Passage
Synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) requires vitamin B5 as a substrate. In bacteria, vitamin B5 is synthesized by condensation of β-alanine and pantoic acid. β-alanine is produced by decarboxylation of L-aspartate, mediated by the enzyme aspartate α-decarboxylase (ADC) . Active ADC is formed when its inactive precursor, PanD, binds to a regulatory complex composed of acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) and a protein known as PanZ. Formation of the PanD-PanZ-AcCoA complex causes the activation loop of PanD to fold into a β-pleated sheet, resulting in PanD autocleavage. Researchers hypothesize that this conformational change allows the Thr57 residue to cleave the N-terminal end of PanD to form ADC.The limited information on the role of PanZ in the synthesis of CoA has stimulated an investigation of its effect on ADC activity. Escherichia coli cells were provided with varying concentrations of PanZ, and the rate of β-alanine production was measured in three different conditions (Figure 1) . Reaction vessels were maintained at pH 6 to ensure optimal decarboxylation activity.
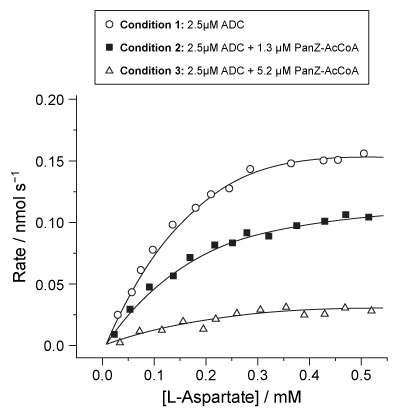 Figure 1 Catalytic activity of ADC in E. coli with increasing concentrations of L-aspartate
Figure 1 Catalytic activity of ADC in E. coli with increasing concentrations of L-aspartate
Adapted from Monteiro DC, Patel V, Bartlett CP, et al. The structure of the PanD/PanZ protein complex reveals negative feedback regulation of pantothenate biosynthesis by coenzyme A. Chem Biol. 2015;22(4) :492-503.
-ADC isolated from the Gram-negative bacteria Alcaligenes faecalis showed a sigmoidal dependence on L-aspartate concentration. Which of the following could be the Hill coefficient for this form of ADC?
A) 0
B) 0.5
C) 1
D) 2
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q93: Activity assays were performed to determine the
Q94: Passage
Synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) requires vitamin
Q95: Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME), or chronic fatigue syndrome
Q96: Studies on the catalytic activity of hexokinase
Q97: Acetylation of lysine residues in histones increases
Q99: Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME), or chronic fatigue syndrome
Q100: Passage
Myalgic encephalopathy (ME), or chronic fatigue syndrome
Q101: Passage
ATP synthase, also known as Complex V,
Q102: Passage
A newborn girl is diagnosed with a
Q103: Passage
Human gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (hGGT) is an enzyme
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents