Passage
The sirtuins are a class of enzymes that regulate various metabolic processes by removing post-translational modifications from enzymes. SIRT4 is an autosomally encoded sirtuin protein that colocalizes with the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. It deacylates lysine residues on certain metabolic proteins by removing methylglutaryl and hydroxymethylglutaryl units. Methylglutaryl-CoA and hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA are intermediates in leucine catabolism, and scientists hypothesized that SIRT4 regulates this pathway. To test their hypothesis, livers from wild-type (WT) and SIRT4 knockout (KO) mice were treated with α-keto acid derivatives of several amino acids, including the derivative of leucine, α-ketoisocaproate (αKIC) . Figures 1 and 2 show the rate of oxidation of α-keto acids and oxygen consumption in both WT and KO livers, respectively.
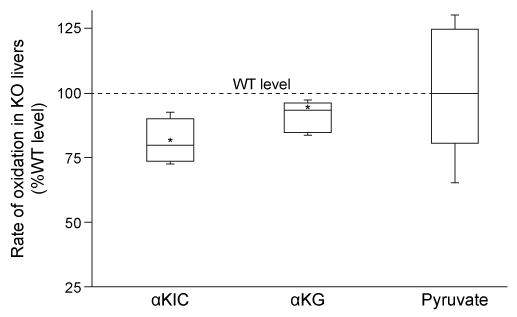 Figure 1 Box plot showing the rate of oxidation of α-ketoisocaproate (αKIC) , α-ketoglutarate (αKG) , and pyruvate in SIRT4 knockout livers (Note: Asterisk indicates p < 0.05 relative to WT level)
Figure 1 Box plot showing the rate of oxidation of α-ketoisocaproate (αKIC) , α-ketoglutarate (αKG) , and pyruvate in SIRT4 knockout livers (Note: Asterisk indicates p < 0.05 relative to WT level)
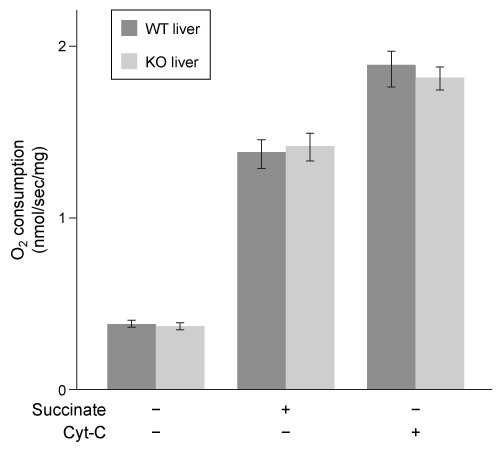 Figure 2 Oxygen consumption in WT and KO livers in the presence and absence of succinate and reduced cytochrome C (Cyt-C) Because leucine is known to regulate insulin secretion, scientists injected WT and KO mice with leucine and measured plasma insulin levels over time. They then injected mice with insulin and monitored blood glucose levels (Figure 3) .
Figure 2 Oxygen consumption in WT and KO livers in the presence and absence of succinate and reduced cytochrome C (Cyt-C) Because leucine is known to regulate insulin secretion, scientists injected WT and KO mice with leucine and measured plasma insulin levels over time. They then injected mice with insulin and monitored blood glucose levels (Figure 3) .
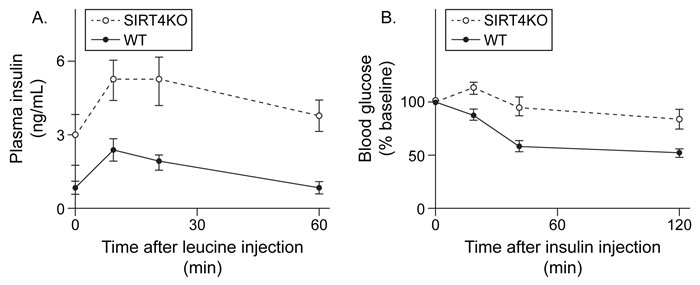 Figure 3 (A) Plasma insulin levels after injection with leucine and (B) blood glucose levels after injection with insulin in both WT and KO mice
Figure 3 (A) Plasma insulin levels after injection with leucine and (B) blood glucose levels after injection with insulin in both WT and KO mice
Adapted from Anderson KA, Huynh FK, Fisher-Wellman K, et al. SIRT4 Is a Lysine Deacylase that Controls Leucine Metabolism and Insulin Secretion. Cell Metab. 2017;25(4) :838-855.e15.
-In the absence of SIRT4, the electrochemical potential across the inner mitochondrial membrane:
A) is increased relative to mitochondria in the presence of SIRT4.
B) is decreased relative to mitochondria in the presence of SIRT4.
C) is not changed relative to mitochondria in the presence of SIRT4.
D) is increased relative to mitochondria with SIRT4 only when Cyt-C is added.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q230: Passage
Physical activity produces an increased energy requirement
Q231: Passage
Many cephalopods can change color to blend
Q232: Passage
The ABO blood groups are determined by
Q233: Passage
The ABO blood groups are determined by
Q234: Passage
The sirtuins are a class of enzymes
Q236: Passage
Many cephalopods can change color to blend
Q237: In the electron transport chain, four electrons
Q238: A certain enzyme uses Mn2+ as a
Q239: Passage
The ABO blood groups are determined by
Q240: Passage
Physical activity produces an increased energy requirement
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents