Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is used to study the movement of molecules in live cells. During FRAP, the fluorescence of a green fluorescent protein (GFP) -tagged molecule is first measured and then photodestroyed in targeted cell regions. Researchers then assess the time course for fluorescence recovery, which is an indicator of molecular mobility of the GFP-tagged protein into the photodestroyed region. The average time required to recover 80% of the pre-bleach fluorescence of protein histone 1 (H1) fused to GFP (H1-GFP) in the photodestroyed region is given as t80.FRAP was used to analyze the mobility of the architectural H1 alone and in the presence of high-mobility group (HMG) proteins. HMG proteins are dynamic modifiers that have been shown to have opposite effects but similar binding sites on chromatin structure.
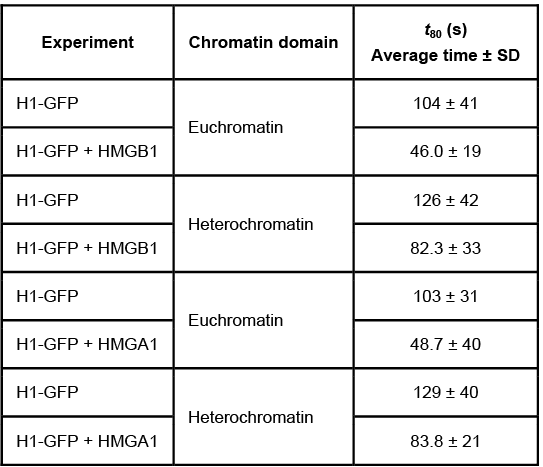
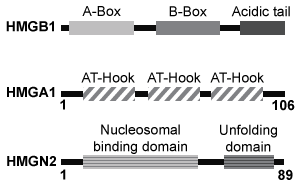 Figure 1 Unique chromatin binding motifs of HMG proteinsDuring analysis, HMGA1 and HMGB1 were microinjected into the cytoplasm of mouse embryonic fibroblast cells expressing H1-GFP. FRAP was performed on euchromatin and heterochromatin. Euchromatin and heterochromatin domains were identified as regions weakly and strongly stained by H1-GFP, respectively. The relative intensity of H1-GFP fluorescence in euchromatin and heterochromatin of uninjected and injected cells was assessed, and t80 results are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Effect of HMGB1 and HMGA1 on H1-GFP Mobility
Figure 1 Unique chromatin binding motifs of HMG proteinsDuring analysis, HMGA1 and HMGB1 were microinjected into the cytoplasm of mouse embryonic fibroblast cells expressing H1-GFP. FRAP was performed on euchromatin and heterochromatin. Euchromatin and heterochromatin domains were identified as regions weakly and strongly stained by H1-GFP, respectively. The relative intensity of H1-GFP fluorescence in euchromatin and heterochromatin of uninjected and injected cells was assessed, and t80 results are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Effect of HMGB1 and HMGA1 on H1-GFP Mobility
 Adapted from Catez F, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Reeves R, Misteli T, Bustin M. Network of dynamic interactions between histone H1 and high-mobility-group proteins in chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(10) :4321-8.
Adapted from Catez F, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Reeves R, Misteli T, Bustin M. Network of dynamic interactions between histone H1 and high-mobility-group proteins in chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(10) :4321-8.
-The molecules in Figure 1 were analyzed using gel electrophoresis, and the results are shown below. Which of the following describes the correct experimental methodology? 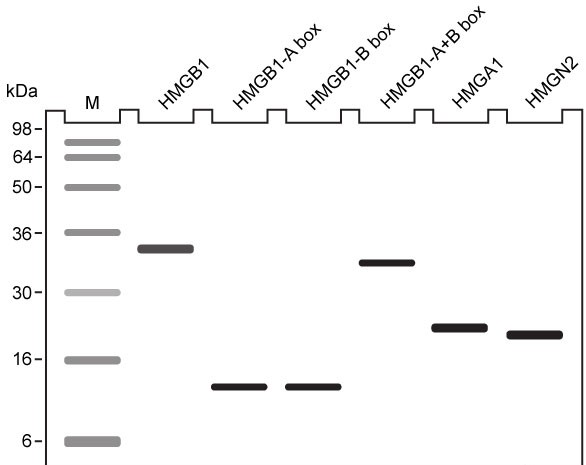
A) The intrinsic charges of the proteins were masked by a reducing agent.
B) The disulfide bonds were disrupted by the detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate.
C) The bands on the gel were stained with a dye that causes DNA to fluoresce.
D) The molecules were run through a highly crosslinked polyacrylamide gel.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q14: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q15: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q16: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q17: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q18: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q20: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q21: Passage
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacterial cells
Q22: Passage
The Bloom syndrome helicase (BLM) transcript is
Q23: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q24: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents