Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) is separated from lymphatic circulation by epithelial cells bound by tight junctions. Within the central nervous system (CNS) , CSF surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord and is believed to function in waste clearance for the CNS analogous to the role of the lymphatic system within the body.This waste clearance system has been dubbed the "glymphatic system." Although the mechanism of clearance is largely unknown, specialized glial cells known as astrocytes appear to modify the interstitial volume between neurons. This increase in interstitial volume allows for greater CSF flow, which increases the efficiency of neurotoxic clearance. Waste products removed from the brain include metabolic products such as ammonia and harmful compounds such as amyloid proteins.Recent advances in imaging technology suggest that interstitial clearance may be modified during sleep. To test this hypothesis, researchers indirectly studied changes in interstitial volume by measuring the percentage of CSF coverage in animal models during the first hour of sleep and again during the first hour of wakefulness (Figure 1) .
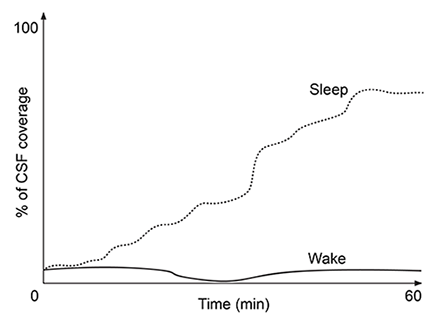 Figure 1. Percentage of CSF coverage of interstitial space during sleep and wakefulness
Figure 1. Percentage of CSF coverage of interstitial space during sleep and wakefulness
-A second study is performed to measure CSF coverage against brain wave frequency, measured by electroencephalography. Which of the following findings would best support the data provided in the passage?
A) 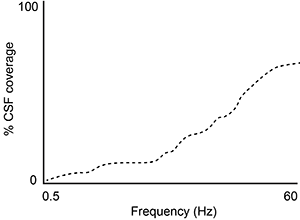
B) 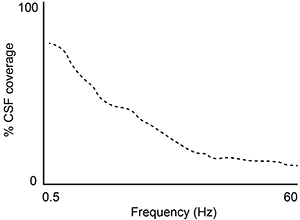
C) 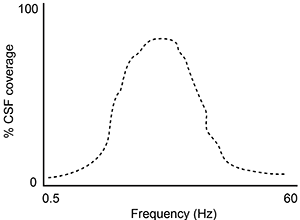
D) 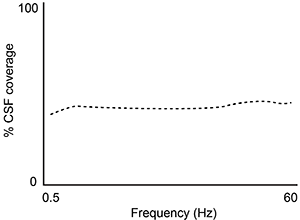
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q2: Passage
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacterial cells
Q3: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Q4: Passage
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacterial cells
Q6: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q7: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q8: Passage
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacterial cells
Q9: Passage
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacterial cells
Q10: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q11: Passage
At the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral spinal
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents