Passage
Antimicrobial peptides are an important component of innate immunity. Since their discovery in 1939, over 5,000 peptides with antimicrobial properties have been isolated from organisms in every domain of life. They have demonstrated activity against enveloped viruses, bacteria, fungi, and even tumor cells and have recently gained interest for their potential in fighting antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Most known antimicrobial peptides are positively charged, but some with negative charges have also been discovered.Frogs are known to secrete a variety of antimicrobial peptides as a major source of immunity. Secretions from a new species of frog were collected and the peptides were separated by cation exchange chromatography. Four of the isolated peptides demonstrated strong antibacterial activity and were characterized by isoelectric focusing and sequencing:
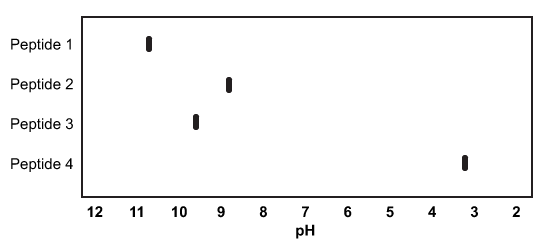 Figure 1 Results of isoelectric focusing of four antimicrobial peptidesTable 1 Amino Acid Compositions of Four Antimicrobial Peptides
Figure 1 Results of isoelectric focusing of four antimicrobial peptidesTable 1 Amino Acid Compositions of Four Antimicrobial Peptides
 Adapted from Wang Z, Wang G. APD: the Antimicrobial Peptide Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(Database issue) :D590-2.
Adapted from Wang Z, Wang G. APD: the Antimicrobial Peptide Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(Database issue) :D590-2.
-One of the challenges of antimicrobial peptides is their short physiological half-life. To solve this problem, some researchers have begun investigating synthetic antimicrobial peptides composed of D-amino acids. Why might these peptides have an increased half-life in the body relative to natural antimicrobial peptides?
A) Proteases cannot act on peptides made of D-amino acids.
B) D-amino acids are more soluble at physiological pH.
C) Peptide bonds between D-amino acids require more energy to break.
D) Hydrolysis of D-peptides is catalyzed by acids instead of bases.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q37: Passage
The bacterium Clostridium difficile secretes protein toxins
Q38: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q39: Passage
The liver plays a central role in
Q40: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q41: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q43: Passage
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) is essential for
Q44: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q45: Passage
Antimicrobial peptides are an important component of
Q46: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q47: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents