mistakes by actors can lead to war between states.
C)Insufficient resolve on both sides leads to war.
D)States fight wars because they are generally costless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the most common reason states have historically gone to war?
A)Two states claim the same territory.
B)A state resents another state's high tariffs on its imports.
C)The populations of two states are composed of two conflicting ethnic groups.
D)A state thinks another state is cheating on an arms-reduction agreement.
A)Two states claim the same territory.
B)A state resents another state's high tariffs on its imports.
C)The populations of two states are composed of two conflicting ethnic groups.
D)A state thinks another state is cheating on an arms-reduction agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the figure,what set of deals does A prefer to war?
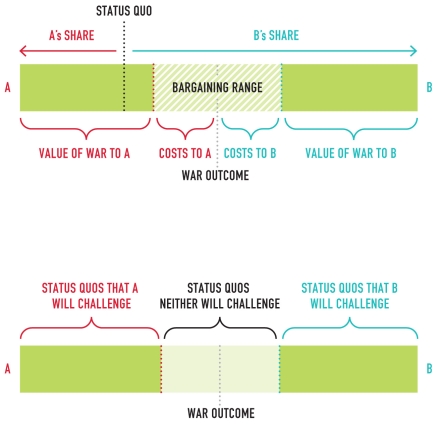
A)Costs to A + costs to B + value of war to B
B)Value of war to A
C)Those in the shaded area labeled "Bargaining Range"
D)Value of war to A + costs to A + costs to B

A)Costs to A + costs to B + value of war to B
B)Value of war to A
C)Those in the shaded area labeled "Bargaining Range"
D)Value of war to A + costs to A + costs to B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In October 1950,the Chinese government warned the United States that crossing the 38th parallel on the Korean peninsula would lead to a Chinese intervention on behalf of North Korea.What type of deterrence is this an example of?
A)Counter deterrence
B)General deterrence
C)Extended deterrence
D)Coercive deterrence
A)Counter deterrence
B)General deterrence
C)Extended deterrence
D)Coercive deterrence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is an explanation for Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990?
A)Iraq wanted to hide its weapons of mass destruction in Kuwait.
B)Kuwait was pumping more oil than the limit to which it had agreed,which decreased the price for Iraq's oil.
C)Iraq wanted to retaliate against Kuwait for selling oil to Iran.
D)The interest Kuwait wanted to charge on its loans to Iraq was too high.
A)Iraq wanted to hide its weapons of mass destruction in Kuwait.
B)Kuwait was pumping more oil than the limit to which it had agreed,which decreased the price for Iraq's oil.
C)Iraq wanted to retaliate against Kuwait for selling oil to Iran.
D)The interest Kuwait wanted to charge on its loans to Iraq was too high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is an example of deterrence?
A)The Soviet Union cutting off trade with Western countries so that they could not use economic sanctions as leverage in arms agreements
B)The United States threatening to attack Iran if it did not cease developing nuclear weapons
C)The Soviet Union placing missiles in Cuba so that it could threaten the United States
D)China attacking when the United States sent troops into North Korea during the Korean War
A)The Soviet Union cutting off trade with Western countries so that they could not use economic sanctions as leverage in arms agreements
B)The United States threatening to attack Iran if it did not cease developing nuclear weapons
C)The Soviet Union placing missiles in Cuba so that it could threaten the United States
D)China attacking when the United States sent troops into North Korea during the Korean War

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A state's resolve is determined by:
A)the amount of resources it is willing to devote to its war effort.
B)whether it wins in the end.
C)the superiority of its armaments.
D)the quality of its military leadership.
A)the amount of resources it is willing to devote to its war effort.
B)whether it wins in the end.
C)the superiority of its armaments.
D)the quality of its military leadership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which is the best definition of total war?
A)A state mobilizes its entire military and economic resources.
B)Most of the states in the world are involved in the war.
C)Most of the states in one region are involved in the war.
D)The war results in at least 1,000 battle deaths.
A)A state mobilizes its entire military and economic resources.
B)Most of the states in the world are involved in the war.
C)Most of the states in one region are involved in the war.
D)The war results in at least 1,000 battle deaths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A risk-return trade-off is the idea that:
A)there is always a risk to selling weapons to other states.
B)states can get the best deal by threatening all-out war with another state.
C)states can reduce the risk of war during a crisis by returning diplomatic messages quickly.
D)states want to minimize the chance of war but also get the best deals they can.
A)there is always a risk to selling weapons to other states.
B)states can get the best deal by threatening all-out war with another state.
C)states can reduce the risk of war during a crisis by returning diplomatic messages quickly.
D)states want to minimize the chance of war but also get the best deals they can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a state has incomplete information,it could refer to:
A)uncertainty about an opponent's capabilities.
B)its reluctance to go to war.
C)doubts about an opponent's willingness to commit to a deal.
D)uncertainty about one's own preferences for war.
A)uncertainty about an opponent's capabilities.
B)its reluctance to go to war.
C)doubts about an opponent's willingness to commit to a deal.
D)uncertainty about one's own preferences for war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following explains the decline in interstate conflict?
A)States no longer have conflicting interests.
B)The United States has been actively deterring wars.
C)The high costs of World War I have been a deterrent.
D)International institutions have helped states overcome important bargaining problems.
A)States no longer have conflicting interests.
B)The United States has been actively deterring wars.
C)The high costs of World War I have been a deterrent.
D)International institutions have helped states overcome important bargaining problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the case of the threat by the United States to attack Afghanistan in 2001,the status quo was:
A)the attack by the United States on Afghanistan.
B)Taliban control of Afghanistan.
C)a continuing insurgency after the war.
D)the defeat of the Taliban.
A)the attack by the United States on Afghanistan.
B)Taliban control of Afghanistan.
C)a continuing insurgency after the war.
D)the defeat of the Taliban.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The United States did not believe China would intervene in the Korean War because:
A)the Chinese government had been an ally of the United States.
B)China had no apparent strategic interest in protecting North Korea.
C)China obviously lacked the capability to effectively launch an attack against U.S.troops.
D)the Chinese government did not pay any real cost in making the threat.
A)the Chinese government had been an ally of the United States.
B)China had no apparent strategic interest in protecting North Korea.
C)China obviously lacked the capability to effectively launch an attack against U.S.troops.
D)the Chinese government did not pay any real cost in making the threat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is an example of compellence?
A)The Soviet Union refusing to return control of the Kurile Islands to Japan
B)The United States invading the Dominican Republic in response to a military coup
C)The United States threatening Cuba if it did not remove Soviet missiles during the Cuban missile crisis
D)The Soviet Union threatening to attack Europe so that it could spread communism
A)The Soviet Union refusing to return control of the Kurile Islands to Japan
B)The United States invading the Dominican Republic in response to a military coup
C)The United States threatening Cuba if it did not remove Soviet missiles during the Cuban missile crisis
D)The Soviet Union threatening to attack Europe so that it could spread communism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why might the spread of democracy lead to an overall decline in war?
A)Democratic regimes tend to have more nuclear weapons.
B)Democratic states do not go to war with other states.
C)The transparency of democratic institutions can help reduce uncertainty about a state's resolve.
D)Democracies are more likely to bargain with rogue regimes.
A)Democratic regimes tend to have more nuclear weapons.
B)Democratic states do not go to war with other states.
C)The transparency of democratic institutions can help reduce uncertainty about a state's resolve.
D)Democracies are more likely to bargain with rogue regimes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Resolve is difficult to measure because it depends on:
A)the quality of a state's military training.
B)how much a state is willing to pay and risk in order to achieve a particular goal.
C)how much a state trusts the other side.
D)how well a state can obscure facts about its armies from opponents.
A)the quality of a state's military training.
B)how much a state is willing to pay and risk in order to achieve a particular goal.
C)how much a state trusts the other side.
D)how well a state can obscure facts about its armies from opponents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is a credible threat?
A)A threat that the target of the threat believes will be carried out
B)A threat made by a reliable ally
C)Any attempt to intimidate opponents by making threats
D)A threat that could possibly be carried out,even if it is unlikely
A)A threat that the target of the threat believes will be carried out
B)A threat made by a reliable ally
C)Any attempt to intimidate opponents by making threats
D)A threat that could possibly be carried out,even if it is unlikely

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements about compellence is true?
A)Compellence is an effort to preserve the status quo by threatening to use force.
B)Compellence is an effort to force other actors to accept international mediation.
C)Compellence is an effort to change the status quo by threatening to use force.
D)Compellence is the effort to force other actors to fulfill their alliance obligations.
A)Compellence is an effort to preserve the status quo by threatening to use force.
B)Compellence is an effort to force other actors to accept international mediation.
C)Compellence is an effort to change the status quo by threatening to use force.
D)Compellence is the effort to force other actors to fulfill their alliance obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During the Cuban missile crisis,the United States put nuclear missile crews on alert and took other advanced steps to prepare for war.This is an example of what?
A)Paying for power
B)Tying hands
C)Extended deterrence
D)Brinksmanship
A)Paying for power
B)Tying hands
C)Extended deterrence
D)Brinksmanship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why is it difficult to make a threat of attack seem credible to an opponent?
A)States are rarely capable of actually attacking other countries.
B)An opponent can often tell when the threatening state is bluffing.
C)Opponents have access to enough information about the other state to discredit its threats.
D)The threat of such a war can seem too costly to be a reasonable option.
A)States are rarely capable of actually attacking other countries.
B)An opponent can often tell when the threatening state is bluffing.
C)Opponents have access to enough information about the other state to discredit its threats.
D)The threat of such a war can seem too costly to be a reasonable option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How is extended deterrence different from general deterrence?
A)Extended deterrence continues for a long time.
B)Extended deterrence applies to a large amount of territory.
C)Extended deterrence applies to a state's allies rather than the state itself.
D)Extended deterrence applies to a country's economic,political,and military infrastructure.
A)Extended deterrence continues for a long time.
B)Extended deterrence applies to a large amount of territory.
C)Extended deterrence applies to a state's allies rather than the state itself.
D)Extended deterrence applies to a country's economic,political,and military infrastructure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements about deterrence is true?
A)Deterrence is an effort to preserve the status quo by threatening to use force.
B)Deterrence is an effort to force other actors to accept international mediation.
C)Deterrence is an effort to change the status quo by threatening to use force.
D)Deterrence is an effort to force other actors to fulfill their alliance obligations.
A)Deterrence is an effort to preserve the status quo by threatening to use force.
B)Deterrence is an effort to force other actors to accept international mediation.
C)Deterrence is an effort to change the status quo by threatening to use force.
D)Deterrence is an effort to force other actors to fulfill their alliance obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How did incomplete information cause Kuwait to make a mistake when Iraq threatened to attack in 1990?
A)Kuwait did not know that Saddam Hussein was willing to wage war and decided not to make sufficient concessions.
B)Kuwait did not know that Saddam Hussein had moved many of his troops to the border between Iraq and Kuwait.
C)Kuwait had decided to make the concessions that Saddam Hussein wanted,but the message to Iraq was not properly sent by Kuwaiti bureaucrats.
D)Kuwait did not know that the United States would come to its aid if a war was to occur.
A)Kuwait did not know that Saddam Hussein was willing to wage war and decided not to make sufficient concessions.
B)Kuwait did not know that Saddam Hussein had moved many of his troops to the border between Iraq and Kuwait.
C)Kuwait had decided to make the concessions that Saddam Hussein wanted,but the message to Iraq was not properly sent by Kuwaiti bureaucrats.
D)Kuwait did not know that the United States would come to its aid if a war was to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following describes a commitment problem?
A)A state cannot be trusted to abide by a deal it made when it was much weaker.
B)A state refuses to commit to signing a cease-fire.
C)Two states are uncertain about the capabilities of their adversaries.
D)A state is unsure of its adversary's willingness to go to war over a disputed good.
A)A state cannot be trusted to abide by a deal it made when it was much weaker.
B)A state refuses to commit to signing a cease-fire.
C)Two states are uncertain about the capabilities of their adversaries.
D)A state is unsure of its adversary's willingness to go to war over a disputed good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
To what does the term "issue indivisibility" refer?
A)The inability to divide a good without destroying its value
B)The belief that one side does not need to give any concessions on an issue
C)The idea that some issues are nonnegotiable
D)The idea that dividing an issue would make both sides worse off
A)The inability to divide a good without destroying its value
B)The belief that one side does not need to give any concessions on an issue
C)The idea that some issues are nonnegotiable
D)The idea that dividing an issue would make both sides worse off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is a preemptive war?
A)A war initiated by a state that anticipates an imminent attack from an adversary
B)A war initiated by a state that anticipates its adversary will become stronger in the future
C)A war initiated by a state when another state refuses to honor its alliance commitments
D)A defensive war fought by a state after it has suffered a surprise attack
A)A war initiated by a state that anticipates an imminent attack from an adversary
B)A war initiated by a state that anticipates its adversary will become stronger in the future
C)A war initiated by a state when another state refuses to honor its alliance commitments
D)A defensive war fought by a state after it has suffered a surprise attack

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is a first-strike advantage?
A)The benefits a state gains by being the first to attack
B)A state's ability to repel a surprise attack by another state
C)The tendency of smaller states to attack larger states first
D)The incentives offered to states that wait for other states to initiate wars
A)The benefits a state gains by being the first to attack
B)A state's ability to repel a surprise attack by another state
C)The tendency of smaller states to attack larger states first
D)The incentives offered to states that wait for other states to initiate wars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is an example of an indivisible good?
A)Whether a state has nuclear weapons
B)Control of a mountain range
C)Access to an oil field on the border of two states
D)Clean drinking water
A)Whether a state has nuclear weapons
B)Control of a mountain range
C)Access to an oil field on the border of two states
D)Clean drinking water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following accurately describes a security dilemma?
A)American efforts to topple the communist regime in North Korea
B)North Korea pursuing nuclear weapons in response to U.S.troops stationed in South Korea
C)A weak state's inability to protect itself from stronger states
D)Israel's threat to prevent Iran from developing nuclear weapons
A)American efforts to topple the communist regime in North Korea
B)North Korea pursuing nuclear weapons in response to U.S.troops stationed in South Korea
C)A weak state's inability to protect itself from stronger states
D)Israel's threat to prevent Iran from developing nuclear weapons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Why do states use brinksmanship?
A)States can signal a high level of resolve by making a threat that appears likely to trigger extraordinary costs.
B)States can make significant threats but know they will always be able to hold back from starting a war.
C)States know that there is no real possibility of a crisis escalating into a devastating nuclear war.
D)A state can pretend to be taking a tough stand to please domestic groups while secretly negotiating a peaceful settlement with other states.
A)States can signal a high level of resolve by making a threat that appears likely to trigger extraordinary costs.
B)States can make significant threats but know they will always be able to hold back from starting a war.
C)States know that there is no real possibility of a crisis escalating into a devastating nuclear war.
D)A state can pretend to be taking a tough stand to please domestic groups while secretly negotiating a peaceful settlement with other states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why might audience costs affect the possibility of war?
A)The states in a dispute may decide to hold secret negotiations so that privileged information will not become public.
B)Members of the United Nations Security Council may feel peer pressure to vote in favor of an intervention to prevent war.
C)An elected leader may make a threat and be compelled to carry it out in order to get reelected.
D)Third-party countries observing a conflict may decide to become involved.
A)The states in a dispute may decide to hold secret negotiations so that privileged information will not become public.
B)Members of the United Nations Security Council may feel peer pressure to vote in favor of an intervention to prevent war.
C)An elected leader may make a threat and be compelled to carry it out in order to get reelected.
D)Third-party countries observing a conflict may decide to become involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Why might preventive war appear attractive to a declining state?
A)A rising power will never agree to any bargain short of war.
B)A rising power will likely acquire WMD in the future,and preemption is the only way to stop them.
C)A rising power cannot credibly commit to not use increased power to make future demands.
D)A war now will eliminate the rising power from ever being a concern in the future.
A)A rising power will never agree to any bargain short of war.
B)A rising power will likely acquire WMD in the future,and preemption is the only way to stop them.
C)A rising power cannot credibly commit to not use increased power to make future demands.
D)A war now will eliminate the rising power from ever being a concern in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is a preventive war?
A)A war launched to prevent human rights abuses in another state
B)A war begun by a state to prevent an adversary from becoming a stronger threat in the future
C)A war launched by a state that fears an adversary is about to attack
D)A war authorized by an international organization to eliminate aggressive states that could threaten world peace
A)A war launched to prevent human rights abuses in another state
B)A war begun by a state to prevent an adversary from becoming a stronger threat in the future
C)A war launched by a state that fears an adversary is about to attack
D)A war authorized by an international organization to eliminate aggressive states that could threaten world peace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The commitment problem most resembles which type of bargaining game?
A)Prisoner's Dilemma
B)Stag Hunt
C)Battle of the Sexes
D)Chicken
A)Prisoner's Dilemma
B)Stag Hunt
C)Battle of the Sexes
D)Chicken

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why is bargaining over future power especially difficult in international relations?
A)States cannot anticipate how much power they may gain in the future.
B)States have secret sources of power that cannot be observed.
C)It is impossible to verify whether a state is abiding by such an agreement.
D)A state cannot make a credible commitment to not use increased power to make further demands.
A)States cannot anticipate how much power they may gain in the future.
B)States have secret sources of power that cannot be observed.
C)It is impossible to verify whether a state is abiding by such an agreement.
D)A state cannot make a credible commitment to not use increased power to make further demands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What do states hope to achieve by engaging in brinksmanship?
A)States want to demonstrate a commitment to bargaining.
B)States seek to generate audience costs.
C)States hope to demonstrate resolve.
D)States aim to gain an adversary's trust.
A)States want to demonstrate a commitment to bargaining.
B)States seek to generate audience costs.
C)States hope to demonstrate resolve.
D)States aim to gain an adversary's trust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A state covets a piece of territory that is valued at $100 million,yet it costs the state $40 million to attain it through war.How much must its adversary need to offer to make a peaceful settlement preferable to war?
A)At least $60 million
B)More than $100 million
C)At least $40 million
D)Exactly $100 million
A)At least $60 million
B)More than $100 million
C)At least $40 million
D)Exactly $100 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following problems make states more likely to go to war?
A)Problems arising from conflicts over goods that are easily split between two states
B)Problems arising from the difficulty of committing to honor a deal
C)Problems arising from international organizations forcing states to comply with an agreement
D)Problems arising from states with dissimilar amounts of power
A)Problems arising from conflicts over goods that are easily split between two states
B)Problems arising from the difficulty of committing to honor a deal
C)Problems arising from international organizations forcing states to comply with an agreement
D)Problems arising from states with dissimilar amounts of power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why might the city of Jerusalem be considered an indivisible good?
A)Israelis and Palestinians both claim the city as their capital.
B)The good concerned is territory,which is difficult to divide.
C)Neither side wants to give up any territory.
D)Jerusalem doesn't hold enough value to be divided and still be considered a good.
A)Israelis and Palestinians both claim the city as their capital.
B)The good concerned is territory,which is difficult to divide.
C)Neither side wants to give up any territory.
D)Jerusalem doesn't hold enough value to be divided and still be considered a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Why might states pay for power?
A)Because power is less costly than bargaining
B)To demonstrate its willingness to go to war,should bargaining fail
C)To gain allies
D)To demonstrate it is the wealthiest state in the system
A)Because power is less costly than bargaining
B)To demonstrate its willingness to go to war,should bargaining fail
C)To gain allies
D)To demonstrate it is the wealthiest state in the system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Linkages can help address issues of indivisibility by:
A)reminding states of other commitments they have made in the past.
B)threatening to tarnish a state's reputation if it does not abide by a deal.
C)increasing the number of states that care about a given issue.
D)creating other dimensions on which states can compromise.
A)reminding states of other commitments they have made in the past.
B)threatening to tarnish a state's reputation if it does not abide by a deal.
C)increasing the number of states that care about a given issue.
D)creating other dimensions on which states can compromise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Once the Soviet Union and the United States acquired large supplies of nuclear weapons,the chances of direct military conflict between the two decreased.This is an example of which way that states can reduce the likelihood of war occurring?
A)Increasing the costs of going to war
B)Increasing transparency
C)Increasing the number of actors involved in a conflict
D)Dividing apparently indivisible goods
A)Increasing the costs of going to war
B)Increasing transparency
C)Increasing the number of actors involved in a conflict
D)Dividing apparently indivisible goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is an example of tying hands?
A)A leader accompanying a threat with troop movements near the adversary's borders
B)A leader,during private negotiations,promising war if an adversary does not back down
C)An elected leader publicly promising war if an adversary does not back down
D)A leader accompanying a public threat with increased military spending
A)A leader accompanying a threat with troop movements near the adversary's borders
B)A leader,during private negotiations,promising war if an adversary does not back down
C)An elected leader publicly promising war if an adversary does not back down
D)A leader accompanying a public threat with increased military spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How can third parties help warring states overcome commitment problems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the difference between compellence and deterrence? Give an example of each (they can be fictional or from history)to illustrate the difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In general,are democratic or autocratic leaders more capable of "tying their hands"? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why have there been fewer conflicts over territory since the end of World War II?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why do states often go to war even when there is usually some division of a good that exists that is more preferable than war?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What are two possible ways that Israelis and Palestinians can reach a successful bargain over Jerusalem despite the seeming indivisibility of the territory?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Explain the risks and benefits of engaging in brinkmanship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the bargaining model of war? How does it explain why war occurs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the difference between a preemptive war and a preventive war?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How does poor and incomplete information contribute to the likelihood of war?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How can we make war less likely? In your answer,make sure to include a discussion of the costs of war,the credibility of commitments,and the divisibility of goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why is war a relatively rare occurrence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What makes a good indivisible,and how do indivisible goods affect the possibility of war?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How do commitment problems affect the likelihood that war will occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Describe three mechanisms that states can use to make their threats more credible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



