Passage
Upon entering muscle cells, glucose is immediately phosphorylated by hexokinase to produce glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) . This phosphorylation event prevents glucose from exiting the cell. G6P may then enter one of three metabolic pathways, depending on the needs of the cell (Figure 1) .
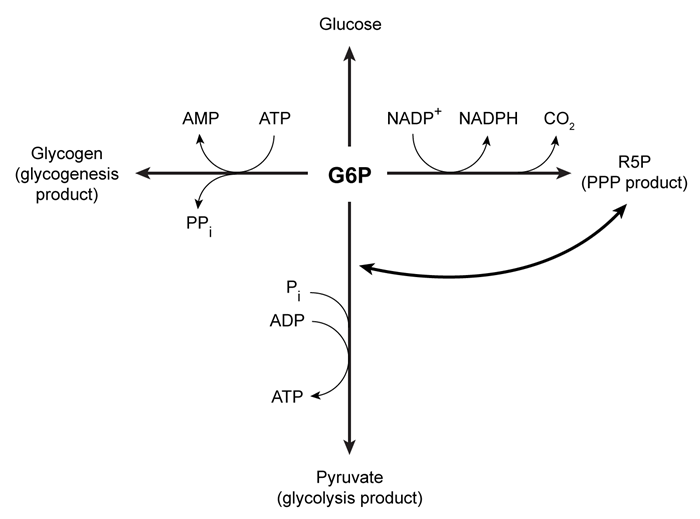 Figure 1 Three potential fates of G6P, determined by the needs of the cellUnder low ATP conditions, G6P enters glycolysis, where it is converted to two pyruvate molecules. The energy released in this process produces a net total of two ATP molecules per glucose molecule consumed. The resulting pyruvate molecules can then enter the mitochondria, where they participate in additional metabolic reactions that produce more ATP.When the cell experiences oxidative stress, G6P enters the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) and produces NADPH, a reducing agent. During this process, G6P loses one carbon atom in the form of CO2 and is converted to ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) , which is required for nucleotide synthesis. In addition to low NADPH conditions, G6P may also enter the PPP during replication, when nucleotides are needed for DNA synthesis. If nucleotides are not needed but energy is, R5P can be converted back to glycolytic intermediates and reenter glycolysis. Each glucose molecule that is converted to R5P prior to glycolysis yields an average of 1.67 ATP molecules.When all the cell's metabolic requirements are met, additional G6P can enter glycogenesis and produce glycogen, which stores glucose for later use; this process consumes ATP. When signal molecules bind G protein-coupled receptors on muscle cells, glycogenolysis is activated to release individual monomers from glycogen, allowing them to enter the appropriate pathway.
Figure 1 Three potential fates of G6P, determined by the needs of the cellUnder low ATP conditions, G6P enters glycolysis, where it is converted to two pyruvate molecules. The energy released in this process produces a net total of two ATP molecules per glucose molecule consumed. The resulting pyruvate molecules can then enter the mitochondria, where they participate in additional metabolic reactions that produce more ATP.When the cell experiences oxidative stress, G6P enters the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) and produces NADPH, a reducing agent. During this process, G6P loses one carbon atom in the form of CO2 and is converted to ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) , which is required for nucleotide synthesis. In addition to low NADPH conditions, G6P may also enter the PPP during replication, when nucleotides are needed for DNA synthesis. If nucleotides are not needed but energy is, R5P can be converted back to glycolytic intermediates and reenter glycolysis. Each glucose molecule that is converted to R5P prior to glycolysis yields an average of 1.67 ATP molecules.When all the cell's metabolic requirements are met, additional G6P can enter glycogenesis and produce glycogen, which stores glucose for later use; this process consumes ATP. When signal molecules bind G protein-coupled receptors on muscle cells, glycogenolysis is activated to release individual monomers from glycogen, allowing them to enter the appropriate pathway.
-When the cell is in need of glucose, glycogenolysis is upregulated, beginning with the activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the production of which of the following molecules?
A) UDP-glucose
B) UDP-galactose
C) Glucose 1-phosphate
D) Glucose 6-phosphate
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q72: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Q73: Passage
Although the structure of the cell membrane
Q74: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Q75: Passage
Although the structure of the cell membrane
Q76: Passage
Although the structure of the cell membrane
Q78: Passage
Although the structure of the cell membrane
Q79: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Q80: Passage
Upon entering muscle cells, glucose is immediately
Q81: Passage
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) is one of the
Q82: Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME), or chronic fatigue syndrome
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents