Passage
Of the biological factors impacting color perception in humans, one of the easiest to study is the number and type of color-sensitive photoreceptors. The human retina typically contains three types of cone photoreceptors, which contain opsin proteins that are sensitive to short (blue) , medium (green) , and long (red) wavelengths of light (Figure 1A) .The genes that encode for medium and long wavelength-sensitive opsin proteins are located on the X chromosome. Mutations in these genes often produce a variant cone type that responds to wavelengths overlapping the response range of one of the normal cone types, so color perception is unaltered (Figure 1B) . However, in a small percentage of women, the variant cone type appears to be sensitive to a range of wavelengths that differs from that of normal cone types (Figure 1C) . It is hypothesized that these "tetrachromatic" women may be able to distinguish more colors than can the normal trichromatic population.
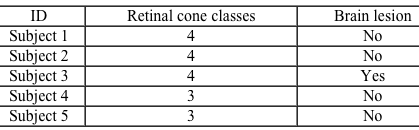
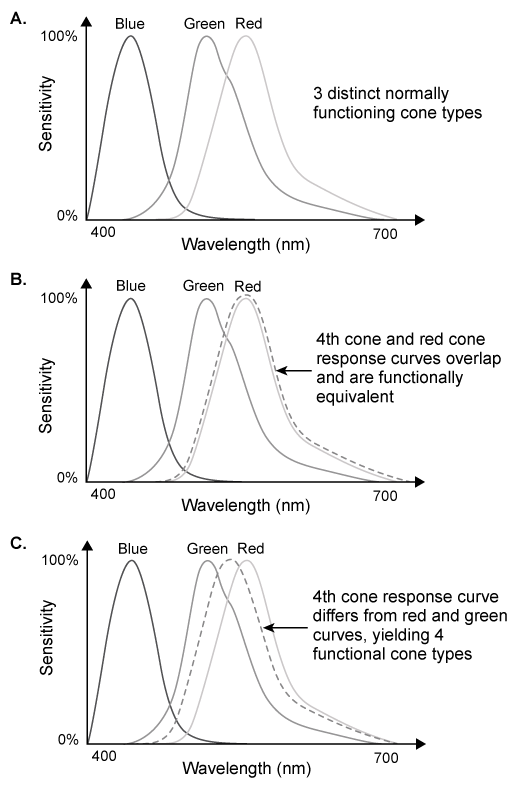 Figure 1 Response curves for (A) three cone types (trichromat, normal color perception) ; (B) four cone types (likely normal color perception) ; and (C) four cone types (tetrachromat, hypothesized enhanced color perception) A researcher conducted a series of tasks to assess the extent to which color perception of tetrachromatic subjects differs from that of trichromatic controls. Three women known to possess four retinal cone classes were recruited for the study. One of the women had experienced a small lesion to her right primary visual cortex the year prior. In addition, two women with normal trichromatic vision were recruited as controls (Table 1) .Table 1 Characteristics of Subjects
Figure 1 Response curves for (A) three cone types (trichromat, normal color perception) ; (B) four cone types (likely normal color perception) ; and (C) four cone types (tetrachromat, hypothesized enhanced color perception) A researcher conducted a series of tasks to assess the extent to which color perception of tetrachromatic subjects differs from that of trichromatic controls. Three women known to possess four retinal cone classes were recruited for the study. One of the women had experienced a small lesion to her right primary visual cortex the year prior. In addition, two women with normal trichromatic vision were recruited as controls (Table 1) .Table 1 Characteristics of Subjects
 In Task 1, participants identified the colors of objects that were stationary (artificial condition) and in motion (natural condition) . Under both conditions, the researcher systematically varied where the objects were presented in the subjects' visual field. Task 2 was a standardized, computer-administered color-discrimination task. Task 3 was an extensive interview that assessed the subjects' subjective experience of color.Subject 1 was able to identify more colors than the controls under all experimental conditions, and Subject 2 and Subject 3 performed marginally better than controls in some of the experimental conditions. Notably, only Subject 1 was able to verbalize her thoughts about her atypical color perception during Task 3, where she described seeing nuances in colors using words she had learned from her mother, who was also a tetrachromat and an artist. The researcher concluded that language likely plays a significant role in color perception: Without a vocabulary for the full variety of colors tetrachromats can perceive, they are limited in their perception despite their biological trait.
In Task 1, participants identified the colors of objects that were stationary (artificial condition) and in motion (natural condition) . Under both conditions, the researcher systematically varied where the objects were presented in the subjects' visual field. Task 2 was a standardized, computer-administered color-discrimination task. Task 3 was an extensive interview that assessed the subjects' subjective experience of color.Subject 1 was able to identify more colors than the controls under all experimental conditions, and Subject 2 and Subject 3 performed marginally better than controls in some of the experimental conditions. Notably, only Subject 1 was able to verbalize her thoughts about her atypical color perception during Task 3, where she described seeing nuances in colors using words she had learned from her mother, who was also a tetrachromat and an artist. The researcher concluded that language likely plays a significant role in color perception: Without a vocabulary for the full variety of colors tetrachromats can perceive, they are limited in their perception despite their biological trait.
S. S. Deeb ©2005 John Wiley & Sons; K. A. Jameson, A. D. Winkler, and K. Goldfarb ©2016 IS&T International Symposium on Electronic Imaging.
-Subject 3 would NOT be able to perceive visual stimuli presented:
A) to the far left of her central fixation point.
B) to the far right of her central fixation point.
C) just above her central fixation point.
D) just below her central fixation point.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q35: Passage
Lucid dreaming occurs when a person becomes
Q36: Passage
Language is a skill acquired during early
Q37: Passage
Numerous studies suggest that physicians make both
Q38: Passage
Of the biological factors impacting color perception
Q39: Passage
Numerous studies suggest that physicians make both
Q41: Passage
Before memories have been consolidated they are
Q42: Passage
Across the lifespan, mental and physical health
Q43: Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can
Q44: Passage
Before memories have been consolidated they are
Q45: Passage
Across the lifespan, mental and physical health
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents