Passage
The lumen of the human gut is lined by a monolayer of epithelial cells that acts as a selectively permeable barrier, preventing the passage of harmful intraluminal foreign antigens, flora, and toxins into the circulation while allowing digestion and absorption of essential dietary nutrients along with the transfer of electrolytes and water.Proteins in the tight junctions of intestinal epithelial cells maintain barrier integrity, but barrier dysfunction occurs when these cells are damaged in the setting of infection, burns, shock, or hypoxia (low oxygen levels) . The transcription factor HIF-1, a heterodimer composed of the macromolecules HIF-1α and HIF-1β, regulates the adaptive cellular response to hypoxia and the consequent expression of tight junction proteins.Researchers assessed the concentration of HIF-1 heterodimer components in human intestinal Caco-2 cells subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) in vitro. Caco-2 cells, a colon-derived cell line, were cultured under specific conditions to mimic the functional and morphological phenotype of wild-type enterocytes lining the small intestine. These cells were prepared and grown as a monolayer on a collagen-coated membrane.Next, the monolayer was cultured in hypoxic conditions and then exposed to atmospheric oxygen levels (normoxia) for 30, 60, and 120 minutes. Protein levels were quantified using direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) , in which an antibody linked to a reporter enzyme was utilized to bind and detect expression of the target molecule (analyte) in a sample. When the colorless substrate of the reporter enzyme was added, the enzyme generated a visible colored product that could be quantified based on color intensity.
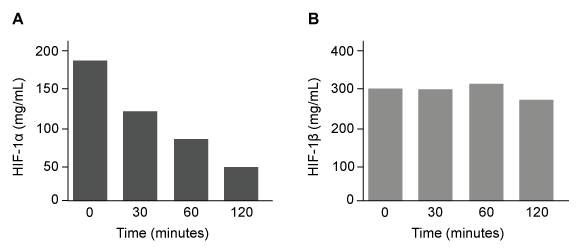 Figure 1 Concentration of (A) HIF-1α and (B) HIF-1β in Caco-2 cells subjected to H/R (Note: 0 minutes = cells cultured in hypoxic conditions) Emodin, an anthraquinone compound that prevents hypoxia-induced epithelial cell disruption, was used in conjunction with a chemical HIF-1α inhibitor (HIF-1α-I) to treat Caco-2 cells in a separate experiment. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was assessed as a measure of barrier function, with higher TEER values indicating a more intact epithelial cell barrier. HIF-1α-I was found to block emodin's protective effect on epithelial barrier integrity.
Figure 1 Concentration of (A) HIF-1α and (B) HIF-1β in Caco-2 cells subjected to H/R (Note: 0 minutes = cells cultured in hypoxic conditions) Emodin, an anthraquinone compound that prevents hypoxia-induced epithelial cell disruption, was used in conjunction with a chemical HIF-1α inhibitor (HIF-1α-I) to treat Caco-2 cells in a separate experiment. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was assessed as a measure of barrier function, with higher TEER values indicating a more intact epithelial cell barrier. HIF-1α-I was found to block emodin's protective effect on epithelial barrier integrity.
Adapted from Lei Q, Qiang F, Chao D, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(6) :1629-39.
-Which graphic depicts the most likely effect of the HIF-1α inhibitor on emodin? (Note: control = cells cultured under normoxic conditions.)
A) 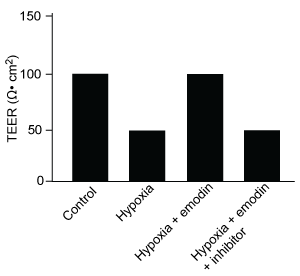
B) 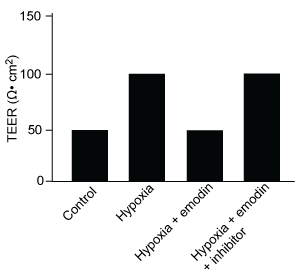
C) 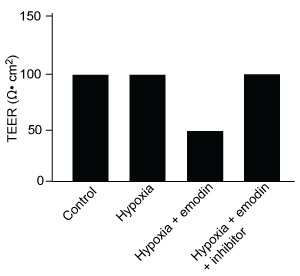
D) 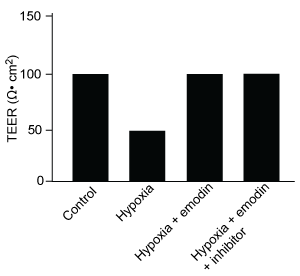
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q10: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q11: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q12: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q13: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q14: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q16: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q17: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q18: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q19: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q20: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents