Passage
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) is essential for the oxidation of toxic aldehydes, and uses NAD+ as the oxidizing agent. Mitochondrial ALDH2 exists as a 220-kD homotetrameric protein containing a catalytic, nucleotide-binding, and coenzyme-binding domain. The most prevalent ALDH2 mutation (ALDH2*2) involves an E to K (E478K) substitution in the catalytic domain that leads to decreased enzymatic activity.Scientists hypothesize that Asian populations have higher rates of ALDH2*2 incidence. The properties of ALDH2 variants in Caucasian and Japanese populations were analyzed in the following experiments.Experiment 1Mitochondrial extracts from both populations were combined in a single mixture and separated by native gel electrophoresis. Proteins 210-230 kD in size were removed from the agarose gel and further isolated using affinity columns with antibodies designed to separate wild-type ALDH2 from ALDH2*2 by binding the catalytic domain of the wild-type but not the mutant protein. Concentrated eluates E1 and E2 were produced by washing the affinity columns with buffers that remove unbound proteins and dislodge bound proteins from antibodies, respectively (Figure 1) .
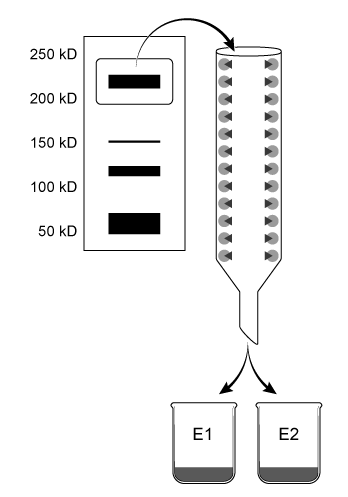 Figure 1 Purification of ALDH2 proteinsALDH2 activity in each eluate was quantified by adding acetaldehyde and NAD+, and then monitoring the rate of NADH production. The results are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1 Purification of ALDH2 proteinsALDH2 activity in each eluate was quantified by adding acetaldehyde and NAD+, and then monitoring the rate of NADH production. The results are shown in Figure 2.
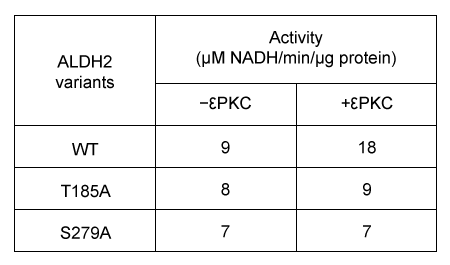
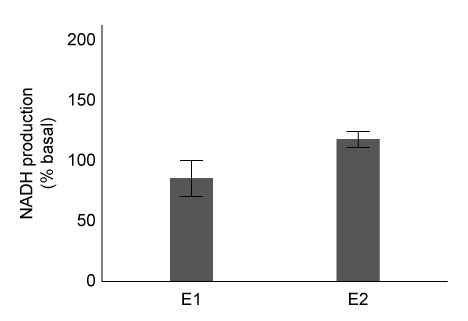 Figure 2 Enzymatic activity of E1 and E2 eluatesExperiment 2Researchers predict that mutations at conserved amino acid sites containing S or T may prevent ALDH2 from being phosphorylated by protein kinase C epsilon (εPKC) . The activity of wild-type ALDH2 (WT) and ALDH2 mutants with substitutions at positions T185 and S279 in the presence or absence of εPKC are summarized in Table 1.Table 1 Effect of εPKC on ALDH2 Variants
Figure 2 Enzymatic activity of E1 and E2 eluatesExperiment 2Researchers predict that mutations at conserved amino acid sites containing S or T may prevent ALDH2 from being phosphorylated by protein kinase C epsilon (εPKC) . The activity of wild-type ALDH2 (WT) and ALDH2 mutants with substitutions at positions T185 and S279 in the presence or absence of εPKC are summarized in Table 1.Table 1 Effect of εPKC on ALDH2 Variants
 Adapted from Chen CH, Ferreira JC, Gross ER, Mochly-rosen D. Targeting aldehyde dehydrogenase 2: new therapeutic opportunities. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(1) :1-34.
Adapted from Chen CH, Ferreira JC, Gross ER, Mochly-rosen D. Targeting aldehyde dehydrogenase 2: new therapeutic opportunities. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(1) :1-34.
-Replacing native gel electrophoresis with nonreducing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) during the purification step results in eluates with no enzymatic activity. The best explanation of this observation would be:
A) ALDH2 must retain its quaternary structure to catalyze reactions.
B) the SDS-PAGE breaks disulfide bonds between ALDH2 subunits.
C) ALDH2 has the mobility of a 55-kD protein in native PAGE.
D) the primary structure of the ALDH2 active site has been modified.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q38: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q39: Passage
The liver plays a central role in
Q40: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q41: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q42: Passage
Antimicrobial peptides are an important component of
Q44: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q45: Passage
Antimicrobial peptides are an important component of
Q46: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q47: Passage
The tumor suppressor p53 is a homotetrameric
Q48: Passage
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) is essential for
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents