Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME) , or chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) , is a physiological disease that affects 0.15% of the human population. Compared with healthy individuals, persons with ME experience reduced phospholipid levels, muscular degeneration, urinary urgency, and other symptoms that contribute to a lower quality of life. Studies in resting subjects have yielded inconsistent data and failed to identify a unique metabolic defect in patients with ME.Analyzing the blood plasma of male and female patients with ME, physicians have observed that male patients display elevated levels of 3-methylhistidine, a marker of protein catabolism. Researchers expanded this finding by measuring the serum concentration of amino acids in blood samples obtained from nonfasting ME patients and healthy controls. Amino acids were classified into separate categories according to their metabolic intermediates.Table 1 Classification of Amino Acids in Blood Plasma
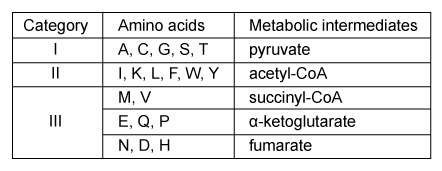
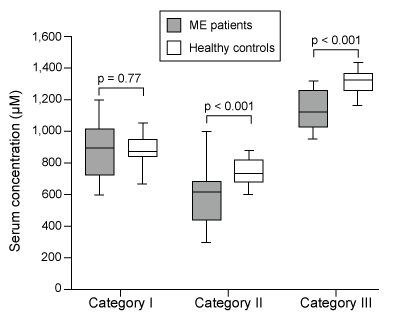 Figure 1 Serum concentrations of amino acids in patients with ME and healthy controls (HC) Next, researchers hypothesized that the inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and impairment of fatty acid oxidation were responsible for the fluctuations in amino acid levels. PDH function and lipid metabolism were studied in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by measuring the gene expression of proteins within regulatory pathways. Researchers monitored the mRNA levels of the inhibitor pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) and of sirtuin 4 (SIRT4) , which removes lipoic acid groups from the PDH complex. They also examined lipid metabolism by measuring the mRNA levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) , a transcription factor that upregulates the uptake of fatty acids. The mRNA level of each protein in PBMCs of patients with ME was evaluated against healthy controls, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1 Serum concentrations of amino acids in patients with ME and healthy controls (HC) Next, researchers hypothesized that the inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and impairment of fatty acid oxidation were responsible for the fluctuations in amino acid levels. PDH function and lipid metabolism were studied in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by measuring the gene expression of proteins within regulatory pathways. Researchers monitored the mRNA levels of the inhibitor pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) and of sirtuin 4 (SIRT4) , which removes lipoic acid groups from the PDH complex. They also examined lipid metabolism by measuring the mRNA levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) , a transcription factor that upregulates the uptake of fatty acids. The mRNA level of each protein in PBMCs of patients with ME was evaluated against healthy controls, as shown in Figure 2.
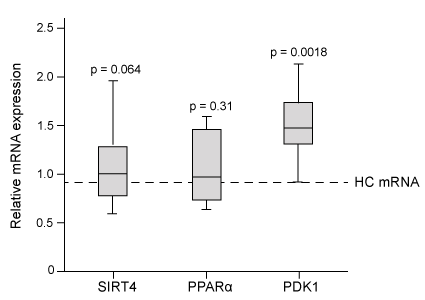 Figure 2 Gene expression of PDK1, SIRT4, and PPARα in PBMCs
Figure 2 Gene expression of PDK1, SIRT4, and PPARα in PBMCs
Adapted from Fluge Ø, Mella O, Bruland O, et al.. JCI Insight. 2016;1(21) :e89376.
-Extended periods of physical exertion in patients with ME result in the conversion of glycine and cysteine to which of the following compounds?
A) Fumarate
B) Lactate
C) Glucose
D) Isocitrate
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q90: Passage
Synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) requires vitamin
Q91: Two possible mechanisms, shown below, were designed
Q92: Passage
Synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) requires vitamin
Q93: Activity assays were performed to determine the
Q94: Passage
Synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) requires vitamin
Q96: Studies on the catalytic activity of hexokinase
Q97: Acetylation of lysine residues in histones increases
Q98: Passage
Synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) requires vitamin
Q99: Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME), or chronic fatigue syndrome
Q100: Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME), or chronic fatigue syndrome
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents