A 76-year-old man with coronary artery disease comes to the office for follow-up 6 months after an uncomplicated coronary artery bypass surgery. The exertional chest pain that was bothering the patient before the surgery has completely resolved. He reports no palpitations, shortness of breath, light-headedness, or syncope. The patient has a history of hypertension, diet-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus, and gout. Medications include low-dose aspirin, metoprolol, and rosuvastatin. He has a 30-pack-year smoking history but quit 5 years ago. The patient does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Physical examination shows an irregular pulse. The chest surgical incision is well healed. There are no heart murmurs, and the lungs are clear on auscultation. There is no peripheral edema. ECG obtained in the office is shown in the exhibit. 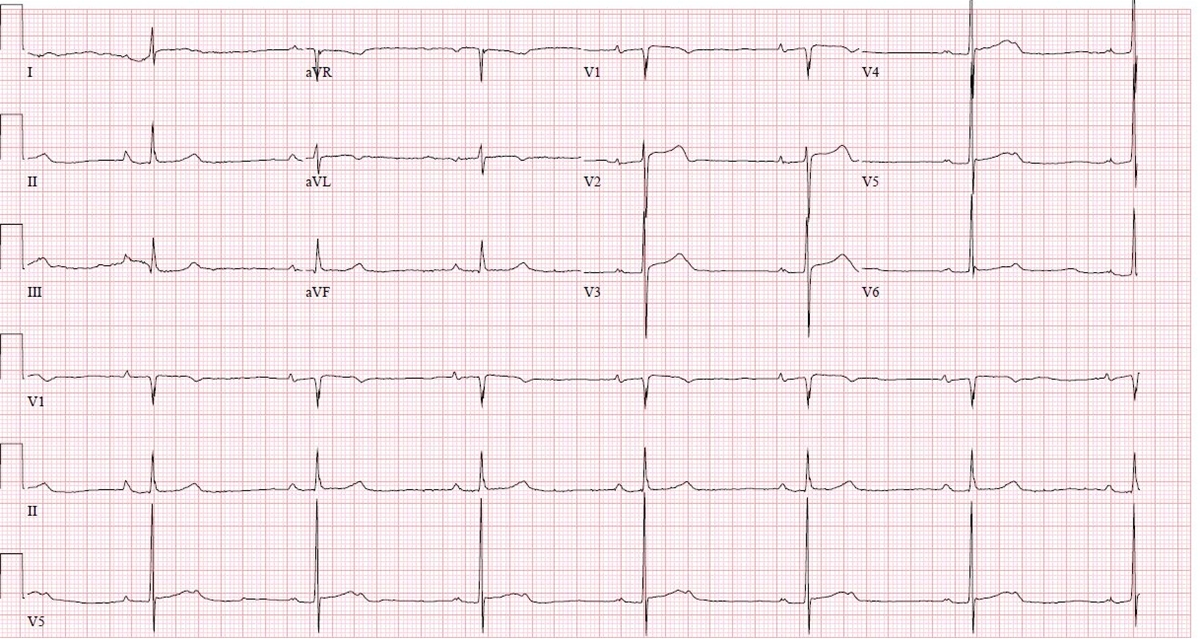
Which of the following is the best management for this patient?
A) Atrioventricular nodal slow pathway ablation
B) Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
C) Flecainide initiation
D) Oral anticoagulant therapy
E) Routine follow-up in 6 months
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: A group of investigators is studying the
Q2: A 46-year-old man comes to the physician
Q3: A study evaluated the relationship between the
Q4: A 68-year-old woman comes to the office
Q5: A group of investigators plans to conduct
Q7: A 65-year-old man is found to have
Q8: A prospective cohort study revealed a strong
Q9: A group of investigators conducted a randomized
Q10: An 82-year-old man comes to the office
Q11: A 44-year-old man comes to the office
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents