A 60-year-old man is found to have an incidental 3.5-cm abdominal aortic aneurysm on an imaging study. He has no associated symptoms. Past medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and hypothyroidism. His medications include aspirin, metformin, glipizide, chlorthalidone, lisinopril, atorvastatin, and levothyroxine. The patient has a 40-pack-year smoking history and continues to smoke 1-2 packs a day. He drinks 3 or 4 glasses of wine daily. His blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. Cardiopulmonary examination is within normal limits. Laboratory results are as follows: 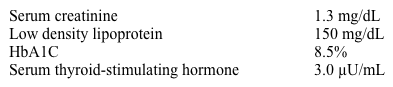 Which of the following interventions would most decrease the likelihood of expansion of this patient's aortic aneurysm?
Which of the following interventions would most decrease the likelihood of expansion of this patient's aortic aneurysm?
A) Aggressive diabetes management
B) Improved blood pressure control
C) Moderation of alcohol intake
D) Optimized hyperlipidemia treatment
E) Smoking cessation
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q42: A 68-year-old man is hospitalized after coronary
Q43: A 74-year-old hospitalized woman is seen for
Q44: A 68-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q45: A 76-year-old man is admitted to the
Q46: A 65-year-old man is brought to the
Q48: A 33-year-old, previously healthy woman is brought
Q49: A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q50: An 11-month-old girl is brought to the
Q51: A 66-year-old woman with systolic left ventricular
Q52: A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents