Deck 3: Solids, Fluids, Waves, Sound, Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Solids, Fluids, Waves, Sound, Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases
1
A standard atmosphere has a pressure versus altitude relation approximated by
? = Poe-?h,
With ? = 0.116 km-1. An aircraft flies at 30,000 ft but maintains a cabin pressure of that at
8000 ft. What force is exerted by air pressure on a square meter of cabin wall area?
A) 4.1 × 104 N
B) 124 N
C) 3.5 × 104 N
D) 7.6 × 104 N
? = Poe-?h,
With ? = 0.116 km-1. An aircraft flies at 30,000 ft but maintains a cabin pressure of that at
8000 ft. What force is exerted by air pressure on a square meter of cabin wall area?
A) 4.1 × 104 N
B) 124 N
C) 3.5 × 104 N
D) 7.6 × 104 N
4.1 × 104 N
2
How much would a lead brick 2.0 in × 2.0 in × 8.0 in weigh if placed in oil with density
? = 0.92 g/cm3? (?Pb = 11.4 g/cm3)
A) 5.5 kg
B) 0.34 kg
C) 6 kg
D) 0.48 kg
? = 0.92 g/cm3? (?Pb = 11.4 g/cm3)
A) 5.5 kg
B) 0.34 kg
C) 6 kg
D) 0.48 kg
5.5 kg
3
How many grams of ethanol (specific gravity 0.80) should be added to 5 grams of chloroform (specific gravity 1.50) if the resulting mixture is to have a specific gravity of 1.20?
A) 2.0 g
B) 2.4 g
C) 1.8 g
D) 4.4 g
E) 1.6 g
A) 2.0 g
B) 2.4 g
C) 1.8 g
D) 4.4 g
E) 1.6 g
2.0 g
4
Both the pressure and volume of a given sample of an ideal gas double. This means that its temperature in Kelvins must
A) double.
B) quadruple.
C) reduce to one-half its original value.
D) reduce to one-fourth its original value.
E) remain unchanged.
A) double.
B) quadruple.
C) reduce to one-half its original value.
D) reduce to one-fourth its original value.
E) remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the equation PV = NkT, the k is known as
A) Avogadro's number.
B) Boltzmann's constant.
C) Planck's constant.
D) the spring (compressibility) constant.
E) compressibility.
A) Avogadro's number.
B) Boltzmann's constant.
C) Planck's constant.
D) the spring (compressibility) constant.
E) compressibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Diffusion is described by
A) Boyle's law.
B) Kepler's law.
C) Charles' law.
D) Graham's law.
E) Archimedes' law.
A) Boyle's law.
B) Kepler's law.
C) Charles' law.
D) Graham's law.
E) Archimedes' law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An ideal gas at STP is first compressed until its volume is half the initial volume, and then it is allowed to expand until its pressure is half the initial pressure. All of this is done while holding the temperature constant. If the initial internal energy of the gas is U, the final internal energy of the gas will be
A) U.
B) 2U.
C) U/2.
D) U/3.
E) U/4.
A) U.
B) 2U.
C) U/2.
D) U/3.
E) U/4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Transverse waves propagate at 43.2 m/s in a string that is subjected to a tension of 60.5 N. If the string is 15.9 m long, what is its mass?
A) 0.515 kg
B) 0.216 kg
C) 0.366 kg
D) 0.597 kg
A) 0.515 kg
B) 0.216 kg
C) 0.366 kg
D) 0.597 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Find the displacement of a simple harmonic wave of amplitude 6.44 m at t = 0.71 s. Assume that the wave number is 2.34 m-1, the angular frequency is 2.88 rad/s, and that the wave is propagating in the +x direction at x = 1.21 m.
A) 4.55 m
B) 1.05 m
C) 3.54 m
D) 2.25 m
A) 4.55 m
B) 1.05 m
C) 3.54 m
D) 2.25 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 500.0 cm rope under a tension of 70.0 N is set into oscillation. The mass density of the rope is 120.0 g/cm. What is the frequency of the first harmonic mode (m = 2)?
A) 0.48 Hz
B) 2.92 Hz
C) 0.0048 Hz
D) 0.153 Hz
A) 0.48 Hz
B) 2.92 Hz
C) 0.0048 Hz
D) 0.153 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a false statement?
A) Sound waves are longitudinal pressure waves.
B) Sound can travel through vacuum.
C) The transverse waves on a vibrating string are different from sound waves.
D) Light travels very much faster than sound.
E) "Pitch" (in music) and frequency have approximately the same meaning.
A) Sound waves are longitudinal pressure waves.
B) Sound can travel through vacuum.
C) The transverse waves on a vibrating string are different from sound waves.
D) Light travels very much faster than sound.
E) "Pitch" (in music) and frequency have approximately the same meaning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If you were to inhale a few breaths from a helium gas balloon, you would probably experience an amusing change in your voice. You would sound like Donald Duck or Alvin the Chipmunk. What is the cause of this curious high-pitched effect?
A) The helium causes your vocal cords to tighten and vibrate at a higher frequency.
B) For a given frequency of vibration of your vocal cords, the wavelength of sound is less in helium than it is in air.
C) Your voice box is resonating at the second harmonic, rather than at the fundamental frequency.
D) Low frequencies are absorbed in helium gas, leaving the high frequency components, which result in the high, squeaky sound.
E) Sound travels faster in helium than in air at a given temperature.
A) The helium causes your vocal cords to tighten and vibrate at a higher frequency.
B) For a given frequency of vibration of your vocal cords, the wavelength of sound is less in helium than it is in air.
C) Your voice box is resonating at the second harmonic, rather than at the fundamental frequency.
D) Low frequencies are absorbed in helium gas, leaving the high frequency components, which result in the high, squeaky sound.
E) Sound travels faster in helium than in air at a given temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
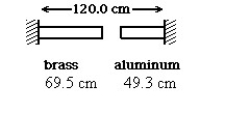 A brass rod is 69.5 cm long and an aluminum rod is 49.3 cm long when both rods are at an initial temperature of 0ºC. The rods are placed in line with a gap of 1.2 cm between them. The distance between the far ends of the rods is maintained at 120.0 cm throughout. The temperature is raised until the two rods are barely in contact. The coefficients of linear expansion of brass and aluminum are 2.0 × 10-5 K-1 and 2.4 × 10-5 K-1, respectively. In the figure, the temperature at which contact of the rods barely occurs, in °C, is closest to:
A brass rod is 69.5 cm long and an aluminum rod is 49.3 cm long when both rods are at an initial temperature of 0ºC. The rods are placed in line with a gap of 1.2 cm between them. The distance between the far ends of the rods is maintained at 120.0 cm throughout. The temperature is raised until the two rods are barely in contact. The coefficients of linear expansion of brass and aluminum are 2.0 × 10-5 K-1 and 2.4 × 10-5 K-1, respectively. In the figure, the temperature at which contact of the rods barely occurs, in °C, is closest to:A) 466
B) 443
C) 420
D) 490
E) 513

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the average kinetic energy of an ideal gas at 842 K? (The value of Boltzmann's constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K.)
A) 1.74 × 10-20 J
B) 5.81 × 10-21 J
C) 1.18 × 10-17 J
D) 3.93 × 10-19 J
A) 1.74 × 10-20 J
B) 5.81 × 10-21 J
C) 1.18 × 10-17 J
D) 3.93 × 10-19 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the total translational kinetic energy in a classroom filled with nitrogen at
1.01 × 105 Pa and 20.7ºC? The dimensions of the classroom are 4.60 m × 5.20 m × 8.80 m.
1.01 × 105 Pa and 20.7ºC? The dimensions of the classroom are 4.60 m × 5.20 m × 8.80 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



