Passage
Although the structure of the cell membrane has been investigated repeatedly, few studies examine the contribution of its lipid components. Lipid composition influences the fluidity and permeability of cell membranes in the human body. Chronic diseases such as atherosclerosis and psoriasis arise from alterations to the lipid composition.Atherosclerosis is caused by the accumulation of cholesterol in the endothelial cells lining the arterial wall. Cholesterol carried by low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is deposited into cell membranes, where it forms cholesterol crystalline domains (CCDs) . In damaged cells, these CCDs increase membrane permeability and contribute to the formation of cholesterol plaques that can potentially block the artery itself.Omega-3 fatty acids (O3FAs) derived from marine animals may be used to slow the development of atherosclerosis. Formulations of O3FA contain varying concentrations of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (Figure 1) . Present research suggests that formulations of O3FA should contain EPA exclusively because it prevents cholesterol from organizing into CCDs. Nonetheless, atherosclerosis is generally treated by administering drugs referred to as statins, which decrease the free cholesterol in blood plasma by inhibiting the production of a cholesterol precursor. Statin therapy combined with O3FAs may be used to reduce atherosclerosis in patients with persistent hypertriglyceridemia (high triglyceride plasma levels) .
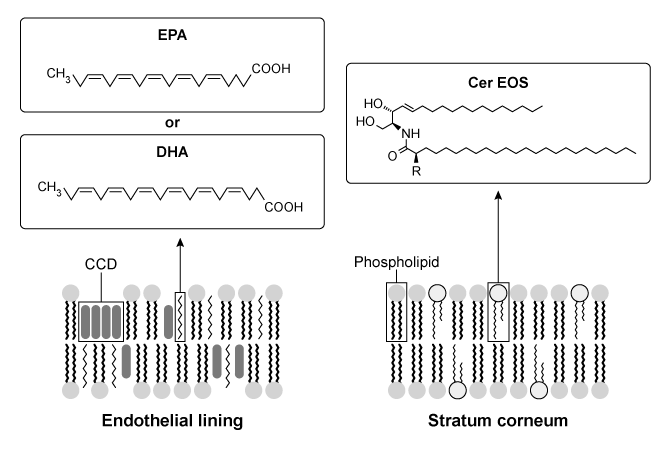 Figure 1 Organization of membranes in endothelial and epidermal cellsWater loss from the uppermost layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum (SC) , is prevented by specialized lipids called ceramides (cer) . Psoriasis is a skin disease in which the permeability of the SC is compromised due to a significant decrease in the level of ceramides. The scarcity of ceramides impedes the formation of a lipid matrix called the long periodicity phase (LPP) in the cell membrane. Increasing the concentration of ceramides such as esterified omega-hydroxyacyl-sphingosine (cer-EOS) has been shown to reduce the permeability of SC cell membranes and may be used to treat psoriasis scabs (Figure 1) .
Figure 1 Organization of membranes in endothelial and epidermal cellsWater loss from the uppermost layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum (SC) , is prevented by specialized lipids called ceramides (cer) . Psoriasis is a skin disease in which the permeability of the SC is compromised due to a significant decrease in the level of ceramides. The scarcity of ceramides impedes the formation of a lipid matrix called the long periodicity phase (LPP) in the cell membrane. Increasing the concentration of ceramides such as esterified omega-hydroxyacyl-sphingosine (cer-EOS) has been shown to reduce the permeability of SC cell membranes and may be used to treat psoriasis scabs (Figure 1) .
Adapted from Mason RP, Jacob RF, Shrivastava S, Sherratt SC, Chattopadhyay A. Eicosapentaenoic acid reduces membrane fluidity, inhibits cholesterol domain formation, and normalizes bilayer width in atherosclerotic-like model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1858(12) :3131-3140.
-What structural feature in the molecules shown in Figure 1 would result in the greatest increase in cell membrane fluidity?
A) cis bond in EPA
B) trans bond in cer-EOS
C) Carboxyl group of DHA
D) Phosphate groups of phospholipids
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q62: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q63: Passage
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) is one of the
Q64: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Q65: Passage
Upon entering muscle cells, glucose is immediately
Q66: Passage
Upon entering muscle cells, glucose is immediately
Q68: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Q69: Passage
Although the structure of the cell membrane
Q70: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Q71: Passage
Upon entering muscle cells, glucose is immediately
Q72: Passage
Dystroglycan (Dg) is a transmembrane protein that
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents